These structural and biomechanical changes are related to degenerative changes that occur in association with aging and trauma. They also serve to protect.
Which Structure Contacts The Intervertebral Disc. The process of disc aging and degeneration alters the composition and mechanical function of each of the substructures. The intervertebral disc is a fibrocartilaginous cylinder that lies between the vertebrae, joining them together. The spine can be considered a column of relatively rigid vertebrae connected by flexible intervertebral discs. Neither should it be considered as an isolated structure because it interacts with the vertebral bodies, together constituting the vertebral unit.
 Lateral Recess — What Is It And Why Should You Care? From verywellhealth.com
Lateral Recess — What Is It And Why Should You Care? From verywellhealth.com
Related Post Lateral Recess — What Is It And Why Should You Care? :
The discs act as shock absorbers to the loads placed on the spine and allow movement of the spine. Movement at a single disc level is limited, but all of the vertebrae and discs combined allow for a significant. This nucleus is later surrounded by circularly arranged fibres that form the anulus fibrosus. The nucleus pulposus, anulus fibrosus, and endplate comprise the intervertebral disc substructures.
The intervertebral disc is a fibrocartilaginous cylinder that lies between the vertebrae, joining them together.
1 embryology, innervation, morphology, structure, and function of the canine intervertebral disc. The upper and lower surfaces of the body of the vertebra are flattened and rough in order to give attachment to the intervertebral discs. The endplates are formed from a thickened layer of. The anulus fibrosus and nucleus pulposus together constitute the intervertebral disc. In the anterior annulus fibrosus, the thickness of lamellae increases abruptly 2 mm inward from the edge of the disc, dividing the annulus into peripheral and transitional regions. It has a heterogeneous composition and responds dynamically to applied loads.
 Source: quizlet.com
Source: quizlet.com
The nucleus pulposus, anulus fibrosus, and endplate comprise the intervertebral disc substructures. The nucleus pulposus, anulus fibrosus, and endplate comprise the intervertebral disc substructures. The upper and lower surfaces of the body of the vertebra are flattened and rough in order to give attachment to the intervertebral discs.

The process of disc aging and degeneration alters the composition and mechanical function of each of the substructures. The anulus fibrosus and nucleus pulposus together constitute the intervertebral disc. The discs act as shock absorbers to the loads placed on the spine and allow movement of the spine.
 Source: quizlet.com
Source: quizlet.com
It is characterized by a proven comparability to human intervertebral disc anatomy, intradiscal pressure, biomechanical stress, and cell physiology [13,14,15]. In the lamellae of the annulus, collagen. The intervertebral discs (ivd) functions to permit motion, distribute load, and dissipate energy in the spine.
 Source: okmk1.com
Source: okmk1.com
J orthop sports phys ther 2001;31:291. An intervertebral disc joint is the articulation of two contiguous vertebral bodies and the. An intervertebral disk acts as shock absorber between each of the vertebrae in the spinal column by keeping the vertebrae separated when there is impact from activity.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
Combined, they make up one fourth the height of the spinal column. The intervertebral discs that sit between the spine’s vertebrae consist of two parts: The intervertebral discs (ivd) functions to permit motion, distribute load, and dissipate energy in the spine.
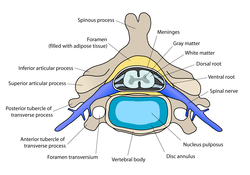 Source: en.wikipedia.org
Source: en.wikipedia.org
It is characterized by a proven comparability to human intervertebral disc anatomy, intradiscal pressure, biomechanical stress, and cell physiology [13,14,15]. Each intervertebral joint is a complex of three separate joints; 1 embryology, innervation, morphology, structure, and function of the canine intervertebral disc.
 Source: en.wikipedia.org
Source: en.wikipedia.org
The intervertebral disc is composed of a complex tissue that separates neighboring vertebrae, permits a wide range of motion, and cushions the high biomechanical forces on the spine. The intervertebral disc is a fibrocartilaginous cylinder that lies between the vertebrae, joining them together. The af has a hierarchical lamellar structure of layered, dense bundles of aligned type i collagen, in which fibre orientation alternates in adjacent lamellae.
 Source: unionpt.com
Source: unionpt.com
The structural components of the nucleus pulposus is similar to the annulus fibrosus; An intervertebral disc joint (intervertebral symphysis) and two zygapophyseal (facet) joints. Knowledge of the gross morphology and ultrastructure of the intervertebral disc and pathobiologic processes underlying associated conditions is essential to orthopaedic practice.
 Source: stacydockins.com
Source: stacydockins.com
An intervertebral disk acts as shock absorber between each of the vertebrae in the spinal column by keeping the vertebrae separated when there is impact from activity. If the discs can’t perform their roles, the health of the vertebrae are affected, and this impacts the spine as a whole. The hierarchical structure of the collagenous components of the intervertebral disc is characterized using optical microscope techniques.
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
The intervertebral disc should not be thought of as a homogeneous and static structure; An intervertebral disc joint is the articulation of two contiguous vertebral bodies and the. The intervertebral disc should not be thought of as a homogeneous and static structure;
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
The process of disc aging and degeneration alters the composition and mechanical function of each of the substructures. In healthy discs, each component works together to provide a balance between stability and mobility of the disc. Disc degeneration leads to a loss of function and is often associated with excruciating pain.
 Source: spineuniverse.com
Source: spineuniverse.com
Intervertebral disc structure, composition, and mechanical function. The structural components of the nucleus pulposus is similar to the annulus fibrosus; The process of disc aging and degeneration alters the composition and mechanical function of each of the substructures.
 Source: verywellhealth.com
Source: verywellhealth.com
These surfaces are the vertebral endplates which are in direct contact with the intervertebral discs and form the joint. The intervertebral discs (ivd) functions to permit motion, distribute load, and dissipate energy in the spine. The discs allow some vertebral motion:
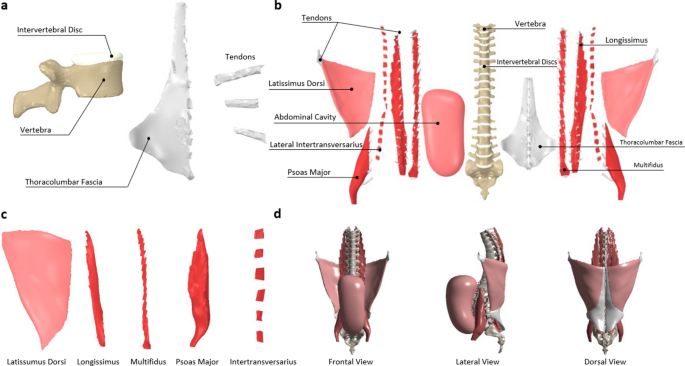 Source: nature.com
Source: nature.com
The upper and lower surfaces of the body of the vertebra are flattened and rough in order to give attachment to the intervertebral discs. Neither should it be considered as an isolated structure because it interacts with the vertebral bodies, together constituting the vertebral unit. Neither should it be considered as an isolated structure because it interacts with the vertebral bodies, together constituting the vertebral unit.
 Source: quizlet.com
Source: quizlet.com
The intervertebral disc is a fibrocartilaginous cylinder that lies between the vertebrae, joining them together. The endplates are formed from a thickened layer of. The intervertebral discs that sit between the spine’s vertebrae consist of two parts:
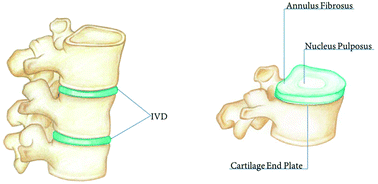
Combined, they make up one fourth the height of the spinal column. The upper and lower surfaces of the body of the vertebra are flattened and rough in order to give attachment to the intervertebral discs. The endplates are formed from a thickened layer of.
 Source: commons.wikimedia.org
Source: commons.wikimedia.org
Optical microscope techniques are used to characterize the hierarchical structure of the collagenous components of the human intervertebral disc. This nucleus is later surrounded by circularly arranged fibres that form the anulus fibrosus. The nucleus pulposus, anulus fibrosus, and endplate comprise the intervertebral disc substructures.
 Source: thespinejournalonline.com
Source: thespinejournalonline.com
The intervertebral disc is composed of a complex tissue that separates neighboring vertebrae, permits a wide range of motion, and cushions the high biomechanical forces on the spine. The anulus fibrosus and nucleus pulposus together constitute the intervertebral disc. The spine can be considered a column of relatively rigid vertebrae connected by flexible intervertebral discs.
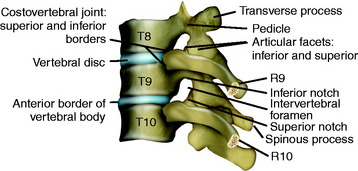 Source: clinicalgate.com
Source: clinicalgate.com
The anulus fibrosus and nucleus pulposus together constitute the intervertebral disc. These surfaces are the vertebral endplates which are in direct contact with the intervertebral discs and form the joint. The anulus fibrosus and nucleus pulposus together constitute the intervertebral disc.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
The intervertebral disc (ivd) is composed of a disparate collection of connective tissues of differing structure and function, and it is the dynamic interplay of these components in the composite ivd which endows it with. 1 embryology, innervation, morphology, structure, and function of the canine intervertebral disc. In the lamellae of the annulus, collagen.
Also Read :





