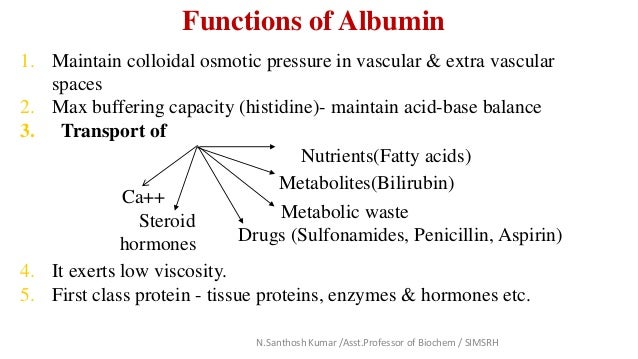
Important amino acid reserve for the body. Albumin helps the body by binding molecules for transport.
Which Plasma Protein Transports Fatty Acids And Some Hormones. High plasma levels of insulin in the blood plasma (e.g. All steroids bind to some extent to plasma proteins. Albumin acts as main fatty acid binding protein in extracellular fluids. Plasma albumin possesses about 7 binding sites for fatty acids with moderate to high affinity, enhancing the concentration of fatty acids by a several orders of magnitude.
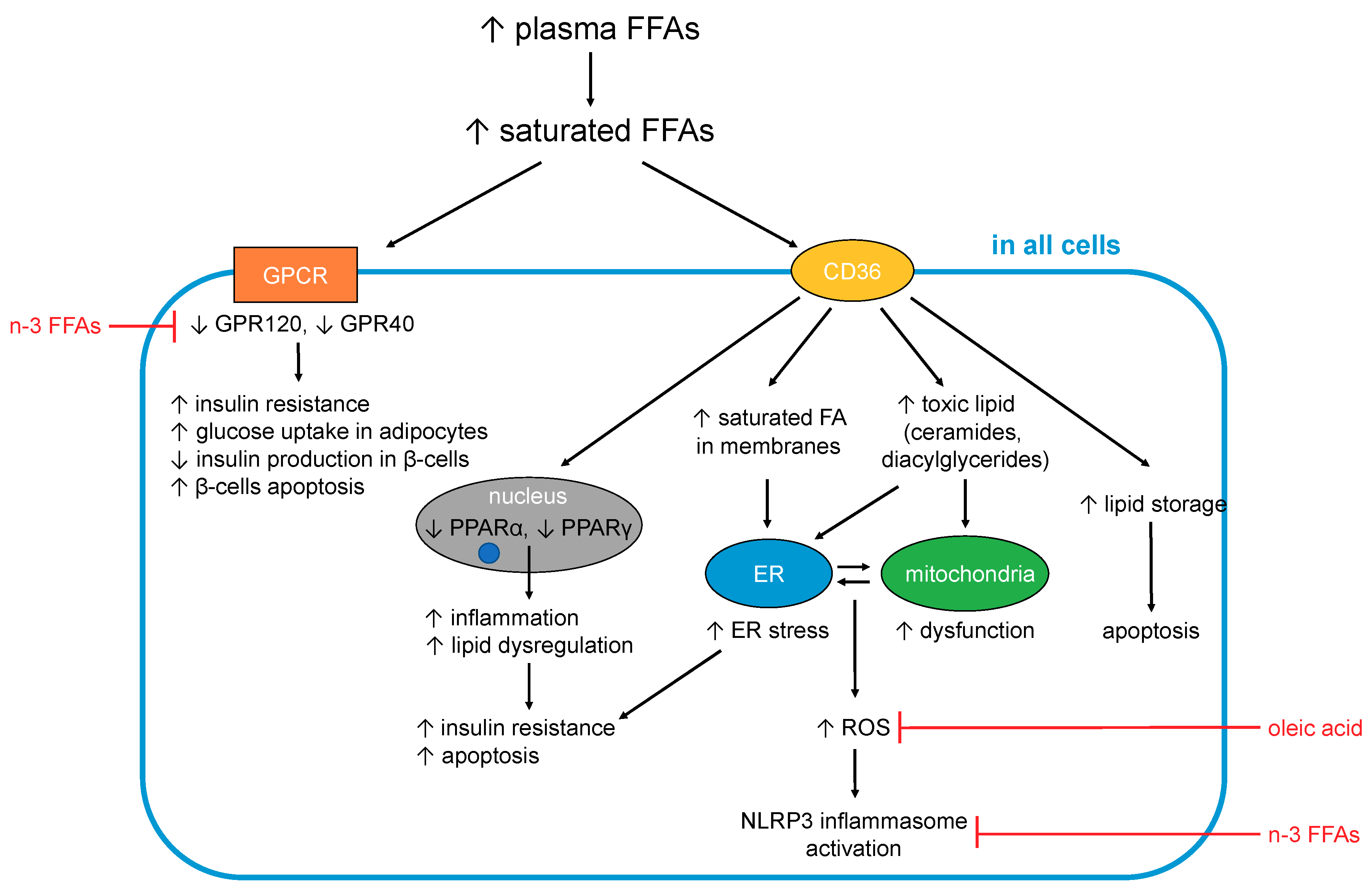
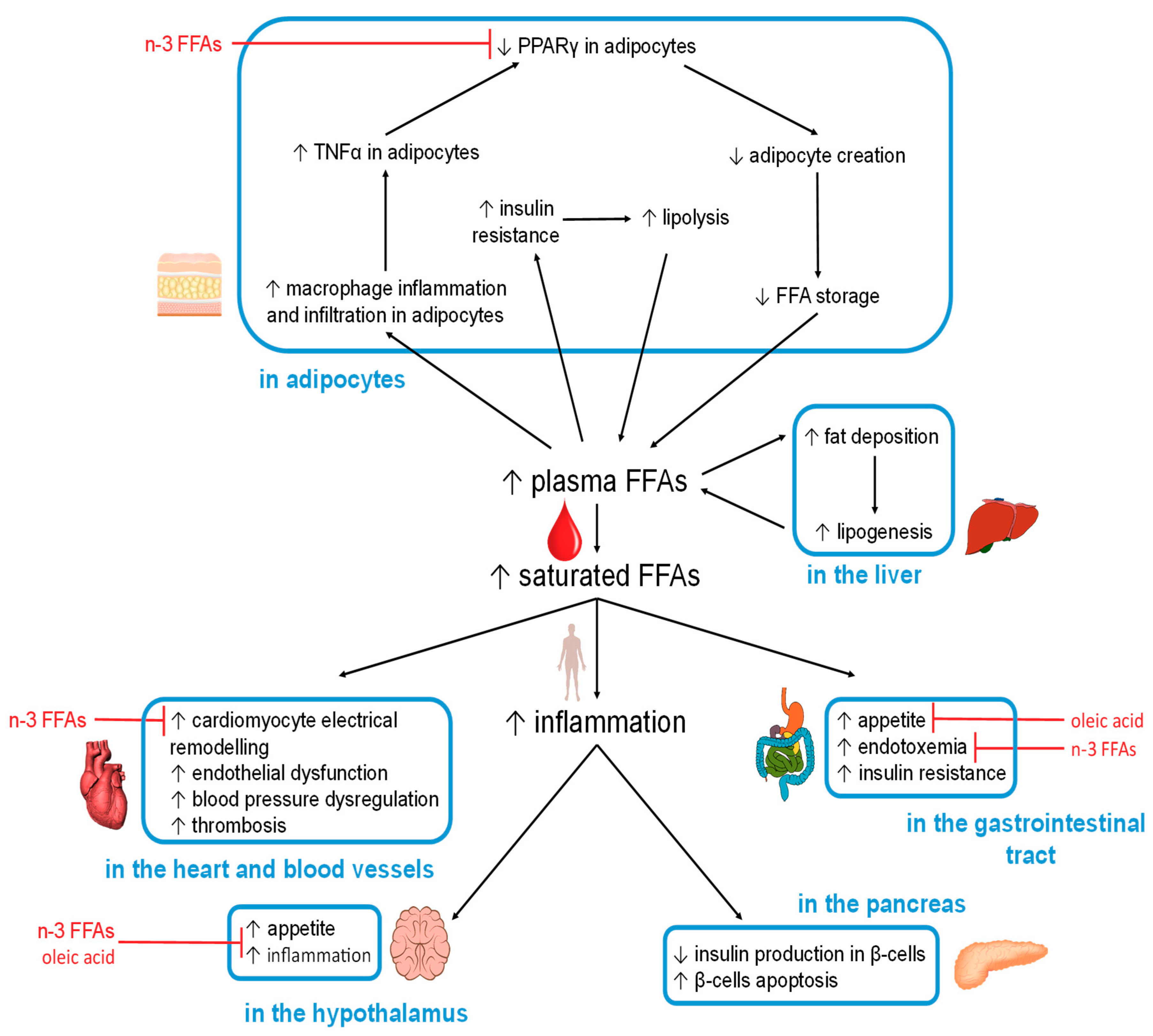 Nutrients | Free Full-Text | Changes In Plasma Free Fatty Acids Associated With Type-2 Diabetes | Html From mdpi.com
Nutrients | Free Full-Text | Changes In Plasma Free Fatty Acids Associated With Type-2 Diabetes | Html From mdpi.com
Related Post Nutrients | Free Full-Text | Changes In Plasma Free Fatty Acids Associated With Type-2 Diabetes | Html :
Serum albumin is the major protein component of blood plasma and is responsible for the circulatory transport of a range of small molecules that include fatty acids, hormones, metal ions and drugs. Transthyretin also binds thyroid hormones. Plasma is the part of the blood that transports dissolved nutrients. The different types of plasma proteins have a number of important functions.
Cholesterol and cholesterol esters are also present in plasma.
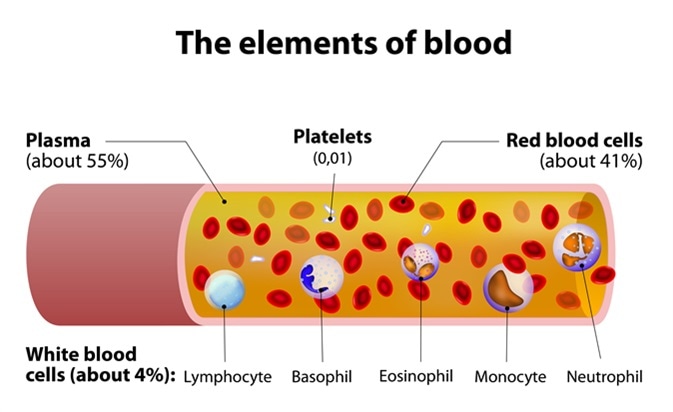
It constitutes 4% of the plasma proteins and required for blood clotting. Transthyretin also binds thyroid hormones. Plasma is the part of the blood that transports dissolved nutrients. Plasma is also a transport medium for nutrients and wastes. A blood clot, air bubble, piece of fatty deposit, or other object that has been carried in the bloodstream to lodge in a vessel and cause an embolism. The different types of plasma proteins have a number of important functions.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
Albumin acts as main fatty acid binding protein in extracellular fluids. Transthyretin also binds thyroid hormones. The plasma transorts waste products such as urea and uricacid to the kidneys, where they are excreted.
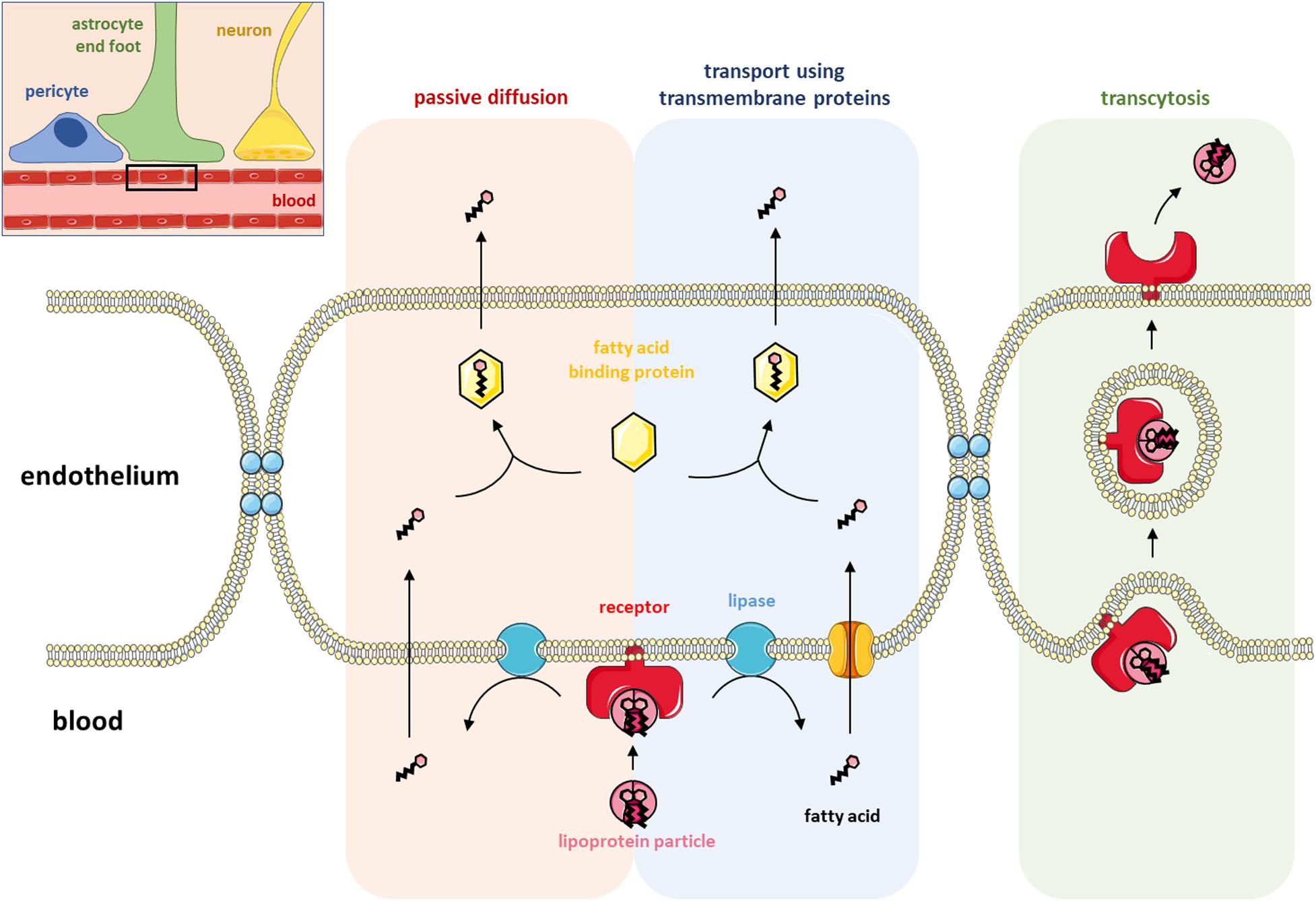 Source: frontiersin.org
Source: frontiersin.org
Albumin acts as main fatty acid binding protein in extracellular fluids. Difference between cell membrane and plasma membrane. Albumin helps the body by binding molecules for transport.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
Despite the high affinity of albumin for fatty acids, uptake of fatty acids by parenchymal cells such as skeletal and cardiac myocytes seems not to. Plasma albumin possesses about 7 binding sites for fatty acids with moderate to high affinity, enhancing the concentration of fatty acids by a several orders of magnitude. A chemical term for fat.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Additionally, fatty acid double bonds can either be cis or trans, creating many different types of fatty acids. Albumin helps the body by binding molecules for transport. All steroids bind to some extent to plasma proteins.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
Despite the high affinity of albumin for fatty acids, uptake of fatty acids by parenchymal cells such as skeletal and cardiac myocytes seems not to. A different group of carrier proteins called glucose transport proteins, or gluts, are involved in transporting glucose and other hexose sugars into cells within the body. Albumin helps the body by binding molecules for transport.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
High plasma levels of insulin in the blood plasma (e.g. It constitutes 4% of the plasma proteins and required for blood clotting. Albumin is the carrier of various hydrophobic substances in the blood such as:
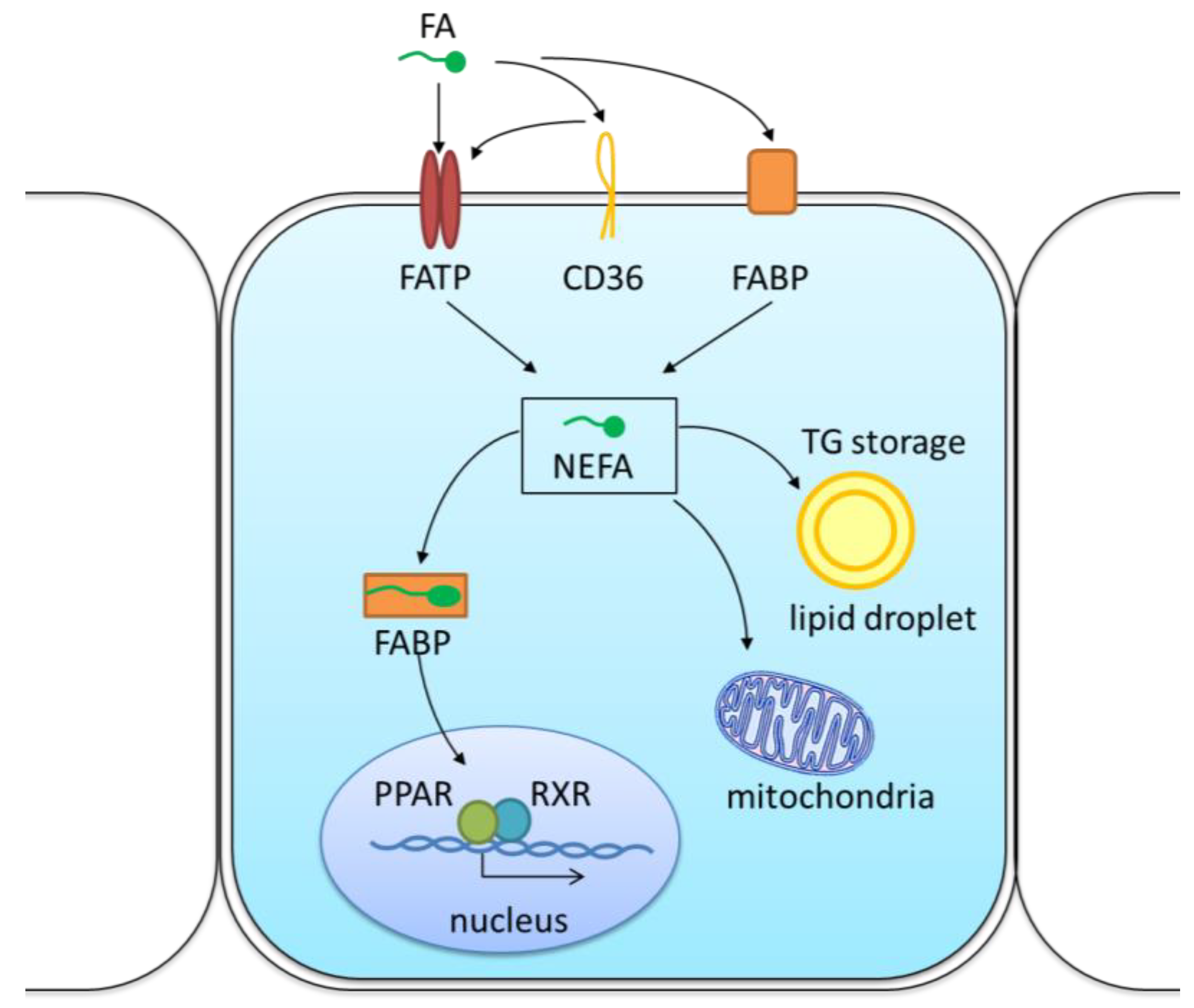 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
A chemical term for fat. Cholesterol and cholesterol esters are also present in plasma. A blood clot, air bubble, piece of fatty deposit, or other object that has been carried in the bloodstream to lodge in a vessel and cause an embolism.
 Source: pt.slideshare.net
Source: pt.slideshare.net
Fatty acids are hydrocarbon chains of differing lengths with various degrees of saturation that end with carboxylic acid groups. Some of those are hormones, fatty acids, medications, and bilirubin. Plasma is also a transport medium for nutrients and wastes.
 Source: studocu.com
Source: studocu.com
Additionally, fatty acid double bonds can either be cis or trans, creating many different types of fatty acids. The hormone insulin, increases the number of gluts on cells, causing them to take glucose from the blood when its levels are high. It aids in the transfer of carbon dioxide, necessary nutrients (organic, inorganic, and plasma proteins), hormones (bound to plasma proteins), waste (urea, uric acid, and creatinine), and other substances (drugs and alcohol) to and from the tissues.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
Plasma is the part of the blood that transports dissolved nutrients. The plasma transorts waste products such as urea and uricacid to the kidneys, where they are excreted. The different types of plasma proteins have a number of important functions.
 Source: news-medical.net
Source: news-medical.net
Additionally, fatty acid double bonds can either be cis or trans, creating many different types of fatty acids. The plasma transorts waste products such as urea and uricacid to the kidneys, where they are excreted. A different group of carrier proteins called glucose transport proteins, or gluts, are involved in transporting glucose and other hexose sugars into cells within the body.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
Plasma albumin possesses about 7 binding sites for fatty acids with moderate to high affinity, enhancing the concentration of fatty acids by a several orders of magnitude. Additionally, fatty acid double bonds can either be cis or trans, creating many different types of fatty acids. Plasma is also a transport medium for nutrients and wastes.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
All steroids bind to some extent to plasma proteins. Lipolysis the breakdown of lipids by hydrolysis. A blood clot, air bubble, piece of fatty deposit, or other object that has been carried in the bloodstream to lodge in a vessel and cause an embolism.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Transthyretin also binds thyroid hormones. Among these is the capacity to transport important nutrients, such as lipids and fatty acids, as well as some trace metals, vitamins, and hormones. Lipogenesis the production of fatty acids.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
It constitutes 4% of the plasma proteins and required for blood clotting. Peptide and protein hormones are, of course, products of translation. A blood clot, air bubble, piece of fatty deposit, or other object that has been carried in the bloodstream to lodge in a vessel and cause an embolism.
 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
Important amino acid reserve for the body. It aids in the transfer of carbon dioxide, necessary nutrients (organic, inorganic, and plasma proteins), hormones (bound to plasma proteins), waste (urea, uric acid, and creatinine), and other substances (drugs and alcohol) to and from the tissues. The different types of plasma proteins have a number of important functions.
 Source: pt.slideshare.net
Source: pt.slideshare.net
A chemical term for fat. It aids in the transfer of carbon dioxide, necessary nutrients (organic, inorganic, and plasma proteins), hormones (bound to plasma proteins), waste (urea, uric acid, and creatinine), and other substances (drugs and alcohol) to and from the tissues. Peptide and protein hormones are, of course, products of translation.
 Source: open.oregonstate.education
Source: open.oregonstate.education
A different group of carrier proteins called glucose transport proteins, or gluts, are involved in transporting glucose and other hexose sugars into cells within the body. Albumin helps the body by binding molecules for transport. The plasma transorts waste products such as urea and uricacid to the kidneys, where they are excreted.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
Albumin acts as main fatty acid binding protein in extracellular fluids. Cholesterol and cholesterol esters are also present in plasma. They are partly responsible for blood viscosity, the regulation of water movement between tissues and.
 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
Albumin acts as main fatty acid binding protein in extracellular fluids. A blood clot, air bubble, piece of fatty deposit, or other object that has been carried in the bloodstream to lodge in a vessel and cause an embolism. An increased level of tbg leads to an increased level of total circulating thyroid hormone, whereas its congenital absence leads to abnormally low levels.
Also Read :