Silverio, d., torker, s., pilyugina, t. (e) the activation energies of catalysts a, b, c, and d all result in the same reaction time.
Which Organic Molecule Serves As A Catalyst. The study of organic reactions. Proposed catalytic mechanism for electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution from btdn. This increases the rate at which a water molecule can act as a nucleophile toward the positive end of the c=o double bond. Catalytic hydrogenation refers to the addition of hydrogen to an organic molecule in the presence of a catalyst.
 Current State And Future Perspectives Of Engineered And Artificial Peroxygenases For The Oxyfunctionalization Of Organic Molecules | Nature Catalysis From nature.com
Current State And Future Perspectives Of Engineered And Artificial Peroxygenases For The Oxyfunctionalization Of Organic Molecules | Nature Catalysis From nature.com
Related Post Current State And Future Perspectives Of Engineered And Artificial Peroxygenases For The Oxyfunctionalization Of Organic Molecules | Nature Catalysis :
Ribozymes are the rna molecules that serve as enzymes. The product of this reaction then loses an h + ion to form. Organic catalysts have a stable framework of carbon atoms, to which more active chemical groups can attach. Olefins are among nature’s most abundant chemical compounds and commonly obtained from.
The role of the acid catalyst is easy to understand.
In 2000, list showed that the amino acid proline could act as a catalyst in an aldol reaction, in which carbon atoms from two different molecules are bonded together, and that it. The product of this reaction then loses an h + ion to form. In 2000, list showed that the amino acid proline could act as a catalyst in an aldol reaction, in which carbon atoms from two different molecules are bonded together, and that it. (e) the activation energies of catalysts a, b, c, and d all result in the same reaction time. Dehydration reaction a chemical reaction in which to molecules become covalently bonded to each other with the removal of a water molecule Which type of substances serves as a catalyst for reactions that break large food molecules into smaller useful molecules?
 Source: onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Source: onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Serine proteases use four of the major catalytic mechanism during the reaction cycle: Proposed catalytic mechanism for electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution from btdn. The construction of catalysts by supramolecular forces has recently become a powerful tool and the role of noncovalent interactions can assist in designing new tools for the construction of effective and selective catalytic systems.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Organic catalysts have a stable framework of carbon atoms, to which more active chemical groups can attach. Which type of substances serves as a catalyst for reactions that break large food molecules into smaller useful molecules? Protonation of the oxygen atom increases the polarity of the carbonyl bond.
 Source: nature.com
Source: nature.com
Because of their similarity in composition and description, they are often mistaken as a. The oxidizing agent can be a metal or another organic molecule. Since fibrinogen is made of chains of amino acids, it is an example of which type of organic molecule?
 Source: onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Source: onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Ribozymes are the rna molecules that serve as enzymes. Organic catalysts have a stable framework of carbon atoms, to which more active chemical groups can attach. Silverio, d., torker, s., pilyugina, t.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
The active site of serine proteases contains a catalytic triad of three amino acids: This increases the rate at which a water molecule can act as a nucleophile toward the positive end of the c=o double bond. The molecule gaining electrons is being reduced.
 Source: onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Source: onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Protonation of the oxygen atom increases the polarity of the carbonyl bond. Organic chemistry is a branch of chemistry that studies the structure, properties and reactions of organic compounds, which contain carbon in covalent bonding. Silverio, d., torker, s., pilyugina, t.
 Source: wou.edu
Source: wou.edu
Which type of substances serves as a catalyst for reactions that break large food molecules into smaller useful molecules? This organocatalyst consists of carbon, hydrogen, sulfur and other nonmetal elements found in organic compounds. Silverio, d., torker, s., pilyugina, t.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
And alcohol production by addition to aldehydes and. In 2000, list showed that the amino acid proline could act as a catalyst in an aldol reaction, in which carbon atoms from two different molecules are bonded together, and that it. They are a subclass of coordination polymers, with the special feature that they are often porous.the organic ligands included are sometimes referred to as struts or linkers, one example being 1,4.
 Source: nature.com
Source: nature.com
The oxidizing agent can be a metal or another organic molecule. Organic chemistry is a branch of chemistry that studies the structure, properties and reactions of organic compounds, which contain carbon in covalent bonding. Enzymes are a specific organic molecule that acts as a catalyst.
 Source: nature.com
Source: nature.com
The process can involve direct addition of hydrogen to the double bond of an unsaturated molecule; Proposed catalytic mechanism for electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution from btdn. The molecule gaining electrons is being reduced.
 Source: www2.estrellamountain.edu
Source: www2.estrellamountain.edu
The product of this reaction then loses an h + ion to form. They are a subclass of coordination polymers, with the special feature that they are often porous.the organic ligands included are sometimes referred to as struts or linkers, one example being 1,4. In 2000, list showed that the amino acid proline could act as a catalyst in an aldol reaction, in which carbon atoms from two different molecules are bonded together, and that it.
 Source: nature.com
Source: nature.com
A macromolecules serving as a catalyst, a chemical agent that increases the rate of a reaction without being consumed by the reaction. The team specifically studied the role of catalysts in the conversion of inert molecules called olefins. Dehydration reaction a chemical reaction in which to molecules become covalently bonded to each other with the removal of a water molecule
 Source: doubtnut.com
Source: doubtnut.com
Silverio, d., torker, s., pilyugina, t. This organocatalyst consists of carbon, hydrogen, sulfur and other nonmetal elements found in organic compounds. Since fibrinogen is made of chains of amino acids, it is an example of which type of organic molecule?
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
A macromolecule, usually a protein, that serves as a biological catalyst, changing the rate of a chemical reaction without being consumed by the reaction. Enzymes are a specific organic molecule that acts as a catalyst. The role of the acid catalyst is easy to understand.
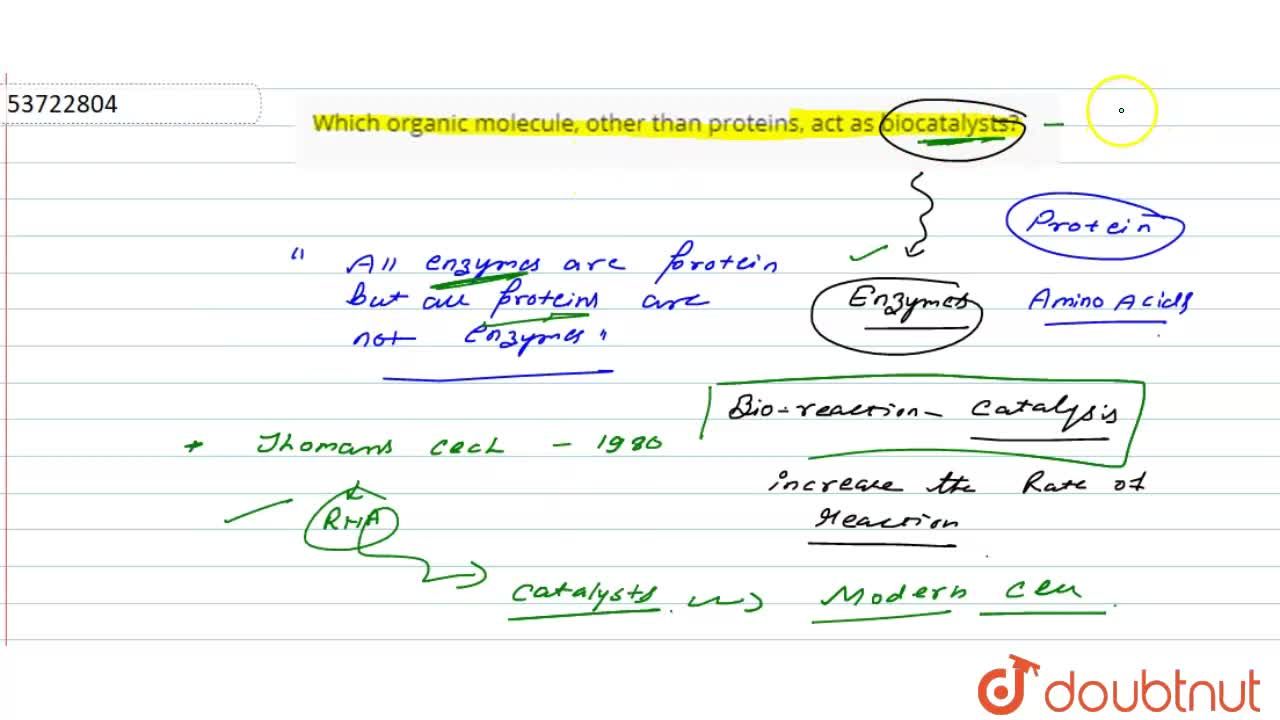 Source: doubtnut.com
Source: doubtnut.com
The molecule gaining electrons is being reduced. Catalytic hydrogenation refers to the addition of hydrogen to an organic molecule in the presence of a catalyst. The product of this reaction then loses an h + ion to form.
 Source: www2.estrellamountain.edu
Source: www2.estrellamountain.edu
The oxidizing agent can be a metal or another organic molecule. The oxidizing agent can be a metal or another organic molecule. The molecule gaining electrons is being reduced.
 Source: brainly.com
Source: brainly.com
The molecule gaining electrons is being reduced. Organic chemistry is a branch of chemistry that studies the structure, properties and reactions of organic compounds, which contain carbon in covalent bonding. Tertiary alcohols, on the other hand, cannot be oxidized.
 Source: onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Source: onlinelibrary.wiley.com
This was achieved through asymmetric organocatalysis, a process in which an organic molecule serves as a catalyst that drives a chemical transformation to one desired product. His, ser (hence the name “serine protease”) and asp. Ribosomal rna (rrna) serves as a catalyst in peptide bond formation during protein synthesis.
 Source: advancedsciencenews.com
Source: advancedsciencenews.com
Our studies indicate that small organic molecules as catalysts have the ability to achieve the level of stereoselectivity that is shown by peptide catalysts under ambient conditions. Simple organic molecules as catalysts for enantioselective synthesis of amines and alcohols. In organic chemistry, organocatalysis is a form of catalysis in which the rate of a chemical reaction is increased by an organic catalyst.
 Source: nature.com
Source: nature.com
Proposed catalytic mechanism for electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution from btdn. These often contain common elements such as oxygen, nitrogen, sulphur or phosphorus. Proposed catalytic mechanism for electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution from btdn.
Also Read :