'typically' chemical synaptic transmission takes place when an influx of calcium ions during a presynaptic nerve impulse triggers exocytosis of neurotransmitter substance from synaptic vesicles. Located at the end of each telodendrion.
Which Of These Ions Triggers Exocytosis Of Synaptic Vesicles. �typically� chemical synaptic transmission takes place when an influx of calcium ions during a presynaptic nerve impulse triggers exocytosis of neurotransmitter substance from synaptic vesicles. It contains synaptic vesicles with neurotransmitters that send messages to the axon�s target. Ca ions bind to a complex of proteins responsible for the exocytosis of synaptic vesicles the neurotransmitter will have no effect in the postsynaptic cell what happens if a drug inhibits neurotransmitter receptors on the postsynaptic cell? These two papers [40 ,41 ] demonstrate that synaptotagmin, a synaptic vesicle protein considered to be a likely candidate for the ca2+ sensor of synaptic exocytosis, is also important for membrane retrieval and vesicle recycling following exocytosis.
 Synaptic Vesicle Recycling - An Overview | Sciencedirect Topics From sciencedirect.com
Synaptic Vesicle Recycling - An Overview | Sciencedirect Topics From sciencedirect.com
Related Post Synaptic Vesicle Recycling - An Overview | Sciencedirect Topics :
Ca 2+ ions from the synaptic cleft pass into the synaptic knob via voltagegated channels. Ca 2+ triggers synaptic vesicle exocytosis, thereby releasing the neurotransmitters contained in the vesicles and initiating synaptic transmission. Signals for triggering neurotransmitter release. Contains neurotransmitters that send messages to.
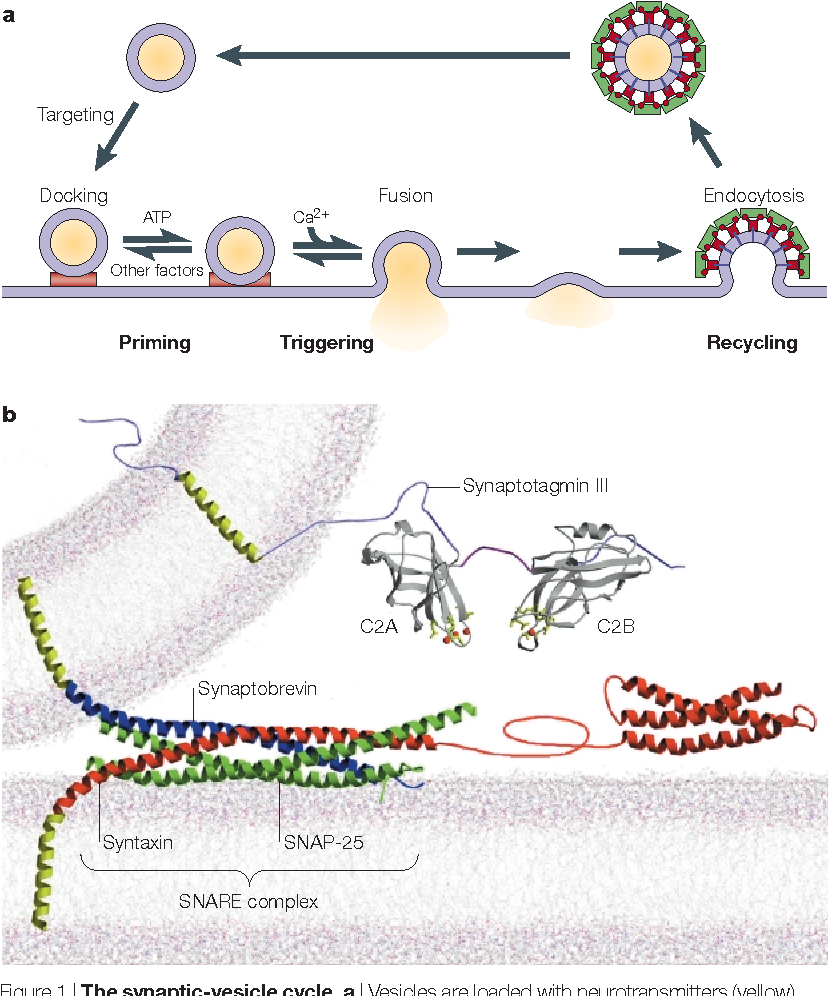
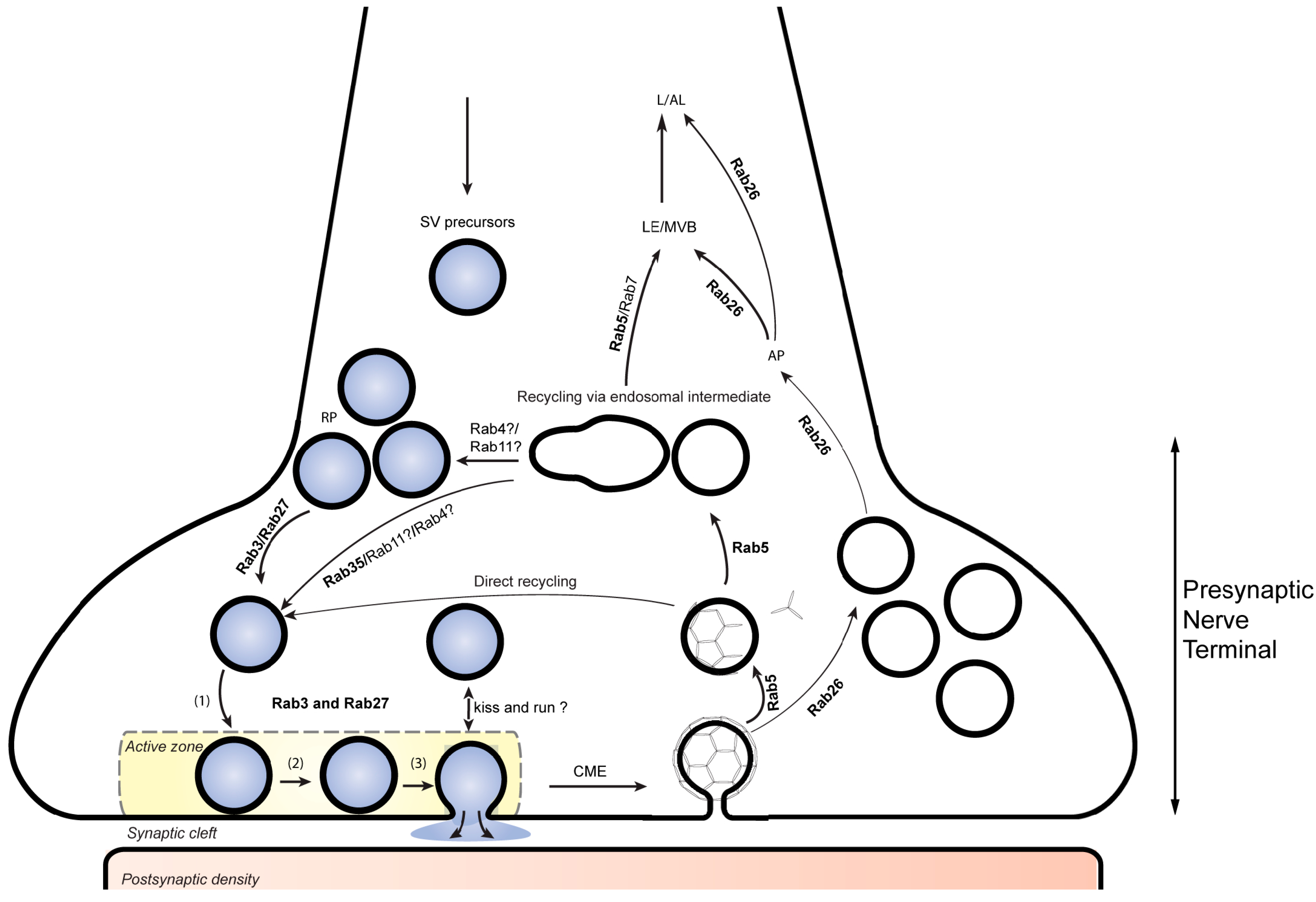
Sudden rise in the cytosolic concentration of ca 2+ , causes the release of a chemical, called neurotransmitter substance, from small synaptic vesicles present there into the synaptic cleft by exocytosis through the presynaptic membrane.
These two papers [40 ,41 ] demonstrate that synaptotagmin, a synaptic vesicle protein considered to be a likely candidate for the ca2+ sensor of synaptic exocytosis, is also important for membrane retrieval and vesicle recycling following exocytosis. When neurotransmitter molecules bind to receptors in the plasma membrane of the receiving neuron, The synaptic vesicles fuse with the presynaptic membrane during this process of exocytosis. Signals for triggering neurotransmitter release. Neurotransmitter diffuses across the synaptic cleft. When calcium ions enter the synaptic terminal, they cause vesicles containing neurotransmitter molecules to fuse to the plasma membrane of the sending neuron.
 Source: semanticscholar.org
Source: semanticscholar.org
What is the role of calcium ions in nerve excitation? The synaptic vesicles fuse with the presynaptic membrane during this process of exocytosis. �typically� chemical synaptic transmission takes place when an influx of calcium ions during a presynaptic nerve impulse triggers exocytosis of neurotransmitter substance from synaptic vesicles.
 Source: nature.com
Source: nature.com
Sudden rise in the cytosolic concentration of ca 2+ , causes the release of a chemical, called neurotransmitter substance, from small synaptic vesicles present there into the synaptic cleft by exocytosis through the presynaptic membrane. Ca 2+ triggers many forms of exocytosis in different types of eukaryotic cells, for example synaptic vesicle exocytosis in neurons, granule exocytosis in mast cells, and hormone exocytosis in endocrine cells. These synapses have neuroreceptors that are sodium channels.

�typically� chemical synaptic transmission takes place when an influx of calcium ions during a presynaptic nerve impulse triggers exocytosis of neurotransmitter substance from synaptic vesicles. �typically� chemical synaptic transmission takes place when an influx of calcium ions during a presynaptic nerve impulse triggers exocytosis of neurotransmitter substance from synaptic vesicles. Neurotransmitter diffuses across the synaptic cleft.
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
When calcium ions enter the synaptic terminal, they cause vesicles containing neurotransmitter molecules to fuse to the plasma membrane of the sending neuron. Ca2+ if a drug inhibits neurotransmitter receptors on the postsynaptic cells:. Action potential promotes the entry of calcium ions into the synaptic knob.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
Signals for triggering neurotransmitter release. When a nerve cell becomes activated, these vesicles fuse with the membrane on the surface. Exocytosis and its counterpart, endocytosis, are used by all cells because most chemical.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
As mentioned above, exocytosis of synaptic vesicles preferentially occurs at the base of the synaptic ribbon (zenisek et al., 2000; One of the proteins that has a crucial role in this secretion event is synaptotagmin i, an abundant constituent of synaptic vesicles that binds ca2+ ions through two c2 domains. This fundamental mechanism was discovered in pioneering work on the neuromuscular junction by katz and miledi (1967).
These two papers [40 ,41 ] demonstrate that synaptotagmin, a synaptic vesicle protein considered to be a likely candidate for the ca2+ sensor of synaptic exocytosis, is also important for membrane retrieval and vesicle recycling following exocytosis. Sudden rise in the cytosolic concentration of ca 2+ , causes the release of a chemical, called neurotransmitter substance, from small synaptic vesicles present there into the synaptic cleft by exocytosis through the presynaptic membrane. When calcium ions enter the synaptic terminal, they cause vesicles containing neurotransmitter molecules to fuse to the plasma membrane of the sending neuron.
 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
Ca2+ if a drug inhibits neurotransmitter receptors on the postsynaptic cells:. When neurotransmitter molecules bind to receptors in the plasma membrane of the receiving neuron, What is the role of calcium ions in nerve excitation?
 Source: quizlet.com
Source: quizlet.com
Neurotransmitter diffuses across the synaptic cleft. Neurotransmitter diffuses across the synaptic cleft. Action potential promotes the entry of calcium ions into the synaptic knob.
 Source: jbc.org
Source: jbc.org
Neurotransmitter diffuses across the synaptic cleft. Located at the end of each telodendrion. The synaptic vesicles fuse with the presynaptic membrane during this process of exocytosis.
 Source: onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Source: onlinelibrary.wiley.com
These synapses have neuroreceptors that are sodium channels. Located at the end of each telodendrion. Action potential promotes the entry of calcium ions into the synaptic knob.
 Source: cell.com
Source: cell.com
These two papers [40 ,41 ] demonstrate that synaptotagmin, a synaptic vesicle protein considered to be a likely candidate for the ca2+ sensor of synaptic exocytosis, is also important for membrane retrieval and vesicle recycling following exocytosis. Binding of the neurotransmitter to the receptor triggers a postsynaptic response specific for that receptor. Ca 2+ ions from the synaptic cleft pass into the synaptic knob via voltagegated channels.
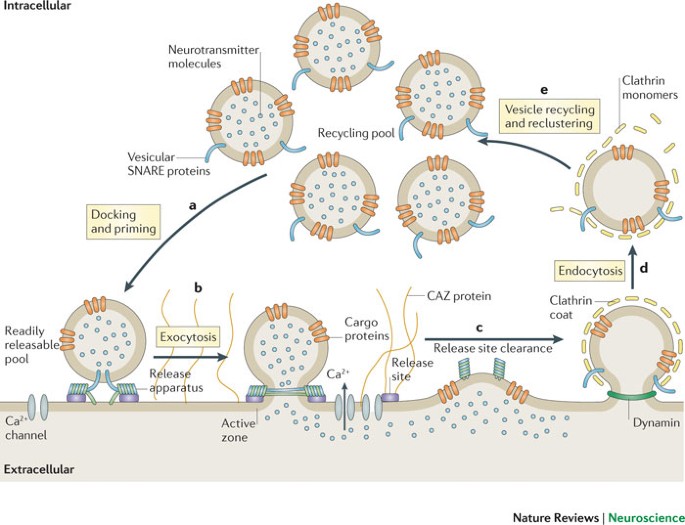 Source: nature.com
Source: nature.com
Ca 2+ ions from the synaptic cleft pass into the synaptic knob via voltagegated channels. The influx of calcium ions into the triggers exocytosis of synaptic vesicles. Two potassium ions into the cytosol and three sodium ions into the extracellular fluid what ion triggers synaptic vesicles to release neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft?

Ca 2+ triggers many forms of exocytosis in different types of eukaryotic cells, for example synaptic vesicle exocytosis in neurons, granule exocytosis in mast cells, and hormone exocytosis in endocrine cells. Advanced two forms of a molecule found in the presynaptic membrane that modulate the effects of calcium ions on synaptic vesicles have been identified (littleton, et al., 1999; Which of these ions triggers exocytosis of synaptic vesicles.
Ca2+ if a drug inhibits neurotransmitter receptors on the postsynaptic cells:. These synapses have neuroreceptors that are sodium channels. Contains neurotransmitters that send messages to.
 Source: quizlet.com
Source: quizlet.com
Chapter 11 (nervous system & tissue) other sets by this creator. When calcium ions enter the synaptic terminal, they cause vesicles containing neurotransmitter molecules to fuse to the plasma membrane of the sending neuron. It contains synaptic vesicles with neurotransmitters that send messages to the axon�s target.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
Binding of the neurotransmitter to the receptor triggers a postsynaptic response specific for that receptor. Ca2+ if a drug inhibits neurotransmitter receptors on the postsynaptic cells:. Sudden rise in the cytosolic concentration of ca 2+ , causes the release of a chemical, called neurotransmitter substance, from small synaptic vesicles present there into the synaptic cleft by exocytosis through the presynaptic membrane.
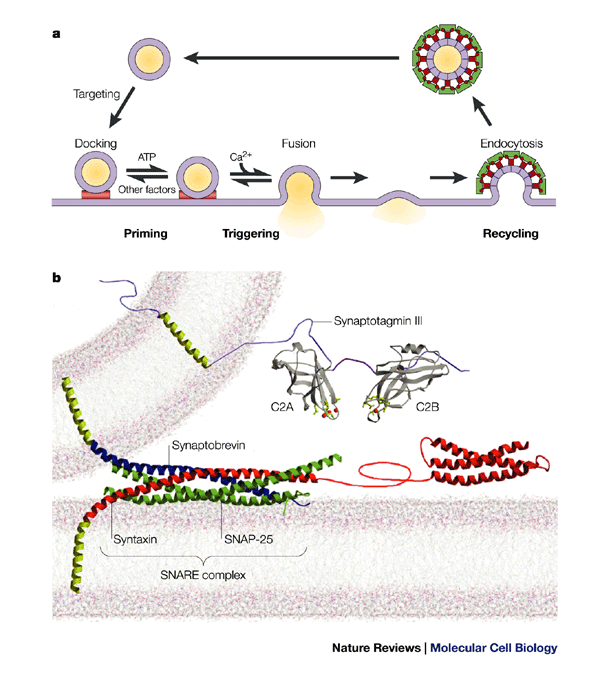 Source: nature.com
Source: nature.com
Chapter 11 (nervous system & tissue) other sets by this creator. Synaptic vesicle release is highly regulated, not only in the coupling of exocytosis to membrane depolarization and cal� influx, but also in the amount of neurotransmitter released per membrane depolarization. Exocytosis and its counterpart, endocytosis, are used by all cells because most chemical.
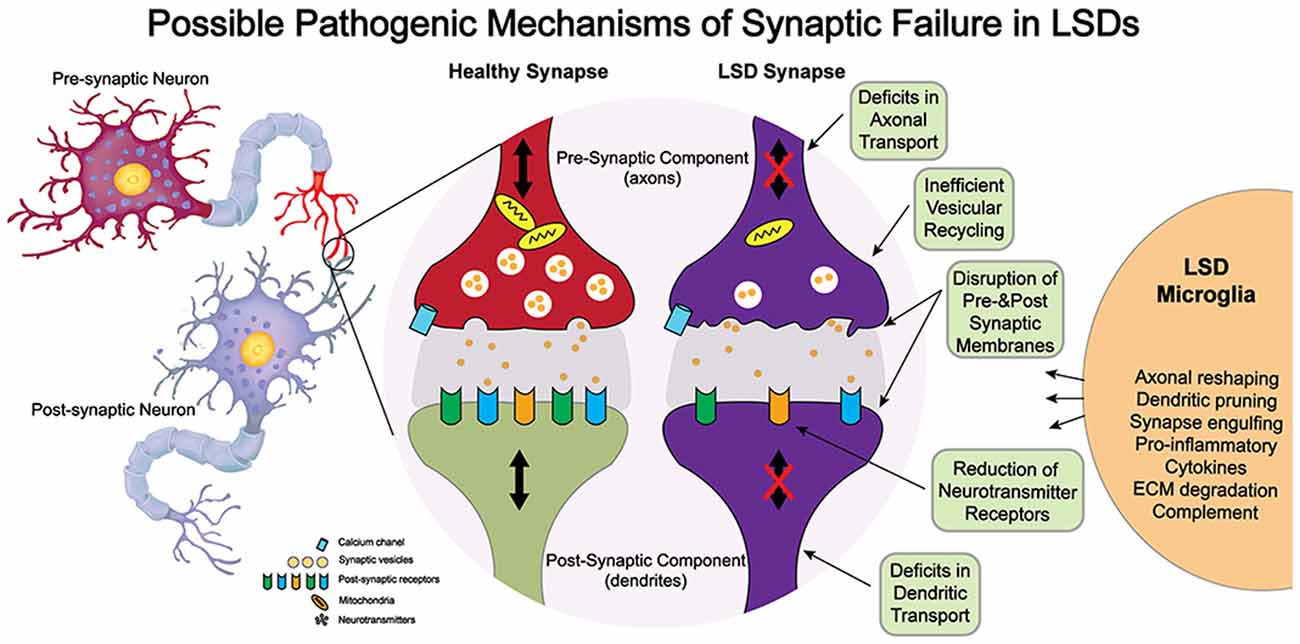 Source: frontiersin.org
Source: frontiersin.org
Neurotransmitter diffuses across the synaptic cleft. It has been fifty years since the discovery that ca2+ triggers the rapid exocytosis of neurotransmitters from neurons. These two papers [40 ,41 ] demonstrate that synaptotagmin, a synaptic vesicle protein considered to be a likely candidate for the ca2+ sensor of synaptic exocytosis, is also important for membrane retrieval and vesicle recycling following exocytosis.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Synaptic vesicle release is highly regulated, not only in the coupling of exocytosis to membrane depolarization and cal� influx, but also in the amount of neurotransmitter released per membrane depolarization. The influx of calcium ions into the triggers exocytosis of synaptic vesicles. Signals for triggering neurotransmitter release.
Also Read :





