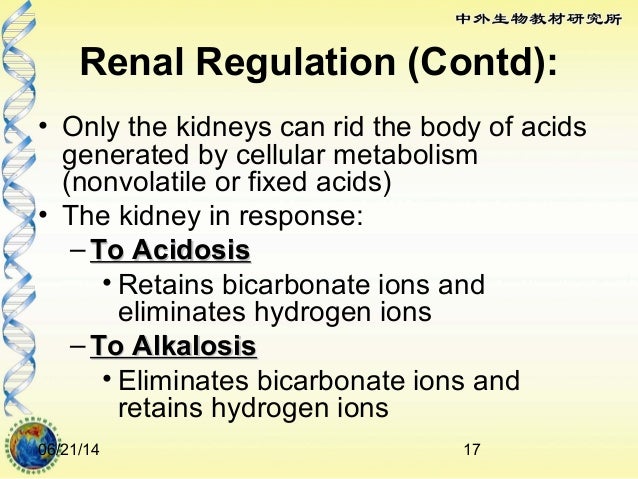
Inability to produce an acidic urine due to increased production of ammonia: The kidney cannot concentrate urine leading to fixed specific gravity 3.
Which Of The Following Is A Renal Response To Acidosis. The normal renal response to metabolic acidosis is to increase acidic nh4 excretion renally. Which of the following is a renal response to acidosis? Inability to produce an acidic urine due to impaired production of ammonia d. When used as a surrogate marker for urine ammonium, uag decreases and becomes negative if the increase in excretion of ammonium (the cation) is robust as part of the normal renal adaptive response to the metabolic acidosis of extrarenal origin, such as diarrhea.
 Chapter 26 Balance Part 2. Acid/Base Balance Biol Ppt Download From slideplayer.com
Chapter 26 Balance Part 2. Acid/Base Balance Biol Ppt Download From slideplayer.com
Related Post Chapter 26 Balance Part 2. Acid/Base Balance Biol Ppt Download :
Increasing secretion of hydrogen ions b. Which of the following is a component of the renal response to metabolic acidosis? Renal tubular acidosis can be divided into different subtypes, each with its own characteristics. Renal correction of hyperkalaemia will result in.
Reabsorption of h + b.
Secretion of hco3 2 into the tubular lumen c. Conservation of potassium the kidney can no produce ammonia to excrete the hydrogen ions 4. What other regular method of water loss accounts for a. The respiratory response to acidosis involves lowering the pco2 Renal response to acidosis acidosis refers to an excess extracellular fluid h + concentration and thus abnormally low ph. Approximately 2500 ml of water is added daily to the ecf through epithelia absorption and metabolic generation.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Arterial concentration of hydrogen ion 22. At the normal ph of 7.40, the ratio of bicarbonate to carbonic acid buffer is 20:1. Secretion of hco3 2 into the tubular lumen c.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
When used as a surrogate marker for urine ammonium, uag decreases and becomes negative if the increase in excretion of ammonium (the cation) is robust as part of the normal renal adaptive response to the metabolic acidosis of extrarenal origin, such as diarrhea. This review describes the physiological processes. Sign in to writing (essays) science.
 Source: derangedphysiology.com
Source: derangedphysiology.com
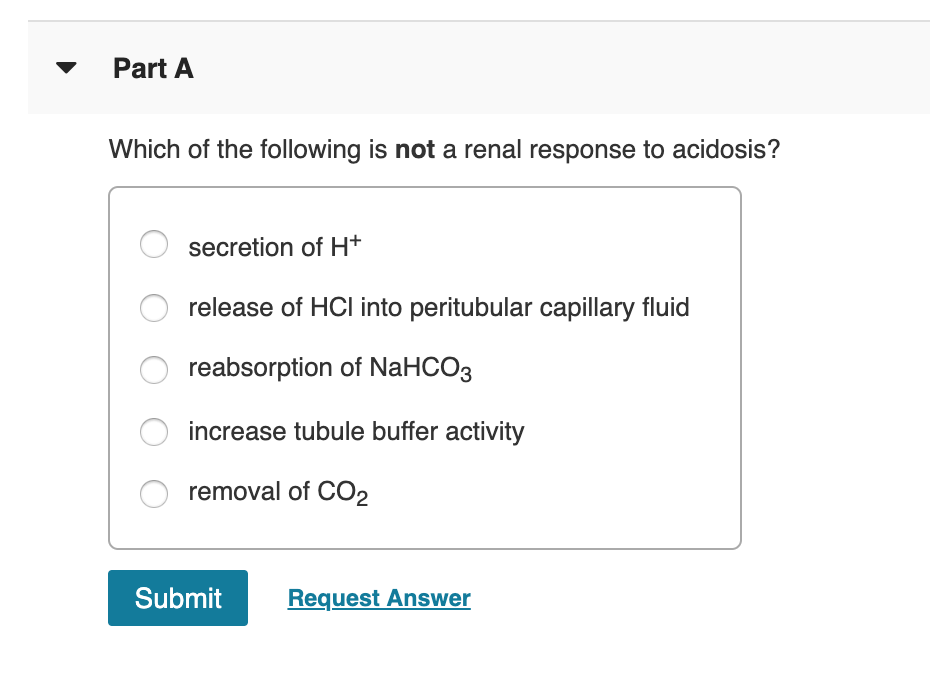
Which of the following is not a renal response to acidosis? Increasing secretion of hydrogen ions b. At the normal ph of 7.40, the ratio of bicarbonate to carbonic acid buffer is 20:1.
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
Secretion of ammonium into the tubular lumen. Sign in to writing (essays) science. Reabsorption of h + b.
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
The overall renal response to acidosis involves the net urinary excretion of hydrogen, resorption of nearly all filtered bicarbonate, and the generation of novel bicarbonate which is added to the extracellular fluid. If the kidneys are also functioning, the renal compensation for acidosis is to excrete acidic urine. The respiratory response to acidosis involves lowering the pco2
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
This problem has been solved! Secretion of ammonium into the tubular lumen. Respiratory acidosis stimulates h+ secretion in two ways
 Source: jasn.asnjournals.org
Source: jasn.asnjournals.org
Secretion of ammonium into the tubular lumen d. Which of the following is a component of the renal response to metabolic acidosis? Renal tubular acidosis can be divided into different subtypes, each with its own characteristics.
 Source: cjasn.asnjournals.org
Source: cjasn.asnjournals.org
Arterial concentration of hydrogen ion 22. Secretion of ammonium into the tubular lumen. A) osmotic pressure b) blood pressure.
 Source: derangedphysiology.com
Source: derangedphysiology.com
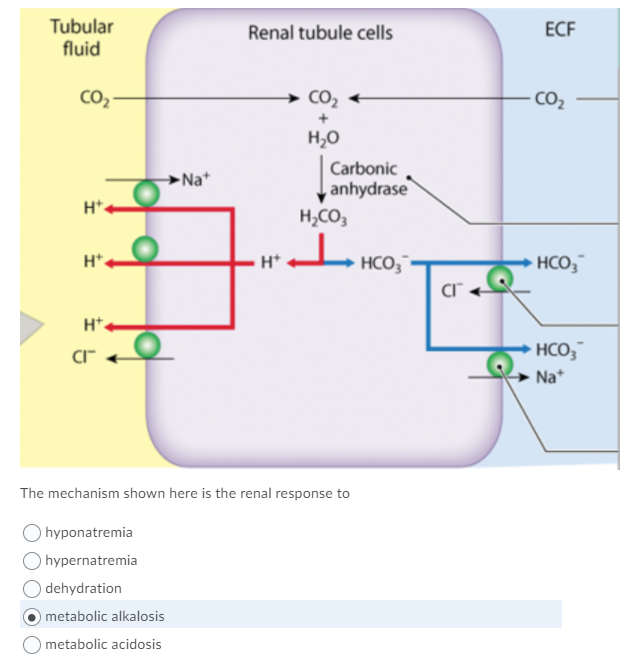
Metabolic acidosis occurs when the blood is too acidic (ph below 7.35) due to too little bicarbonate, a condition called primary bicarbonate deficiency. The overall renal response to acidosis involves the net urinary excretion of hydrogen, resorption of nearly all filtered bicarbonate, and the generation of novel bicarbonate which is added to the extracellular fluid. Renal tubular acidosis can be divided into different subtypes, each with its own characteristics.
 Source: link.springer.com
Source: link.springer.com
The overall renal response to acidosis involves the net urinary excretion of hydrogen, resorption of nearly all filtered bicarbonate, and the generation of novel bicarbonate which is added to the extracellular fluid. The normal renal response to metabolic acidosis is to increase acidic nh4 excretion renally. Sign in to writing (essays) science.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
If the kidneys are also functioning, the renal compensation for acidosis is to excrete acidic urine. A) osmotic pressure b) blood pressure. The normal renal response to metabolic acidosis is to increase acidic nh4 excretion renally.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
Metabolic acidosis occurs in the oliguric phase of acute renal failure as a result of impaired a. The respiratory response to acidosis involves lowering the pco2 Respiratory acidosis b) respiratory alkalosis c) metabolic acidosis with a compensatory respiratory alkalosis.
 Source: quizlet.com
Source: quizlet.com
The kidney cannot concentrate urine leading to fixed specific gravity 3. Release of hcl into peritubular capillary fluid which of the following is a renal response to acidosis? Which of the following is not a renal response to acidosis?
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Therefore, a positive urine anion gap between 20 and 90 meq/l is indicative of low or normal nh4 excretion, seen in renal causes, such as distal renal tubular acidosis. Chronically, the renal excretion of h+ is enhanced as the renal ability to produce ammonium from glutamine is induced. Which of the following is a component of the renal response to metabolic acidosis?
 Source: journals.physiology.org
Source: journals.physiology.org
The respiratory response to acidosis involves lowering the pco2 Renal tubular acidosis can be divided into different subtypes, each with its own characteristics. Renal tubular acidosis (rta) is characterized by hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis caused by either decreased hco 3 − reabsorption (proximal rta) or defective acid excretion (distal rta) in the presence of a normal glomerular filtration rate (gfr).
 Source: austincc.edu
Source: austincc.edu
Increasing secretion of hydrogen ions b. Renal tubular acidosis (rta) is characterized by hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis caused by either decreased hco 3 − reabsorption (proximal rta) or defective acid excretion (distal rta) in the presence of a normal glomerular filtration rate (gfr). See the answer see the answer done loading.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
All of the following are factors that contribute to a patient’s gfr, except: Which of the following is not a response by the kidney to acidosis? Secretion of ammonium into the tubular lumen d.
 Source: doctorlib.info
Source: doctorlib.info
Rta is uncommonly recognized in small animal practice. Renal tubular acidosis (rta) is characterized by hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis caused by either decreased hco 3 − reabsorption (proximal rta) or defective acid excretion (distal rta) in the presence of a normal glomerular filtration rate (gfr). Tests performed to detect renal tubular acidosis after administering an ammonium chloride load include all of the following except:
 Source: quizlet.com
Source: quizlet.com
The overall renal response to acidosis involves the net urinary excretion of hydrogen, resorption of nearly all filtered bicarbonate, and the generation of novel bicarbonate which is added to the extracellular fluid. Which of the following is not a renal response to acidosis? Which of the following is not a response by the kidney to acidosis?
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
C) causes the kidneys to produce a larger volume of. Inability to produce an acidic urine due to impaired production of ammonia d. If the kidneys are also functioning, the renal compensation for acidosis is to excrete acidic urine.
Also Read :