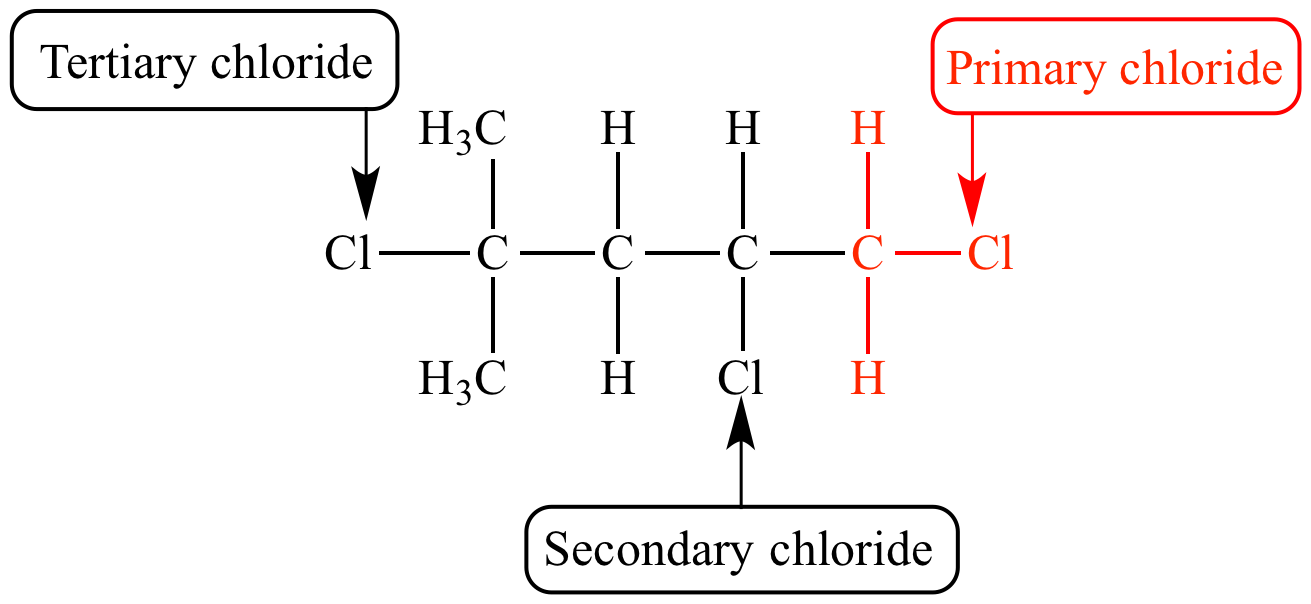
1 ∘ > 2 ∘ > 3 ∘. Because in it cl atom is attached to a primary carbon atom.
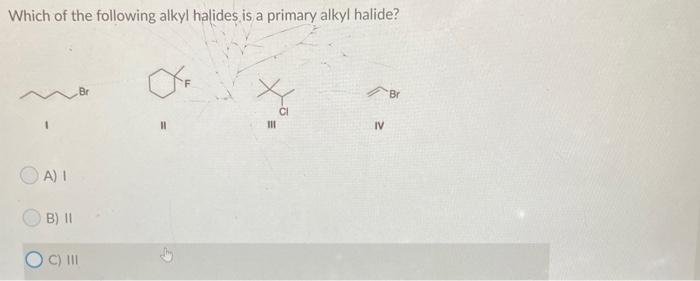
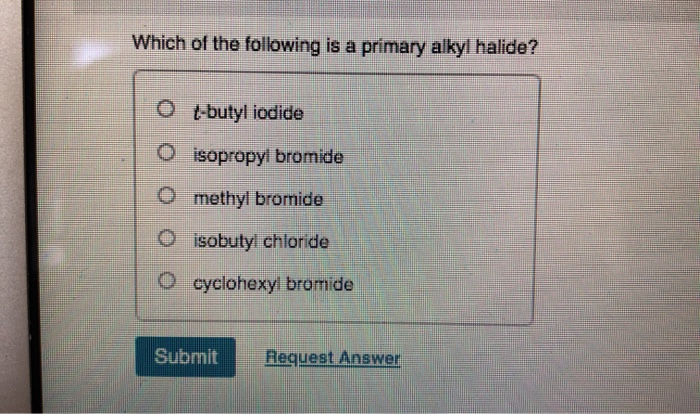
Which Of The Following Is A Primary Alkyl Halide. Which of the following is a 20 halide? C) the reaction rate increases as the leaving group ability increases. Which of the following is a primary alkyl halide? Hence it is primary alkyl halide.

Related Post Solved Testbank, Question 012 Which Of The Following Is A | Chegg.com :
The following reagent is required for the conversion of a primary amine into a primary alkyl halide: Haloalkanes contain halogen atom (s) attached to the sp3 hybridised carbon atom of an alkyl group. Which of the following alkyl halides is a secondary alkyl halide? X x x h 3 c x reactivity toward s n 2 1 2 3 most
The correct option is d.
A) the reaction is fastest with primary alkyl halide. Natalie preston had the following transactions for preston business services for year 1:1) provided services on account for $30,000.2) purchased $7,500 of supplies on account.3) at the end of the year, an adjusting entry was prepared for the supplies that had been used. X x x h 3 c x reactivity toward s n 2 1 2 3 most From the structural perspective, haloalkanes can be classified according to the connectivity of the carbon atom to which the halogen is attached. The correct option is d. S n 2 reaction mechanism is favoured mostly by primary alkyl halide or transition state and polarity of the solvent, s n 2 reaction mechanism is.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
It is can be seen in its structure. In primary (1°) haloalkanes, the carbon that carries the halogen atom is only attached to one other alkyl group. For c h x 3 c l, the carbon which carries the halogen atom has no other alkyl groups attached, yet my class notes say the alkyl halide has a primary centre.
 Source: chem.ucla.edu
Source: chem.ucla.edu
Which of the following is a primary alkyl halide? Which of the following is a primary alkyl halide? What is a primary alkyl halide.
 Source: brainly.in
Source: brainly.in
Among isomeric alkyl halides, the boiling point decreases with the increase in branching in the alkyl group, because with branching the molecule attains a spherical shape with less. Which of the following is a vinyl halide? Which of the following is a primary alkyl halide?
![Solved] (A) (A) (C) 6. Which Of The Following Is A Tertiary Alkyl Halide? (A) Ch3Br (B) (Ch3)3Cbr (C) (Ch3)2Ci- Source: coursehero.com
From the structural perspective, haloalkanes can be classified according to the connectivity of the carbon atom to which the halogen is attached. This carbon is attached to only one carbon atom. It is the best method for the laboratory preparation of both simple and mixed ethers and involves the action of sodium alkoxide (formed by reaction between alcohol and sodium metal) on a suitable alkyl halide.
From alkyl halides, ethers can be prepared by the following methods by williamson’s synthesis. Which of the following is a 20 halide? Grignard reaction can be written as:
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
Which of the following is a vinyl halide? For c h x 3 c l, the carbon which carries the halogen atom has no other alkyl groups attached, yet my class notes say the alkyl halide has a primary centre. It doesn�t make a difference how much massive gathering is appended to it.

D) the reaction rate increases as the strength of the nucleophile increases. An alkyl halide(haloalkane) in which the halogenatom (f, cl, br, or i) is bondedto a. The following reagent is required for the conversion of a primary amine into a primary alkyl halide:
 Source: chemistrysteps.com
Source: chemistrysteps.com
Among isomeric alkyl halides, the boiling point decreases with the increase in branching in the alkyl group, because with branching the molecule attains a spherical shape with less. Primary alkyl halide (1 o alkyl halide; Mechanisms depend on the following order:
 Source: numerade.com
Source: numerade.com
Primary, secondary, and tertiary alkyl halides are determined by the number of adjacent carbons to the carbon the halide group is attached to (that�s a mouthful, i know). They are secondary or tertiary halides. Natalie preston had the following transactions for preston business services for year 1:1) provided services on account for $30,000.2) purchased $7,500 of supplies on account.3) at the end of the year, an adjusting entry was prepared for the supplies that had been used.
 Source: toppr.com
Source: toppr.com
Which of the following statements about an sn1 reaction mechanism is true? 1 ∘ > 2 ∘ > 3 ∘. In elimination reactions of alkyl halide which site is more susceptible for the attack of base.
 Source: masterorganicchemistry.com
Source: masterorganicchemistry.com
प्राथमिक एल्किल हैलाइड की क्या प्राथमिकता होगी? While others are not primary halides. The following reagent is required for the conversion of a primary amine into a primary alkyl halide:
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
Bromine atom is attached to a primary carbon i.e. 1 ∘ > 2 ∘ > 3 ∘. C) the reaction rate increases as the leaving group ability increases.
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
In this type of haloalkanes, the carbon atom which carries the halogen atom is directly bonded to three. In this type of haloalkanes, the carbon atom which carries the halogen atom is directly bonded to three. A primary alkyl halide would prefer to undergo _____.
In elimination reactions of alkyl halide which site is more susceptible for the attack of base. An example is chloroethane ($\ce{ch3ch2cl}$). An alkyl halide (haloalkane) in which the halogen atom (f, cl, br, or i) is bonded to a primary carbon.
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
Natalie preston had the following transactions for preston business services for year 1:1) provided services on account for $30,000.2) purchased $7,500 of supplies on account.3) at the end of the year, an adjusting entry was prepared for the supplies that had been used. Bromine atom is attached to a primary carbon i.e. It is can be seen in its structure.

The reactivity of alkyl halide towards s n 1 and s n 2 reactions depends on various factors such as steric hindrance, stability of intermediate or transition state, and polarity of the solvent. An alkyl halide(haloalkane) in which the halogenatom (f, cl, br, or i) is bondedto a. They are secondary or tertiary halides.
 Source: study.com
Source: study.com
Grignard reaction can be written as: The reactivity of alkyl halide towards s n 1 and s n 2 reactions depends on various factors such as steric hindrance, stability of intermediate or transition state, and polarity of the solvent. S n 2 reaction mechanism is favoured mostly by primary alkyl halide or transition state and polarity of the solvent, s n 2 reaction mechanism is.

It doesn�t make a difference how much massive gathering is appended to it. S n 2 reaction mechanism is favoured mostly by primary alkyl halide or transition state and polarity of the solvent, s n 2 reaction mechanism is. The reactivity of alkyl halide towards s n 1 and s n 2 reactions depends on various factors such as steric hindrance, stability of intermediate or transition state, and polarity of the solvent.
 Source: doubtnut.com
Source: doubtnut.com
In this sort of haloalkane, the carbon which is clung to the halogen family will be simply connected to one other alkyl gathering. Thus methyl chloride c h 3 c l is a primary halide. It doesn�t make a difference how much massive gathering is appended to it.

Primary, secondary, and tertiary alkyl halides are determined by the number of adjacent carbons to the carbon the halide group is attached to (that�s a mouthful, i know). प्राथमिक एल्किल हैलाइड की क्या प्राथमिकता होगी? Because there is only one carbon bonded to the carbon that the chlorine is bonded to, it is a primary alkyl halide.
Also Read :