Striated muscle is formed during development by the fusion of small individual muscle cells called myoblasts into larger, multinucleated myotubes. These cells become committed muscle precursor cells, or myoblasts, which fuse to form multinucleated myotubes that consist of terminally differentiated muscle cells.
Which Muscle Tissue Is Multinucleated. There are three basic types of muscle tissue (skeletal, smooth, and cardiac) classified according to appearance of their contractile cells and location. The cells are multinucleated as a result of the fusion of the many myoblasts that fuse to form each long muscle fiber. Classification of muscle cells striated vs. The cells are multinucleated as a result of the fusion of the many myoblasts that fuse to form each long muscle fiber.
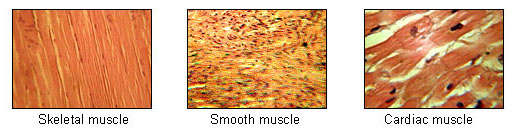 Seer Training: Muscle Tissue From training.seer.cancer.gov
Seer Training: Muscle Tissue From training.seer.cancer.gov
Related Post Seer Training: Muscle Tissue :
Skeletal muscles maintain posture, stabilize bones and joints, control internal movement, and generate heat. Block is attached to a vertical rod by means of two strings of equal length. Cardiac muscle forms the contractile walls of the heart. Their control is quick, forceful, and usually voluntary caused by the interaction of thin actin filaments and thick myosin filaments whose molecular configuration allows them to slide upon one another.
Easy muscle cells are spindle formed, have a single, centrally situated nucleus, and.
Skeletal muscles smooth muscle tissue There are 3 types of muscle cells in the human body; Blood vessels and nerves enter the connective tissue and branch in the cell. Muscle tissues are specialized for contraction and include the skeletal muscles of the body, the heart, and the muscular walls of hollow organs. (a) how many revolutions per minute must the system make in order for the tension in the upper string to be. The nuclei of the myotube are still located centrally in the muscle fibre.
 Source: stevegallik.org
Source: stevegallik.org
Muscles attach to bones directly or through tendons or aponeuroses. The cells are multinucleated as a result of the fusion of the many myoblasts that fuse to form each long muscle fiber. Smooth muscle cells are strictly mononucleated, and cardiac muscle cells are mononucleated in humans.
 Source: brainly.in
Source: brainly.in
Easy muscle cells are spindle formed, have a single, centrally situated nucleus, and. Cardiac muscle has branching fibers, one. Skeletal muscles maintain posture, stabilize bones and joints, control internal movement, and generate heat.
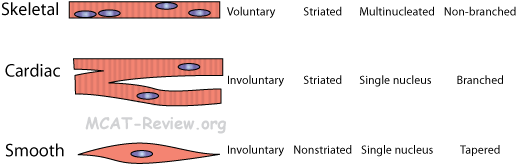 Source: mcat-review.org
Source: mcat-review.org
Smooth muscle cells are spindle shaped, have a single, centrally located nucleus, and lack striations. Skeletal muscle fibers are long cylindrical, multinucleated, striated, and under voluntary control. There are 3 types of muscle cells in the human body;
 Source: quizlet.com
Source: quizlet.com
Their control is quick, forceful, and usually voluntary caused by the interaction of thin actin filaments and thick myosin filaments whose molecular configuration allows them to slide upon one another. The cells of these tissues are multinucleated. Classification of muscle cells striated vs.
 Source: en.wikipedia.org
Source: en.wikipedia.org
The cells of cardiac muscle, known as cardiomyocytes, also appear striated under the microscope. These cells become committed muscle precursor cells, or myoblasts, which fuse to form multinucleated myotubes that consist of terminally differentiated muscle cells. Multinucleate cells (multinucleated or polynuclear cells) are eukaryotic cells that have more than one nucleus per cell, i.e., multiple nuclei share one common cytoplasm.
 Source: quizlet.com
Source: quizlet.com
Smooth muscle cells are strictly mononucleated, and cardiac muscle cells are mononucleated in humans. Mitosis in multinucleate cells can occur either in a coordinated, synchronous manner where all nuclei divide simultaneously or asynchronously where individual nuclei divide independently in time and space. Easy muscle cells are spindle formed, have a single, centrally situated nucleus, and.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Skeletal muscle fibers are cylindrical, multinucleated, striated, and underneath voluntary management. What muscle tissue has cylindrical cells? I mean, every muscle fiber is formed by the fusion of many cells (myoblasts).
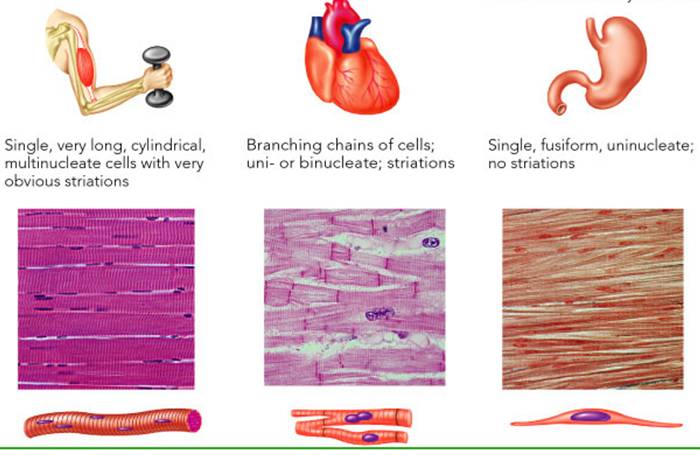 Source: austincc.edu
Source: austincc.edu
But most importantly, ability to synthesize and secrete skeletal muscle proteins that are frequently lost due to increased muscle contraction. Multinucleate cells (multinucleated or polynuclear cells) are eukaryotic cells that have more than one nucleus per cell, i.e., multiple nuclei share one common cytoplasm. Striated, multinucleated (less than skeletal), only in heart, involuntary control, pumps blood.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Skeletal muscles maintain posture, stabilize bones and joints, control internal movement, and generate heat. Each nucleus regulates the metabolic requirements of the sarcoplasm around it. There are 3 types of muscle cells in the human body;
![Solved] What Are Three Types Of Muscle Cells In Their Respective Fiber Anatomy? | Course Hero](https://www.coursehero.com/qa/attachment/16167885/ “Solved] What Are Three Types Of Muscle Cells In Their Respective Fiber Anatomy? | Course Hero”) Source: coursehero.com
Cardiac muscle forms the contractile walls of the heart. Blood vessels and nerves enter the connective tissue and branch in the cell. The nuclei of the myotube are still located centrally in the muscle fibre.
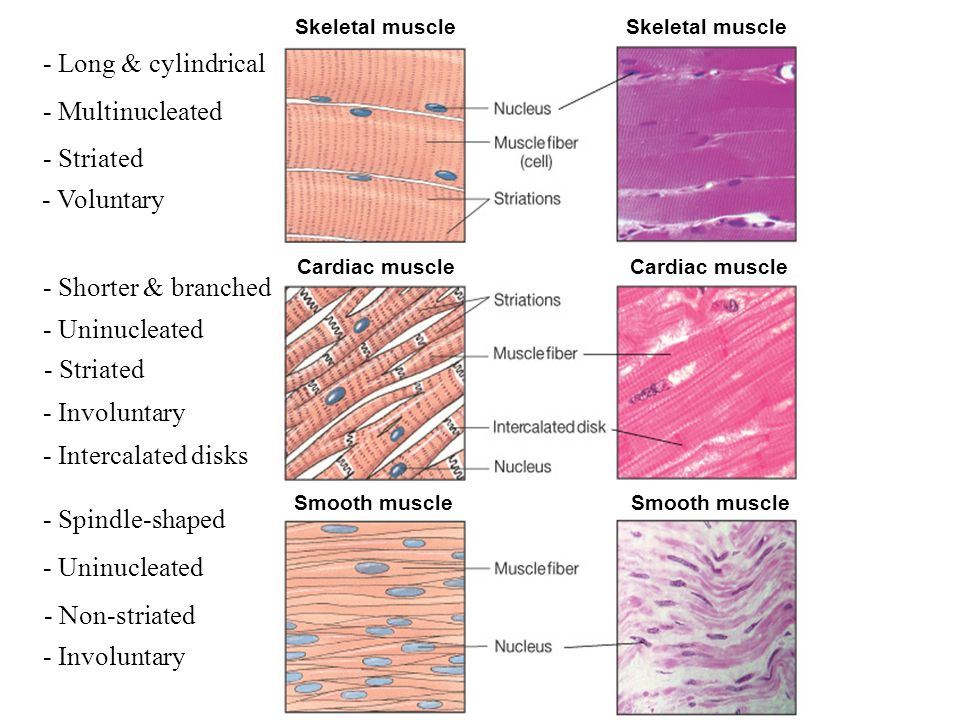 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
Each nucleus regulates the metabolic requirements of the sarcoplasm around it. The cells are multinucleated as a result of the fusion of the many myoblasts that fuse to form each long muscle fiber. Skeletal muscle fibers are long, multinucleated cells.
 Source: quizlet.com
Source: quizlet.com
I mean, every muscle fiber is formed by the fusion of many cells (myoblasts). They bring about the movement of the organs of the body. Skeletal muscle fibers are long, multinucleated cells.
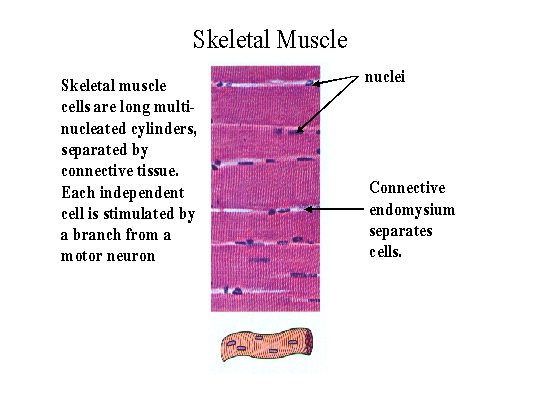 Source: unm.edu
Source: unm.edu
I mean, every muscle fiber is formed by the fusion of many cells (myoblasts). The cells are multinucleated as a result of the fusion of the many myoblasts that fuse to form each long muscle fiber. Striated, multinucleated (less than skeletal), only in heart, involuntary control, pumps blood.
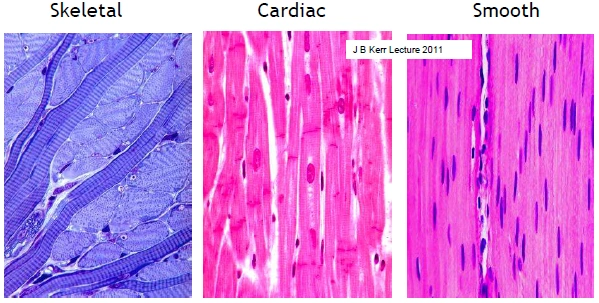 Source: viarevision.fandom.com
Source: viarevision.fandom.com
There are 3 types of muscle cells in the human body; Prove that the product of the 2nd and 3rd terms of an a.p. The cells of cardiac muscle, known as cardiomyocytes, also appear striated under the microscope.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Smooth muscle cells are spindle shaped, have a single, centrally located nucleus, and lack striations. Classification of muscle cells striated vs. Prove that the product of the 2nd and 3rd terms of an a.p.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
But most importantly, ability to synthesize and secrete skeletal muscle proteins that are frequently lost due to increased muscle contraction. Cardiac muscle forms the contractile walls of the heart. Cardiac muscle has branching fibers, one.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
The cells are multinucleated as a result of the fusion of the many myoblasts that fuse to form each long muscle fiber. Blood vessels and nerves enter the connective tissue and branch in the cell. Their control is quick, forceful, and usually voluntary caused by the interaction of thin actin filaments and thick myosin filaments whose molecular configuration allows them to slide upon one another.

Components of a skeletal muscle. The terms muscle cell and muscle fiber are synonymous. Easy muscle cells are spindle formed, have a single, centrally situated nucleus, and.
 Source: training.seer.cancer.gov
Source: training.seer.cancer.gov
Skeletal muscle fibers are cylindrical, multinucleated, striated, and under voluntary control. Muscle tissues are specialized for contraction and include the skeletal muscles of the body, the heart, and the muscular walls of hollow organs. Skeletal muscle tissue is arranged in bundles surrounded by connective tissue.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
(a) how many revolutions per minute must the system make in order for the tension in the upper string to be. They are called involuntary muscles. Blood vessels and nerves enter the connective tissue and branch in the cell.
Also Read :