It addresses the way in which movement of ions controls the cell shape and regulates ph. This all results in a significant saving of atp by the hair cell.
Which Movement Of Ions Produces Epsps In Cochlea Hair Cells. The open channels pass inward current, carried primarily by potassium and calcium ions, which depolarizes the hair cell and initiates the sensory signal. A) influx of na+ b) efflux of ca++ c) influx of k+ and ca++ d) efflux of k+ Acting like motor cells, outer hair cells produce forces that are driven by graded changes in membrane potential. At the base of the hair cells is a network of cochlear nerve endings, which lead to the spiral ganglion of corti in the modiolus of the cochlea.
 Apoptosis In Inner Ear Sensory Hair Cells - Sciencedirect From sciencedirect.com
Apoptosis In Inner Ear Sensory Hair Cells - Sciencedirect From sciencedirect.com
Related Post Apoptosis In Inner Ear Sensory Hair Cells - Sciencedirect :
Outer hair cells connect to only 10 percent of the afferent neurons, and each afferent neuron innervates many hair cells. Four canals, including the cochlea, detect indirect movement of hair cells. ·neurons are stimulated ·olfactory receptors detect vaporized odor molecules ·signal. Vibrations are caused to the endolymph of the scala media.
[solved] which movement of ions produces epsps in cochlea hair cells?
The inner ear and cochlea¶. Acting like motor cells, outer hair cells produce forces that are driven by graded changes in membrane potential. Vibration of the stapes in the inner ear causes the vibration of the oval window at the base of the cochlea [1]. The spiral ganglion sends axons. This protein, known as prestin, is a member of a transporter superfamily slc26. Whereas the perilymph is rich in sodium ions, the endolymph is rich in potassium ions, which produces an ionic, electrical potential.
 Source: en.wikipedia.org
Source: en.wikipedia.org
The open channels pass inward current, carried primarily by potassium and calcium ions, which depolarizes the hair cell and initiates the sensory signal. The functional and structural properties of prestin are described in this review. As the waves move inside the cochlea, they cause other structures to move, and this eventually causes hair cells (that are part of the organ.
 Source: febs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Source: febs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
In the perilymph, a wave is set up by the movement of the oval window. Our first task is to understand how outer hair cell inhibition alters the response of inner hair cells. The open channels pass inward current, carried primarily by potassium and calcium ions, which depolarizes the hair cell and initiates the sensory signal.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
A) influx of na + b) efflux of ca ++ c) efflux of k + d) influx of k + and ca ++ 139) 140) fusing of the ossicles (otosclerosis) results in ________. A circular canal detects movement via fluid that stimulates the oval window. The hair cells are arranged in four rows in the organ of corti along the entire length of the cochlear coil.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Vibrations are caused to the endolymph of the scala media. Watch this video to learn more about how the structures of the ear convert sound waves into a neural signal by moving the “hairs,” or stereocilia, of the cochlear duct. Patients suffering from myotonic dystrophy also have a concurrent high risk of sensorineural hearing loss (wright et al., 1988).
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
Four canals, including the cochlea, detect indirect movement of hair cells. This all results in a significant saving of atp by the hair cell. Through mechanotransduction, hair cells detect movement in their environment.
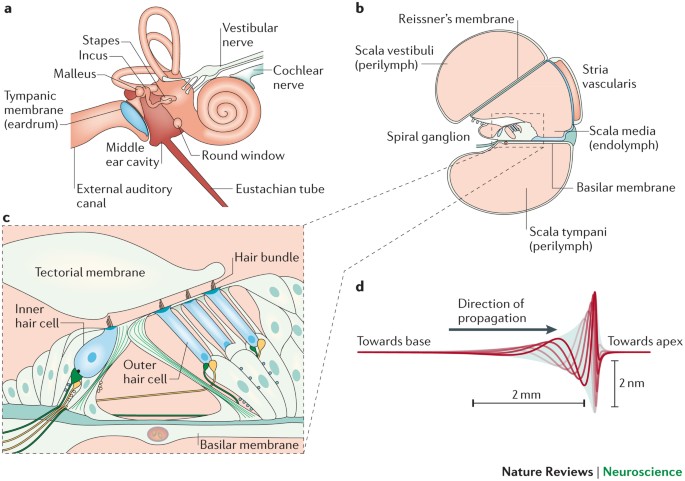 Source: nature.com
Source: nature.com
A) influx of na + b) efflux of ca ++ c) efflux of k + d) influx of k + and ca ++ 139) 140) fusing of the ossicles (otosclerosis) results in ________. Whereas the perilymph is rich in sodium ions, the endolymph is rich in potassium ions, which produces an ionic, electrical potential. In mammals, the auditory hair cells are located within the spiral organ of corti on the thin basilar membrane in the cochlea of the inner ear.
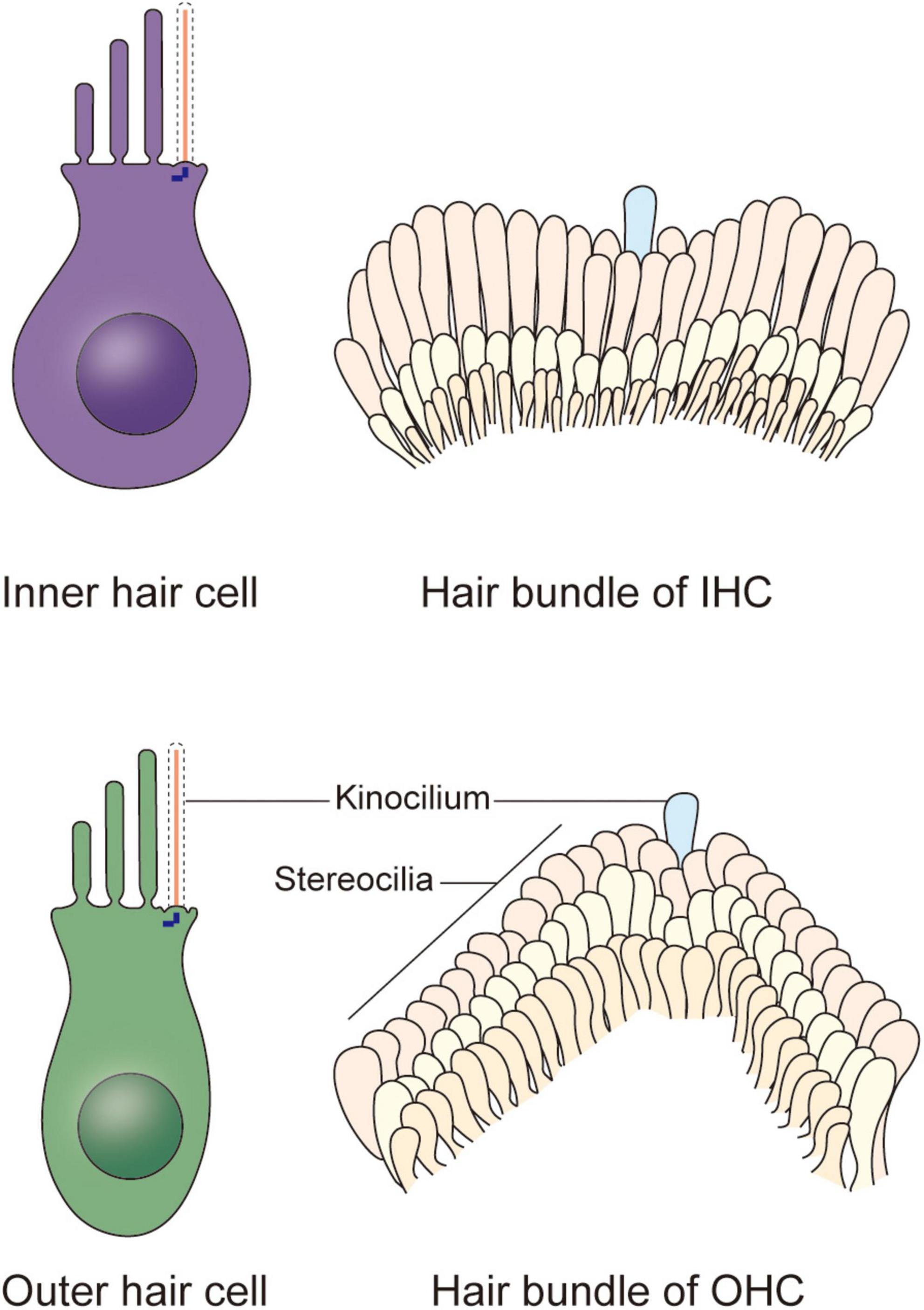 Source: frontiersin.org
Source: frontiersin.org
Our first task is to understand how outer hair cell inhibition alters the response of inner hair cells. The forces depend on the presence of a motor protein in the lateral membrane of the cells. In mammals, the auditory hair cells are located within the spiral organ of corti on the thin basilar membrane in the cochlea of the inner ear.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
The functional and structural properties of prestin are described in this review. [solved] which movement of ions produces epsps in cochlea hair cells? Hair cells are the sensory receptors of both the auditory system and the vestibular system in the ears of all vertebrates, and in the lateral line organ of fishes.
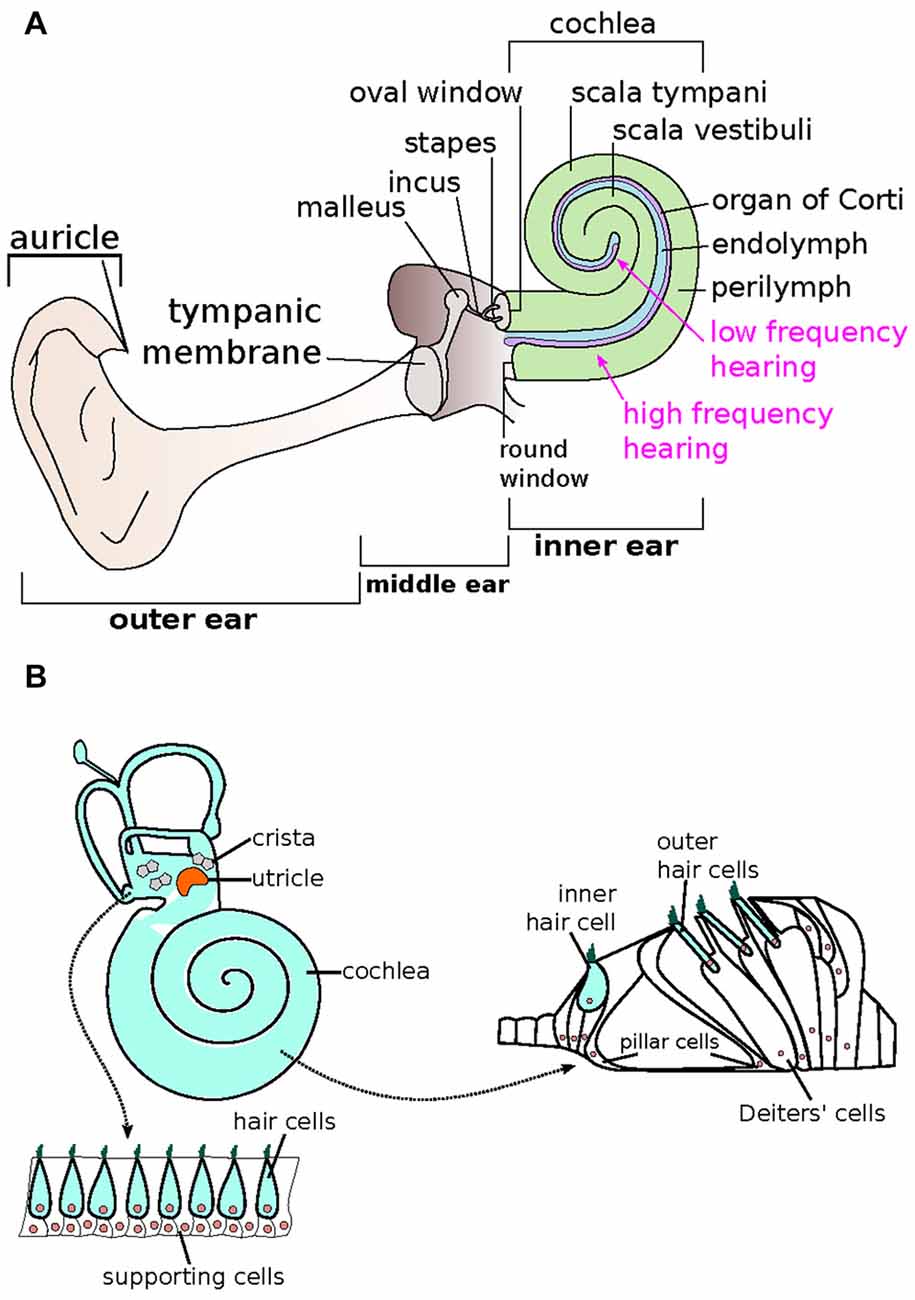 Source: frontiersin.org
Source: frontiersin.org
Auditory hair cells, which reside in the sensory epithelium of the cochlea and utricle, have bundles of cilia that transduce the energy of sound and motion to electrical impulses that travel to the brain over the acoustic nerve. The hair cells are held in place by the reticular lamina, a rigid structure supported by the pillar cells, or rods of corti, which are attached to the basilar fibres. Hair cells adapt to sustained bundle deflections by adjusting channel open probability back toward the resting value.
 Source: en.wikipedia.org
Source: en.wikipedia.org
The fluid in the cochlea, the oval window, and the round window all serve to control the movement of sound waves around the basilar membrane [1]. The forces depend on the presence of a motor protein in the lateral membrane of the cells. ·neurons are stimulated ·olfactory receptors detect vaporized odor molecules ·signal.
 Source: pnas.org
Source: pnas.org
The hair cells are arranged in four rows in the organ of corti along the entire length of the cochlear coil. Patients suffering from myotonic dystrophy also have a concurrent high risk of sensorineural hearing loss (wright et al., 1988). A circular canal detects movement via fluid that stimulates the oval window.
 Source: onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Source: onlinelibrary.wiley.com
The basilar movements help in bending the hair cells when they are pressed against the tectorial membrane. A circular canal detects movement via fluid that stimulates the oval window. The inner ear and cochlea¶.
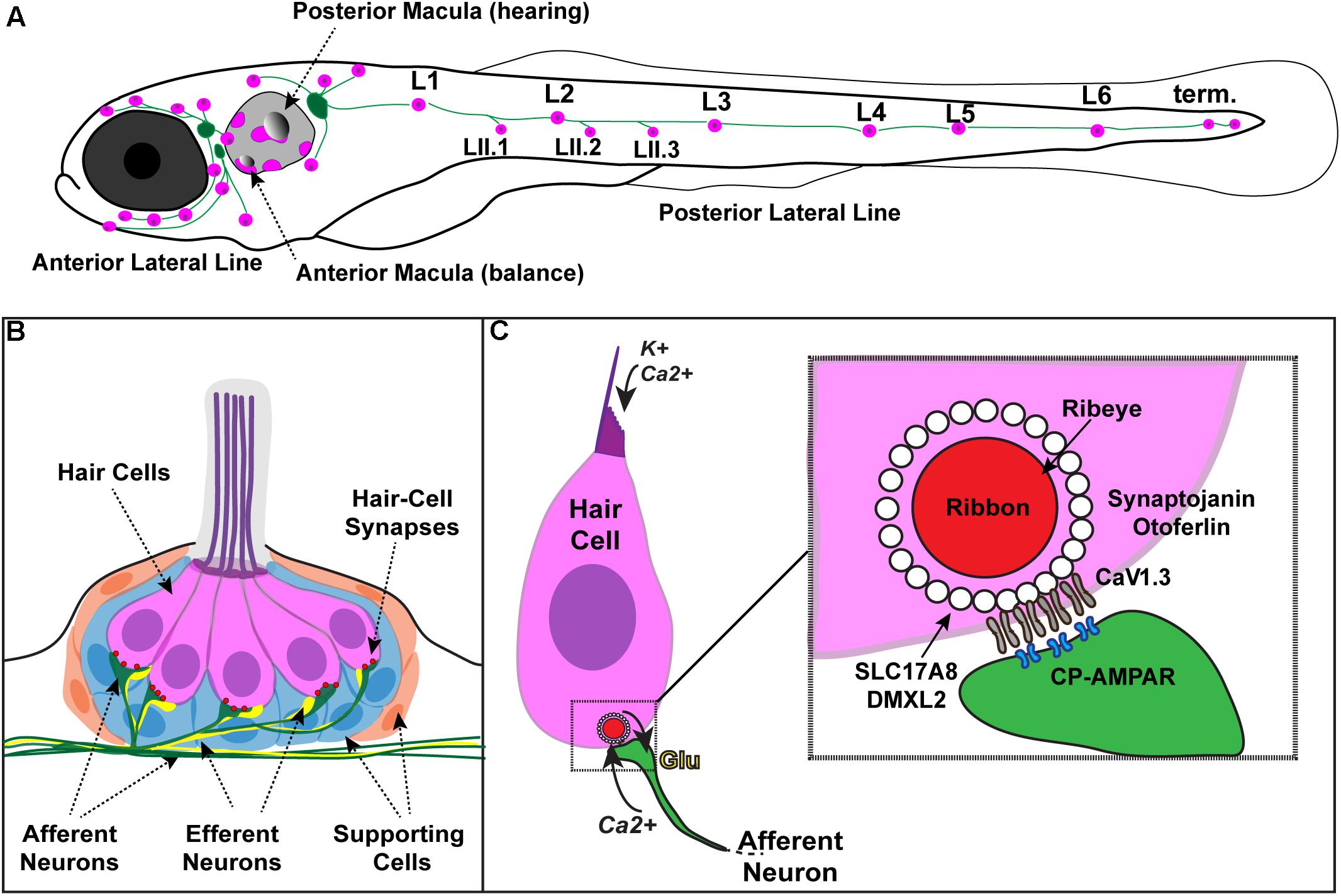 Source: frontiersin.org
Source: frontiersin.org
Our first task is to understand how outer hair cell inhibition alters the response of inner hair cells. This opening image is a ‘whole mount’ view of the rat cochlea. Four canals, including the cochlea, detect indirect movement of hair cells.
 Source: journals.physiology.org
Source: journals.physiology.org
Transduction without tip links in cochlear hair cells is mediated by ion channels with permeation properties distinct from those of. The functional and structural properties of prestin are described in this review. In the basilar membrane, a wave is induced by the endolymph in the waves.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
The afferent, bipolar neurons that convey auditory information travel from the cochlea to the medulla, through the pons and midbrain in the brainstem, finally reaching the primary auditory cortex in the temporal lobe. Whereas the perilymph is rich in sodium ions, the endolymph is rich in potassium ions, which produces an ionic, electrical potential. As the footplate of the stapes presses on the oval window at the base of the cochlea, it pressurizes the fluid in the scala vestibule or vestibular canal, a channel that runs the length of the cochlear spiral.given that the cochlea is a closed system, this pressure has to be dissipated somehow, or the stapes footplate would be pushing.
 Source: researchfeatures.com
Source: researchfeatures.com
- which movement of ions produces epsps in cochlea hair cells? Three rows consist of outer hair cells (ohcs) and one row consists of inner hair cells (ihcs). 139) which movement of ions produces epsps in cochlea hair cells?
 Source: doctorlib.info
Source: doctorlib.info
In the basilar membrane, a wave is induced by the endolymph in the waves. The stria vascularis, a complex epithelial structure composed of various cell types, produces endolymph and releases it into the cochlea. Watch this video to learn more about how the structures of the ear convert sound waves into a neural signal by moving the “hairs,” or stereocilia, of the cochlear duct.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Our first task is to understand how outer hair cell inhibition alters the response of inner hair cells. Outer hair cells connect to only 10 percent of the afferent neurons, and each afferent neuron innervates many hair cells. Hair cells are the sensory receptors of both the auditory system and the vestibular system in the ears of all vertebrates, and in the lateral line organ of fishes.
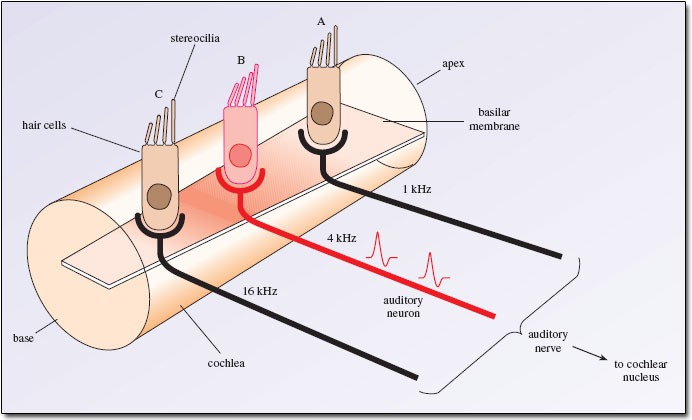 Source: tulane.edu
Source: tulane.edu
- which movement of ions produces epsps in cochlea hair cells? The basilar movements help in bending the hair cells when they are pressed against the tectorial membrane. This leads to a rapid influx of ca 2+ ions into the hair cells, which results in the release of glutamate.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
The stria vascularis, a complex epithelial structure composed of various cell types, produces endolymph and releases it into the cochlea. The hair cells are arranged in four rows in the organ of corti along the entire length of the cochlear coil. A) influx of na + b) efflux of ca ++ c) efflux of k + d) influx of k + and ca ++ 139) 140) fusing of the ossicles (otosclerosis) results in ________.
Also Read :





