6.) the enzyme dna ligase joins the two dna molecules by covalent bonds. C) it has both a 3’→5’ polymerase activity and a 3’→ 5’exonuclease activity.
Which Molecule Catalyzes Covalent Bond Formation Between Fragments Of Dna. Initially, the simplest mechanism of dna replication seemed to be the continuous growth of both new strands, nucleotide by nucleotide, at the replication fork as it moves from one end of a dna molecule to the other. In molecular biology, ligation refers to the joining of two dna fragments through the formation of a phosphodiester bond. Which molecule catalyzes covalent bond formation between fragments of dna. An enzyme known as a ligase catalyzes the ligation reaction.in the cell, ligases repair single and double strand.
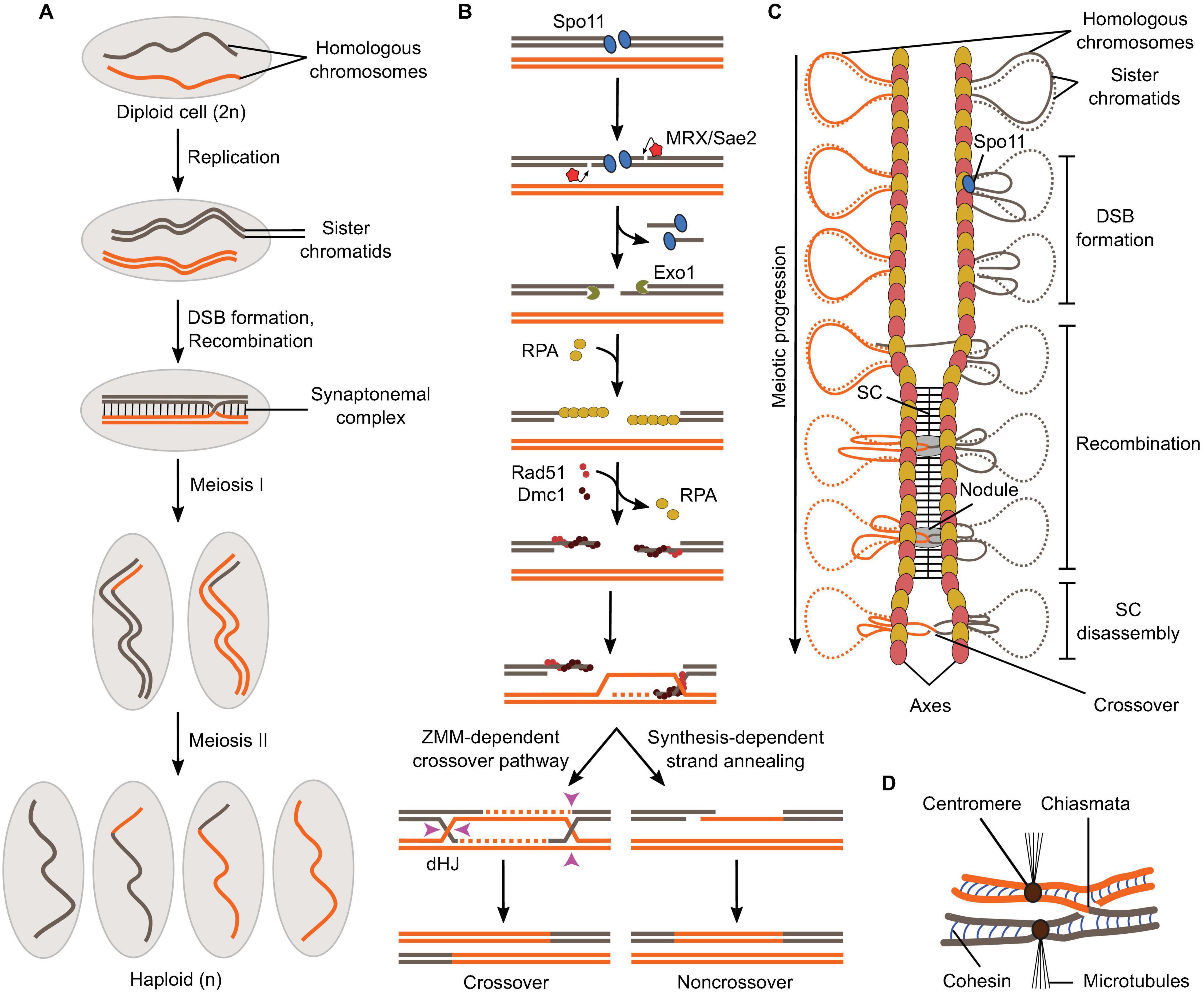 Frontiers | Mechanism And Control Of Meiotic Dna Double-Strand Break Formation In S. Cerevisiae | Cell And Developmental Biology From frontiersin.org
Frontiers | Mechanism And Control Of Meiotic Dna Double-Strand Break Formation In S. Cerevisiae | Cell And Developmental Biology From frontiersin.org
Related Post Frontiers | Mechanism And Control Of Meiotic Dna Double-Strand Break Formation In S. Cerevisiae | Cell And Developmental Biology :
What would first happen to dna molecules treated with dnaase? In molecular biology, ligation refers to the joining of two dna fragments through the formation of a phosphodiester bond. Which molecule catalyzes covalent bond formation between fragments of dna. Initially, the simplest mechanism of dna replication seemed to be the continuous growth of both new strands, nucleotide by nucleotide, at the replication fork as it moves from one end of a dna molecule to the other.
D) it uses ribonucleoside triphosphates as substrates and removes supercoils.
6.) the enzyme dna ligase joins the two dna molecules by covalent bonds. B) adds nucleotides to the 5′ end of a growing dna strand.c) adds nucleotides to the 3′ end of a growing dna strand.d) makes covalent bonds to attach dna fragments together.e) binds to dna and keeps the replication fork open. The bond is the result of a condensation reaction between a hydroxyl group of two sugar groups and a phosphate group. An enzyme that requires the presence of a double stranded nucleic acid primer to catalyze the addition of nucleotides to the 3� end of a growing dna strand. Dna ligase catalyzes the formation of two covalent phosphodiester bonds between. When nucleotides are incorporated into dna, adjacent nucleotides are linked by a phosphodiester bond:
 Source: wou.edu
Source: wou.edu
Example question #4 a covalent bond is the sharing of electrons between atoms. What would first happen to dna molecules treated with dnaase? This enzyme, which the cell normally uses in dna replication is a dna pasting enzyme that catalyzes the formation of covalent bonds between adjacent nucleotides, joining the strands.
 Source: nature.com
Source: nature.com
An enzyme that requires the presence of a double stranded nucleic acid primer to catalyze the addition of nucleotides to the 3� end of a growing dna strand. Made in replication the lagging strand of dna unlike the leading strand. 27) dna polymerase can be described as and enzyme that _____.a) produces a primer needed for dna replication.
![Siroheme- And [Fe4-S4]-Dependent Nira From Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Is A Sulfite Reductase With A Covalent Cys-Tyr Bond In The Active Site* - Journal Of Biological Chemistry Siroheme- And [Fe4-S4]-Dependent Nira From Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Is A Sulfite Reductase With A Covalent Cys-Tyr Bond In The Active Site* - Journal Of Biological Chemistry](https://els-jbs-prod-cdn.jbs.elsevierhealth.com/cms/attachment/95c58240-d8b9-40a1-babb-126cdda7f1ff/gr1_lrg.jpg) Source: jbc.org
Source: jbc.org
B) it is a multimeric enzyme that catalyzes the formation of covalent phosphodiester bonds. A dna ligase catalyzes the formation of a phosphodiester bond between juxtaposed 5’ phosphate and 3’ hydroxyl termini in duplex dna. Which molecule catalyzes covalent bond formation between fragments of dna.
 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
Which molecule catalyzes covalent bond formation between fragments of dna. A covalent bond is stronger than a hydrogen bond (hydrogen bonds hold pairs of nucleotides together on opposite strands in dna). The diester bond between phosphoric acid and two sugar molecules in the dna and rna backbone links two nucelotides together to form oligonucleotide polymers.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
Dna ligase enzyme catalyse the joining together of phosphodiester bonds of dna. Enzyme in dna replication responsible for denaturing the double helix ahead of. When nucleotides are incorporated into dna, adjacent nucleotides are linked by a phosphodiester bond:
 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
D) it uses ribonucleoside triphosphates as substrates and removes supercoils. Which molecule a) helicase catalyzes covalent bond formation between fragments of dna after primers have been replaced b) ligase c) telomerase d) primase e) nuclease 10)in an analysis of the nucleotide composition of dna, which of the following will be found? Made in replication the lagging strand of dna unlike the leading strand.

This enzyme, which the cell normally uses in dna replication is a dna pasting enzyme that catalyzes the formation of covalent bonds between adjacent nucleotides, joining the strands. During dna replication, all of the following proteins are important for separating the dna strands and allowing movement of the replication fork except dna polymerase this molecule catalyzes covalent bond formation between fragments of dna. A covalent bond is stronger than a hydrogen bond (hydrogen bonds hold pairs of nucleotides together on opposite strands in dna).
 Source: onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Source: onlinelibrary.wiley.com
A) it transcribes one dna strand of a gene using an rna primer for initiation. The bond is the result of a condensation reaction between a hydroxyl group of two sugar groups and a phosphate group. An enzyme known as a ligase catalyzes the ligation reaction.in the cell, ligases repair single and double strand.
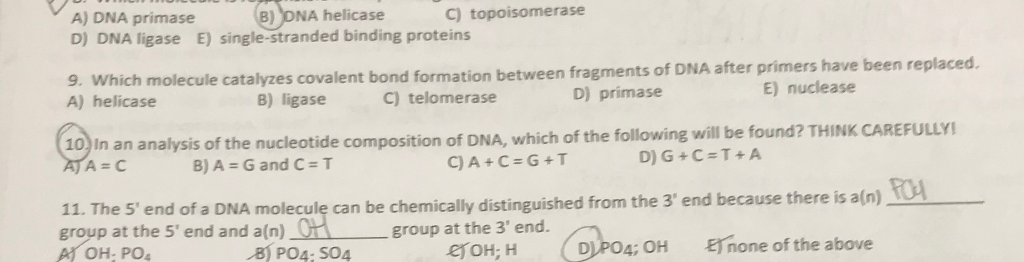 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
Dna polymerases catalyze the formation of a phosphodiester bond efficiently only if the base on the incoming nucleoside triphosphate is complementary to the base on the template strand. This enzyme, which the cell normally uses in dna replication is a dna pasting enzyme that catalyzes the formation of covalent bonds between adjacent nucleotides, joining the strands. Thus, the covalent bond is crucial to the backbone of the dna.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
It is used in replication as well as repair of the dna. What covalent bonds form the backbone of a dna strand? During dna replication, all of the following proteins are important for separating the dna strands and allowing movement of the replication fork except dna polymerase this molecule catalyzes covalent bond formation between fragments of dna.
 Source: jbc.org
Source: jbc.org
Dna ligase is the enzyme which catalyzes the formation of phosphodiester in dna molecule. A covalent bond is stronger than a hydrogen bond (hydrogen bonds hold pairs of nucleotides together on opposite strands in dna). An enzyme known as a ligase catalyzes the ligation reaction.in the cell, ligases repair single and double strand.
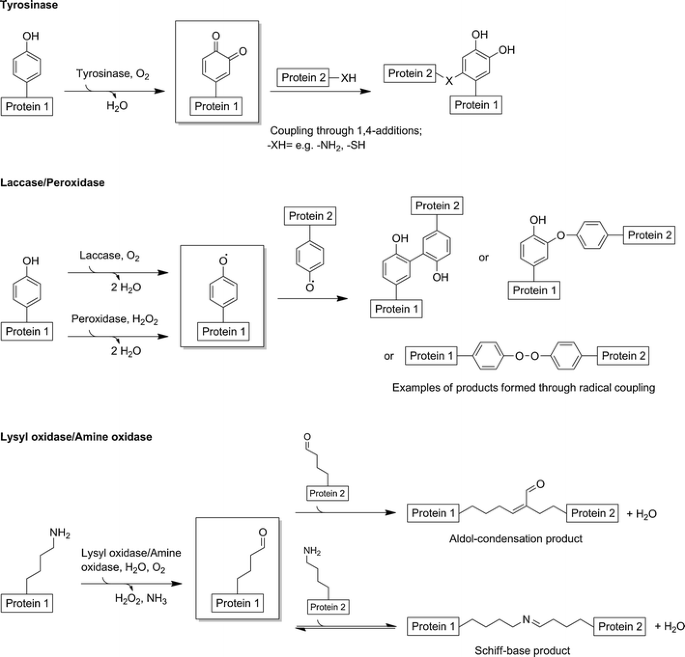 Source: link.springer.com
Source: link.springer.com
Which molecule catalyzes covalent bond formation between fragments of dna. Source for information on dna ligase: During dna replication, all of the following proteins are important for separating the dna strands and allowing movement of the replication fork except dna polymerase this molecule catalyzes covalent bond formation between fragments of dna.
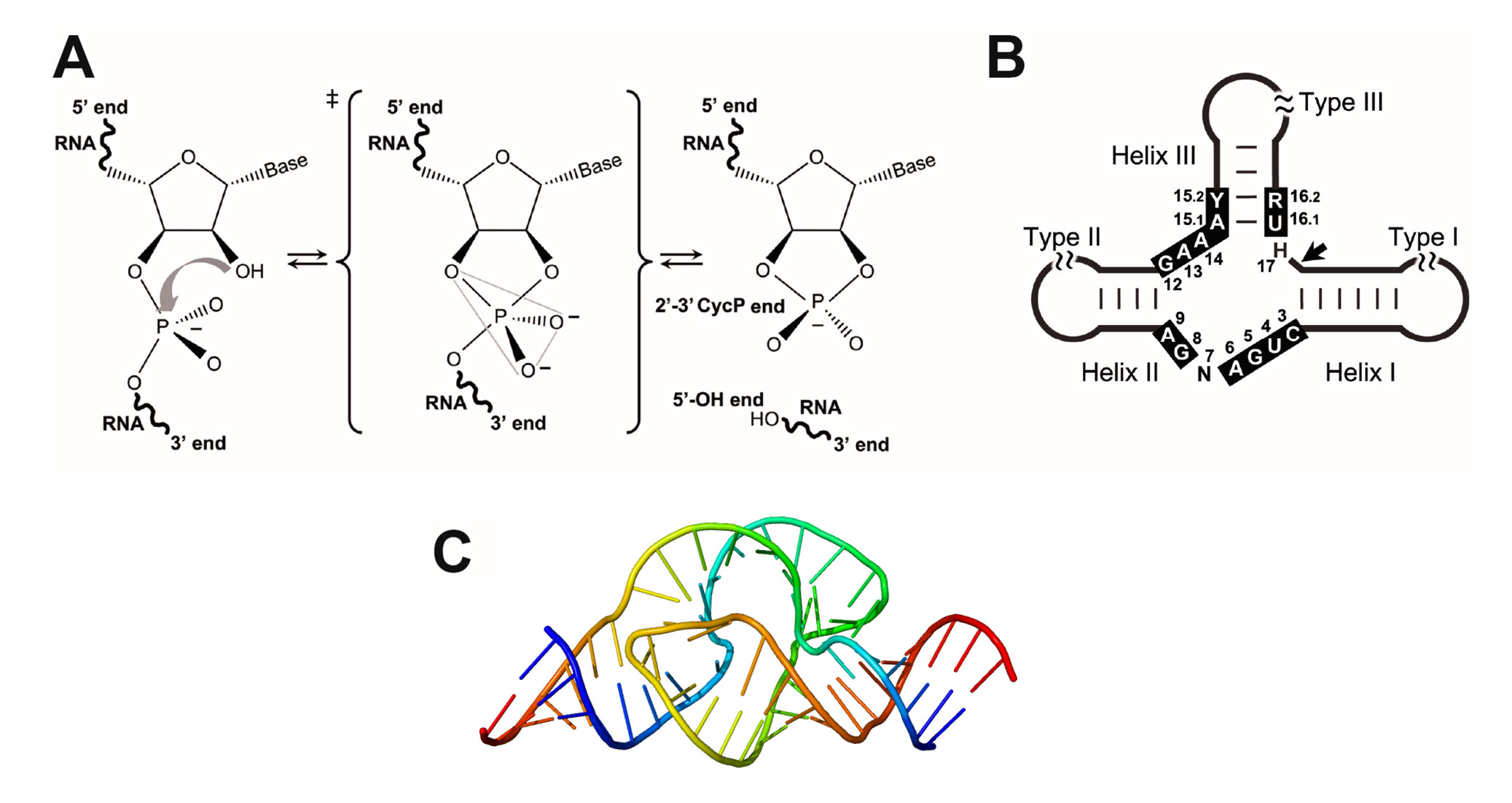 Source: wou.edu
Source: wou.edu
Technology (see genetic engineering) as it ensures that the foreign dna (e.g. Example question #4 a covalent bond is the sharing of electrons between atoms. What is a ligation reaction?
 Source: frontiersin.org
Source: frontiersin.org
C) it has both a 3’→5’ polymerase activity and a 3’→ 5’exonuclease activity. Which molecule a) helicase catalyzes covalent bond formation between fragments of dna after primers have been replaced b) ligase c) telomerase d) primase e) nuclease 10)in an analysis of the nucleotide composition of dna, which of the following will be found? Dna ligase catalyzes covalent bond formation between the 3′oh and 5′po 4 on dna (phosphodiester bond).
 Source: nyaspubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Source: nyaspubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
The diester bond between phosphoric acid and two sugar molecules in the dna and rna backbone links two nucelotides together to form oligonucleotide polymers. Dna ligase is the enzyme which catalyzes the formation of phosphodiester in dna molecule. 6.) the enzyme dna ligase joins the two dna molecules by covalent bonds.
 Source: onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Source: onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Dna ligase catalyzes covalent bond formation between the 3′oh and 5′po 4 on dna (phosphodiester bond). In molecular biology, ligation refers to the joining of two dna fragments through the formation of a phosphodiester bond. It is used in replication as well as repair of the dna.
 Source: jbc.org
Source: jbc.org
Technology (see genetic engineering) as it ensures that the foreign dna (e.g. Dna ligase catalyzes the formation of two covalent phosphodiester bonds between. The major enzyme involved in dna replication that synthesizes the new dna strand by adding nucleotides to an existing chain.
 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
Dnaase is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of the covalent bonds that join nucleotides together. Phosphodiester bonds are strong covalent bonds between. C) it has both a 3’→5’ polymerase activity and a 3’→ 5’exonuclease activity.
 Source: chemistry-europe.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Source: chemistry-europe.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Dna ligase is the enzyme which catalyzes the formation of phosphodiester in dna molecule. The major enzyme involved in dna replication that synthesizes the new dna strand by adding nucleotides to an existing chain. When nucleotides are incorporated into dna, adjacent nucleotides are linked by a phosphodiester bond:
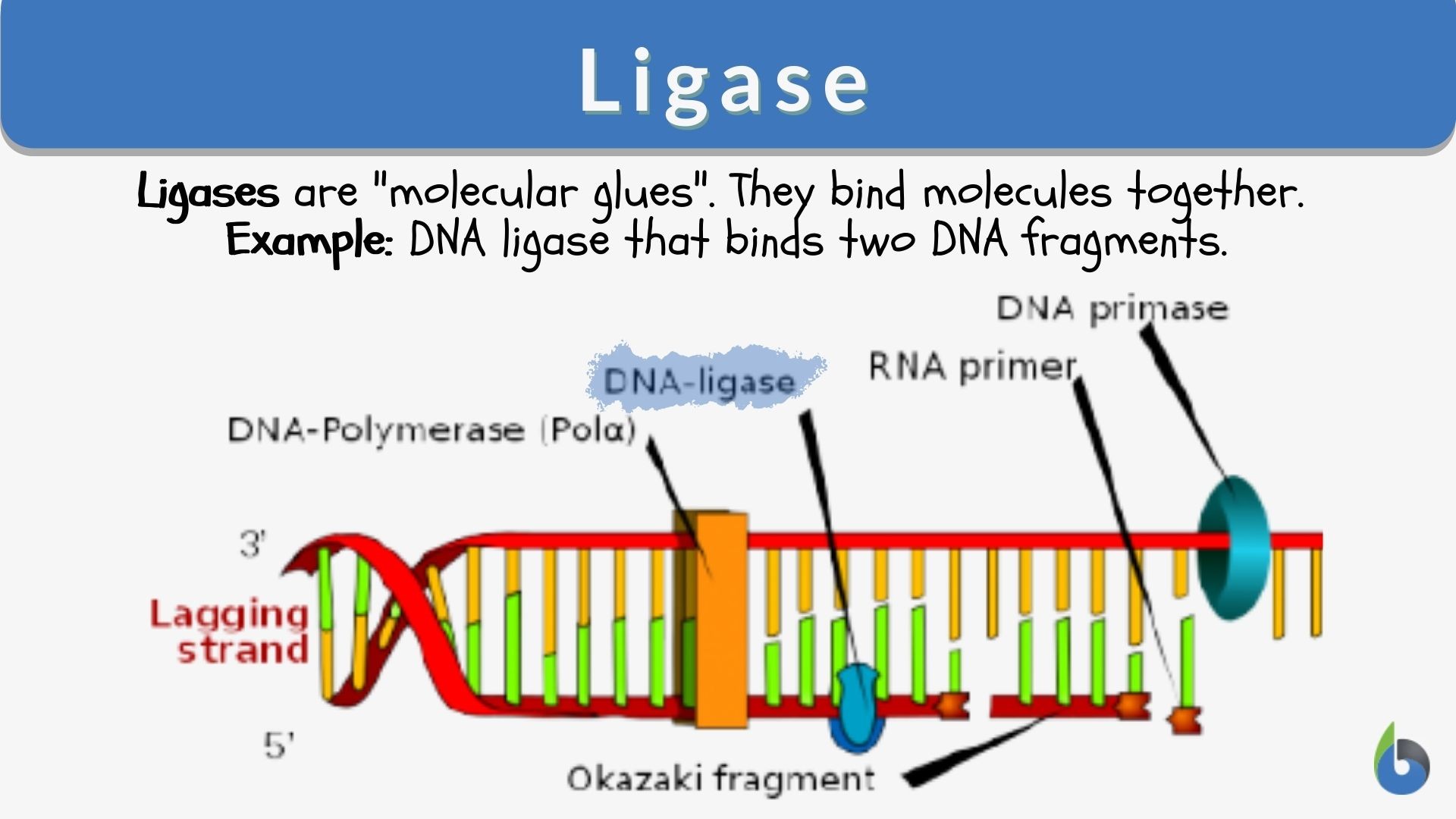 Source: biologyonline.com
Source: biologyonline.com
Example question #4 a covalent bond is the sharing of electrons between atoms. The formation of a phosphodiester bridge is catalyzed by dna polymerases. Dna ligase the enzyme that joins the 5� and 3� ends of polynucleotide chains by the formation of a phosphodiester bond between them.
Also Read :





