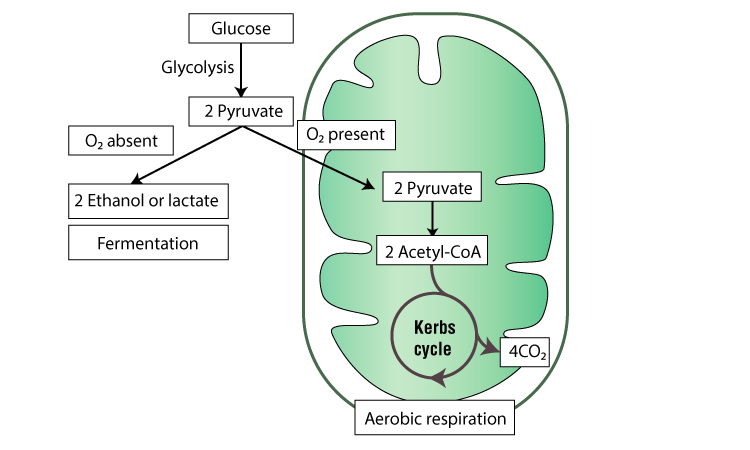
Ultimately, respiration results in the complete oxidation of glucose, and the transfer of energy from the chemical bonds of glucose to the chemical bonds of atp. Aerobic respiration and fermentation share an initial pathway, called “glycolysis,” in which one glucose molecule is converted into two pyruvate molecules.
Which Metabolic Pathway Is Common To Cellular Respiration And Fermentation. The final electron acceptor of the electron transport chain that functions in aerobic oxidative phosphorylation is (a) oxygen. Fermentation and cellular respiration begin the same way, with glycolysis. The final electron acceptor of the electron transport chain that functions in oxidative phosphorylation is 59. What is an example of a metabolic pathway?
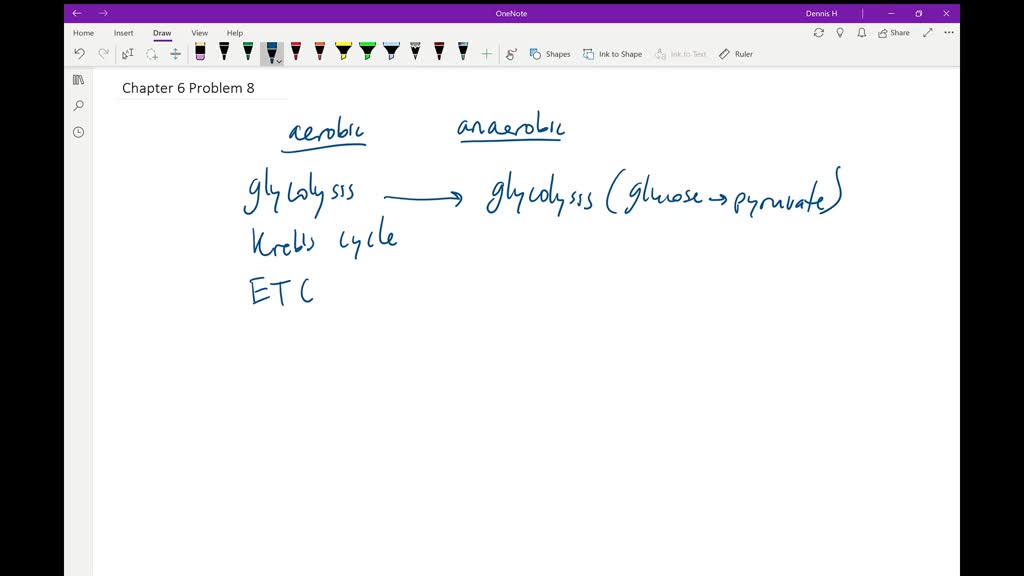 Solved:______ Is A Metabolic Pathway Common To Both Fermentation And Cellular Respiration. From numerade.com
Solved:______ Is A Metabolic Pathway Common To Both Fermentation And Cellular Respiration. From numerade.com
Related Post Solved:______ Is A Metabolic Pathway Common To Both Fermentation And Cellular Respiration. :
The redox balance (balance on nadh consumption and generation) must balance. (a) the citric acid cycle (b) the electron transport chain (c) glycolysis (d) reduction of pyruvate to lactate. It is an enzyme controlled 10 steps reaction by which glucose, fructose or sucrose is reduced to form 3 carbon compound pyruvate with the production of atp and nadh. There are three main parts to the cellular respiration pathway.
Partial oxidation of glucose by glycolysis results in the formation of 2 molecules of pyruvate.
Principles and methodologies” stephanopoulos, aristidou, and nielsen, academic press, 1998 1. There are three main parts to the cellular respiration pathway. The atp made during fermentation is generated by _____. It occurs in the cytosol of the cells. A) atp, co2, and ethanol (ethyl alcohol) So, the correct answer is glycolysis.

Under anaerobic conditions, the absence of oxygen, pyruvic acid can be routed by the organism into one of three pathways: Problem 3 the final electron acceptor of the electron transport chain that. So, the correct answer is glycolysis.
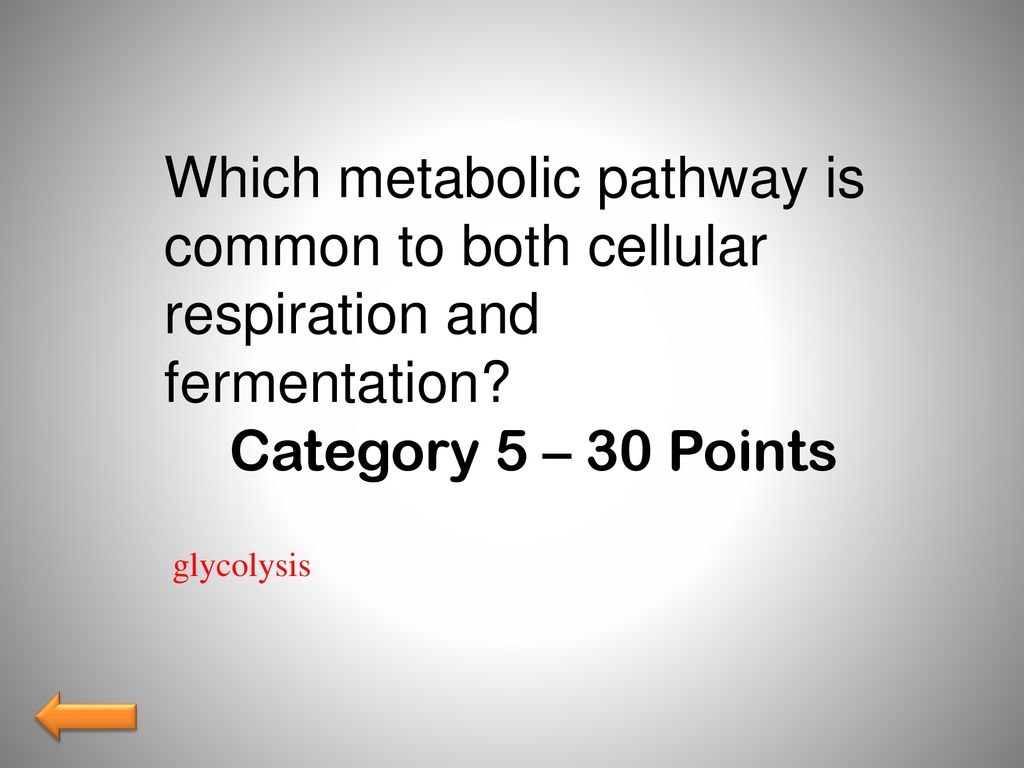 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
Glycolysis is the common pathway in both aerobic respiration and fermentation. If aerobic respiration does not occur, nadh must be reoxidized to nad + for reuse as an electron carrier for the glycolytic pathway to continue. The final electron acceptor of the electron transport chain that functions in oxidative phosphorylation is 59.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
Ultimately, respiration results in the complete oxidation of glucose, and the transfer of energy from the chemical bonds of glucose to the chemical bonds of atp. See also what does explorer mean. The first law of thermodynamics states this, this pathway consumes energy to build up polymers from monomers, this molecule provides energy coupling between exergonic and endergonic reactions, increasing the substrate concentration in enzymatic reaction would overcome which type of inhibition
 Source: numerade.com
Source: numerade.com
What metabolic stage is part of both cellular respiration and fermentation? The electron transport chain e. These parts are glycolysis, the tricarboxylic acid cycle (kreb�s cycle), and.
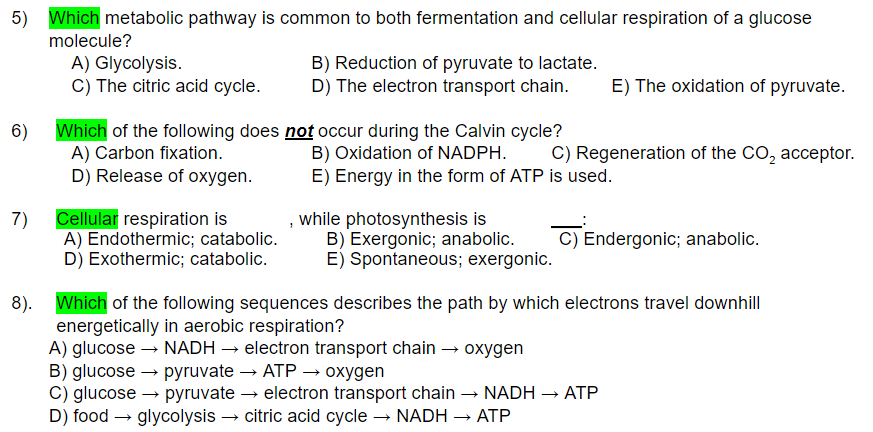 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
(a) the citric acid cycle (b) the electron transport chain (c) glycolysis (d) reduction of pyruvate to lactate. Occurs in almost all living cells, serving as the starting point for fermentation or cellular respiration cirtic acid cycle a chemical cycle involving 8 steps that completes the metabolic breakdown of glucose molecules begun in glycolysis by oxidizing acetyl coa to carbon dioxide; Fermentation reacts nadh with an endogenous, organic electron acceptor.
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
A) atp, co2, and ethanol (ethyl alcohol) There are three main parts to the cellular respiration pathway. In the absence of oxygen, yeast cells can obtain energy by fermentation, resulting in the production of _____.

Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway common to both fermentation and cellular respiration of a glucose molecule. Glycolysis is a part of cellular respiration and is common to both aerobic and anaerobic respiration. Sugars, glycerol from fats, and some types of amino acids can enter cellular respiration during glycolysis.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
The electron transport chain e. In the absence of oxygen, yeast cells can obtain energy by fermentation, resulting in the production of _____. Which metabolic pathway is common to both fermentation and cellular respiration of a glucose molecule?
 Source: bartleby.com
Source: bartleby.com
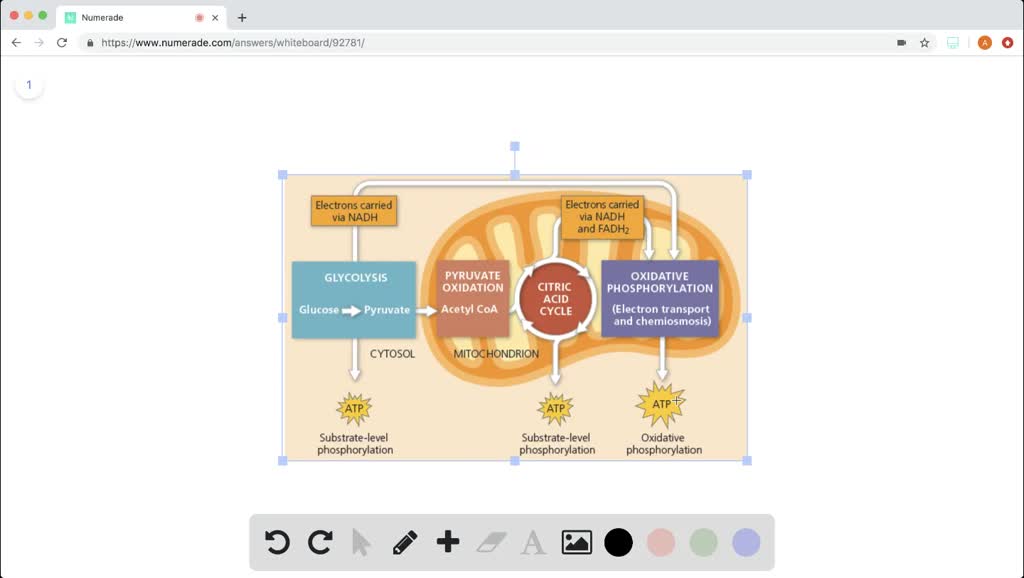
The three stages of nutrient breakdown are the following: Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway that occurs in the cytosol of the cell and splits glucose into two. Occurs within the mitochondrion in euk, and in the cytosol in prok.
 Source: byjus.com
Source: byjus.com
The first law of thermodynamics states this, this pathway consumes energy to build up polymers from monomers, this molecule provides energy coupling between exergonic and endergonic reactions, increasing the substrate concentration in enzymatic reaction would overcome which type of inhibition There are three steps of cellular respiration and they always occur in this order: The processes of making and breaking down glucose molecules are both examples of metabolic pathways.
 Source: numerade.com
Source: numerade.com
Problem 3 the final electron acceptor of the electron transport chain that. Ultimately, respiration results in the complete oxidation of glucose, and the transfer of energy from the chemical bonds of glucose to the chemical bonds of atp. So, the correct answer is glycolysis.
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
Which of the following metabolic pathways produce(s) the most atp, per. Glycolysis is the common pathway in both aerobic respiration and fermentation. Partial oxidation of glucose by glycolysis results in the formation of 2 molecules of pyruvate.

Under anaerobic conditions, the absence of oxygen, pyruvic acid can be routed by the organism into one of three pathways: Which metabolic pathway is common to both fermentation and cellular respiration of a glucose molecule? The electron transport chain e.
 Source: numerade.com
Source: numerade.com
Which metabolic pathway is common to both cellular respiration and fermentation? Fermentation reacts nadh with an endogenous, organic electron acceptor. There are three steps of cellular respiration and they always occur in this order:
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
The citric acid cycle b. Under anaerobic conditions, the absence of oxygen, pyruvic acid can be routed by the organism into one of three pathways: Problem 3 the final electron acceptor of the electron transport chain that.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
Sugars, glycerol from fats, and some types of amino acids can enter cellular respiration during glycolysis. Occurs in almost all living cells, serving as the starting point for fermentation or cellular respiration cirtic acid cycle a chemical cycle involving 8 steps that completes the metabolic breakdown of glucose molecules begun in glycolysis by oxidizing acetyl coa to carbon dioxide; A metabolic pathway is a series of connected chemical reactions that feed one another.
 Source: numerade.com
Source: numerade.com
Aerobic respiration and fermentation share an initial pathway, called “glycolysis,” in which one glucose molecule is converted into two pyruvate molecules. The electron transport chain e. Glycolysis, the kreb’s cycles, and the electron transport chain, all which go through a series of redox reactions.
 Source: byjus.com
Source: byjus.com
Sugars, glycerol from fats, and some types of amino acids can enter cellular respiration during glycolysis. (a) the citric acid cycle (b) the electron transport chain (c) glycolysis (d) reduction of pyruvate to lactate. The citric acid cycle b.
 Source: numerade.com
Source: numerade.com
A metabolic pathway is a series of connected chemical reactions that feed one another. In the absence of oxygen, yeast cells can obtain energy by fermentation, resulting in the production of _____. Principles of me and mixed acid fermentation “metabolic engineering:
 Source: imle.in
Source: imle.in
Glycolysis is a part of cellular respiration and is common to both aerobic and anaerobic respiration. Glycolysis is a part of cellular respiration and is common to both aerobic and anaerobic respiration. Citric acid cycle (or kreb cycle) stage 3:
Also Read :