Secondary protein structures are caused by hydrogen bonding between adjacent amine and carboxyl groups. Secondary amines still form hydrogen bonds, but having the nitrogen atom in the middle of the chain rather than at the end makes the permanent dipole on the molecule slightly less.
Which Is A General Representation Of A Secondary Amine. Rr��n r� 3° amine rhn h 1° amine rhn r� 2° amine hhn h ammonia • amines are organic derivatives of ammonia, nh3, in which one or more of the three h’s is replaced by a carbon group. Amines are classified according to the number of carbon atoms bonded directly to the nitrogen atom. Our collection is the largest in the.
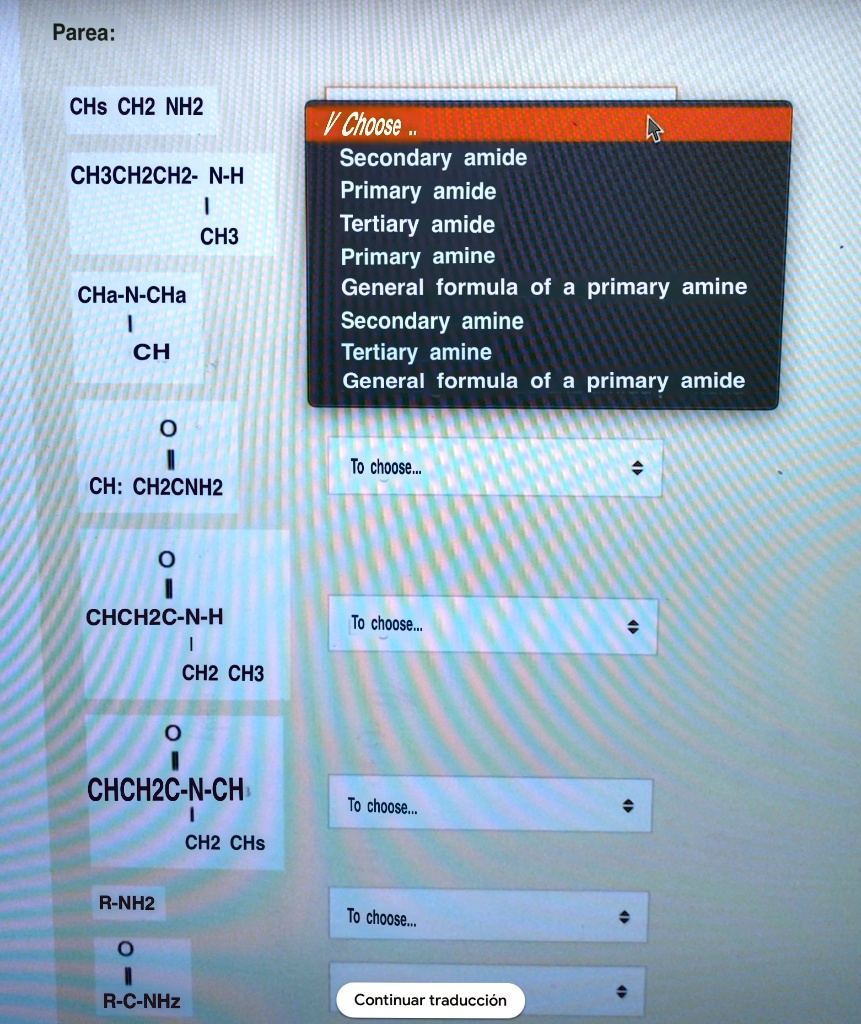 Solved:parea: Chs Ch2 Nh2 Choose Secondary Amide Primary Amide Tertiary Amide Primary Amine General Formula Of Primary Amine Secondary Amine Tertiary Amine General Formula Of Primary Amide Chbchzch2- N-H Ch3 Cha-N-Cha Ch From numerade.com
Solved:parea: Chs Ch2 Nh2 Choose Secondary Amide Primary Amide Tertiary Amide Primary Amine General Formula Of Primary Amine Secondary Amine Tertiary Amine General Formula Of Primary Amide Chbchzch2- N-H Ch3 Cha-N-Cha Ch From numerade.com
Related Post Solved:parea: Chs Ch2 Nh2 Choose Secondary Amide Primary Amide Tertiary Amide Primary Amine General Formula Of Primary Amine Secondary Amine Tertiary Amine General Formula Of Primary Amide Chbchzch2- N-H Ch3 Cha-N-Cha Ch :
Amides are not in general accessible by the direct condensation of amines with carboxylic acids for two reasons: Amines have a lone pair so can form a bond with an h⁺ ion when acting as a base. Peptide bonds join the amine group on one amino acid with the r group of another amino acid. If one of the �h� atom of nh3 is replace by r = alkyl group, they are referred as primary amine.
Amines are classified according to the number of carbon atoms bonded directly to the nitrogen atom.
• amines are classified as primary (1°), secondary (2°), or tertiary (3°), depending on how many carbon groups are connected to the nitrogen atom. Has one alkyl (or aryl) group on the nitrogen atom, a secondary (2°) amine a compound that has two alkyl or aryl groups on the nitrogen atom. Our collection is the largest in the. Amines are organic compound obtained from ammonia by replacement of one or more hydrogen atoms by organic groups. Amines have a lone pair so can form a bond with an h⁺ ion when acting as a base. In present case, option c has 2 �h� atoms of nh3 replaced by alkyl group.
 Source: quizlet.com
Source: quizlet.com
Our collection is the largest in the. In present case, option c has 2 �h� atoms of nh3 replaced by alkyl group. (1) the compound ethylammonium chloride is an amine salt.
 Source: doubtnut.com
Source: doubtnut.com
If two ‘h’ atoms of nh3 are replace by same or different alkyl group, they are referred as secondary amine. In amine amines are classified as primary, secondary, or tertiary depending on whether one, two, or three of the hydrogen atoms of ammonia have been replaced by organic groups. If two �h� atoms of nh3 are replace by same or different alkyl group, they are referred as secondary amine.
 Source: commons.wikimedia.org
Source: commons.wikimedia.org
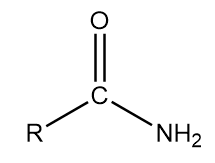
In the usual nomenclature, one adds the term amide to the stem of the parent acid�s name. Peptide bonds join the amine group on one amino acid with the r group of another amino acid. In addition sulfur (s) is present in the side chains of cysteine and methionine, and selenium (se) in the less.
![⚗️[Please See The Attatched Photo] Which Is A General Representation Of A Secondary Amine? A. An N - Brainly.com ⚗️[Please See The Attatched Photo] Which Is A General Representation Of A Secondary Amine? A. An N - Brainly.com](https://us-static.z-dn.net/files/d46/f64451acdafb46095cb1e9270f0d7886.jpg) Source: brainly.com
Source: brainly.com
• amines are organic derivatives of ammonia, nh3, in which one or more of the three h’s is replaced by a carbon group. Peptide bonds join the amine group on one amino acid with the r group of another amino acid. Important representatives include dimethylamine , while an example of an aromatic amine would be diphenylamine.
 Source: quizlet.com
Source: quizlet.com
Option creason:amines are organic compound obtained from ammonia by replacement of one or more hydrogen atoms by organic groups.if one of the ‘h’ atom of nh3 is replace by r = alkyl group, they are referred as primary amine. It is represented by general formula r 2 n h. The boiling point of the secondary amine is a little lower than the corresponding primary amine with the same number of carbon atoms.
 Source: quizlet.com
Source: quizlet.com
Has one alkyl (or aryl) group on the nitrogen atom, a secondary (2°) amine a compound that has two alkyl or aryl groups on the nitrogen atom. Peptide bonds join the amine group on one amino acid with the r group of another amino acid. Important representatives include dimethylamine , while an example of an aromatic amine would be diphenylamine.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
What is the physical state of most amides. It is represented by general formula r 2 n h. In the usual nomenclature, one adds the term amide to the stem of the parent acid�s name.
![Best Answer] Which Is A General Representation Of A Secondary Amine?(Pictures Are In Order) A. - Brainly.com](https://us-static.z-dn.net/files/daa/1acabae2c49adac9b129337e3e00eff3.jpg “Best Answer] Which Is A General Representation Of A Secondary Amine?(Pictures Are In Order) A. - Brainly.com”) Source: brainly.com
Has one alkyl (or aryl) group on the nitrogen atom, a secondary (2°) amine a compound that has two alkyl or aryl groups on the nitrogen atom. (2) amides, like amines, can be classified as primary, secondary, and tertiary. Rr��n r� 3° amine rhn h 1° amine rhn r� 2° amine hhn h ammonia
 Source: toppr.com
Source: toppr.com
Amines are classified according to the number of carbon atoms bonded directly to the nitrogen atom. (1) the compound ethylammonium chloride is an amine salt. (3) the primary amines are insoluble in water.
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
Amines have a lone pair so can form a bond with an h⁺ ion when acting as a base. Our collection is the largest in the. First, both components are readily deactivated by a transfer of a proton from the acid to the amine and second, the hydroxy unit on the carbonyl of the acid is a relatively poor leaving group.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
In secondary amine, 2 alkyl groups and one hydrogen atom are directly attached to n atom. What is the physical state of most amides. In present case, option c has 2 �h� atoms of nh3 replaced by alkyl group.
 Source: ochempal.org
Source: ochempal.org
Rr��n r� 3° amine rhn h 1° amine rhn r� 2° amine hhn h ammonia Rr��n r� 3° amine rhn h 1° amine rhn r� 2° amine hhn h ammonia Peptide bonds join the amine group on one amino acid with the r group of another amino acid.
 Source: numerade.com
Source: numerade.com
• amines are organic derivatives of ammonia, nh3, in which one or more of the three h’s is replaced by a carbon group. Rr��n r� 3° amine rhn h 1° amine rhn r� 2° amine hhn h ammonia The elements present in every amino acid are carbon (c), hydrogen (h), oxygen (o), and nitrogen (n);
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
For instance, the amide derived from acetic acid is named acetamide (ch 3 conh 2).iupac recommends ethanamide, but this and related formal names are rarely encountered.when the amide is derived from a primary or secondary amine, the substituents on nitrogen are indicated. Hence it is secondary amine. Our collection is the largest in the.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
In the usual nomenclature, one adds the term amide to the stem of the parent acid�s name. A primary (1°) amine has one alkyl (or aryl) group on the nitrogen atom, a secondary (2°) amine has two, and a tertiary (3°) amine has three (figure 5.1 the structure of amines compared to water, an alcohol, and an ether). For instance, the amide derived from acetic acid is named acetamide (ch 3 conh 2).iupac recommends ethanamide, but this and related formal names are rarely encountered.when the amide is derived from a primary or secondary amine, the substituents on nitrogen are indicated.
![Best Answer] Which Is A General Representation Of A Secondary Amine?(Pictures Are In Order) A. - Brainly.com](https://us-static.z-dn.net/files/ddc/dc3de4af6e632cd1a6e39ed2a90cdaf2.jpg “Best Answer] Which Is A General Representation Of A Secondary Amine?(Pictures Are In Order) A. - Brainly.com”) Source: brainly.com
If two ‘h’ atoms of nh3 are replace by same or different alkyl group, they are referred as secondary amine. (3) the primary amines are insoluble in water. Amines have a lone pair so can form a bond with an h⁺ ion when acting as a base.
 Source: ochempal.org
Source: ochempal.org
In the usual nomenclature, one adds the term amide to the stem of the parent acid�s name. Amino acids are organic compounds that contain amino (−nh + 3) and carboxylate −co − 2 functional groups, along with a side chain (r group) specific to each amino acid. Amines are classified according to the number of carbon atoms bonded directly to the nitrogen atom.
 Source: doubtnut.com
Source: doubtnut.com
In chemical notation these three classes are represented as rnh 2 , r 2 nh, and r 3 n, respectively. • amines are organic derivatives of ammonia, nh3, in which one or more of the three h’s is replaced by a carbon group. • amines are classified as primary (1°), secondary (2°), or tertiary (3°), depending on how many carbon groups are connected to the nitrogen atom.
 Source: vedantu.com
Source: vedantu.com
Important representatives include dimethylamine , while an example of an aromatic amine would be diphenylamine. Our collection is the largest in the. What is the physical state of most amides.
 Source: polymerdatabase.com
Source: polymerdatabase.com
In chemical notation these three classes are represented as rnh 2 , r 2 nh, and r 3 n, respectively. Peptide bonds join the amine group on one amino acid with the r group of another amino acid. In present case, option c has 2 �h� atoms of nh3 replaced by alkyl group.
Also Read :