The enzyme dna polymerase catalyses the formation of the new strands and only adds new nucleotides starting from the 5' end and proceeding towards the 3' end. Which enzyme recognizes a specific nucleotide sequence (~4 to 8 nucleotides in length) and catalyzes the digestion of the nucleic acid at that site, causing a break in the dna strand?
Which Enzyme Catalyzes The Elongation Of A Dna Strand. It is also the major enzyme complex for the prokaryotic dna reproduction. Coli, the enzyme primase is used to attach a 5 to 10 base ribonucleotide strand complementary to the parental dna strand. During dna replication, dna helicases unwind dna at positions called origins where synthesis will be initiated. Dna helicase is the enzyme that unwinds the dna double helix by breaking the hydrogen bonds down the center of the strand.
 Quia - 9Ap Chapter 16 - Molecular Basis Of Inheritance (Detailed) From quia.com
Quia - 9Ap Chapter 16 - Molecular Basis Of Inheritance (Detailed) From quia.com
Related Post Quia - 9Ap Chapter 16 - Molecular Basis Of Inheritance (Detailed) :
Dna polymerase iii at a specific area of a chromosome, the following sequence of nucleotides is present where the chain opens to form a replication fork:3� c c t a g g c t g c a a t c c 5�an rna primer is formed starting at the underlined t (t) of the template. C) it joins okazaki fragments together. A dna strand has the sequence accgagctt. Dna polymerase enzyme catalyses the reaction of adding nucleotide to growing complementary daughter strand of dna in the direction of 5�.
Dna polymerase catalyzes the joining of a nucleotide to a growing dna strand.
Dna polymerase iii o c.primase o d.topoisomerase Dna polymerase during elongation, an enzyme called dna polymerase adds dna nucleotides to the 3′ end of the newly synthesized polynucleotide strand. During dna replication, dna helicases unwind dna at positions called origins where synthesis will be initiated. C ) dna polymerase iii. What determines the nucleotide sequence of the newly synthesized strand during dna replication? Dna polymerase iii o c.primase o d.topoisomerase ;
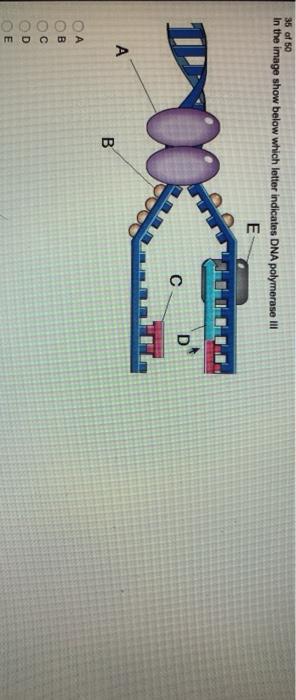
The two separated strands will act as templates for making the new strands of dna. Dna polymerase is the name of the enzyme that separates the two strands of dna during replication. This enzyme is very important to dna elongation and it works by creating two pairs of identical dna strands from from a single strand of the parent dna.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
Dna polymerase during elongation, an enzyme called dna polymerase adds dna nucleotides to the 3′ end of the newly synthesized polynucleotide strand. Asked apr 25, 2019 in uncategorized by jillianerin101012 which enzyme recognizes a specific nucleotide sequence (~4 to 8 nucleotides in length) and catalyzes the digestion of the nucleic acid at that site, causing a break in the dna strand? A new dna strand elongates only in the 5� to 3� direction because _____.
This enzyme is very important to dna elongation and it works by creating two pairs of identical dna strands from from a single strand of the parent dna. A) primase b) dna ligase c) dna polymerase iii d) topoisomerase e) helicase. Which enzyme catalyzes the elongation of a dna strand in the 5� 3� direction?
 Source: examians.com
Source: examians.com
The particular dna polymerase catalyzing the reaction Whichever dna strand is transcribed, the rna polymerase reads the template strand from 3′ to 5′. O a helicase o b.
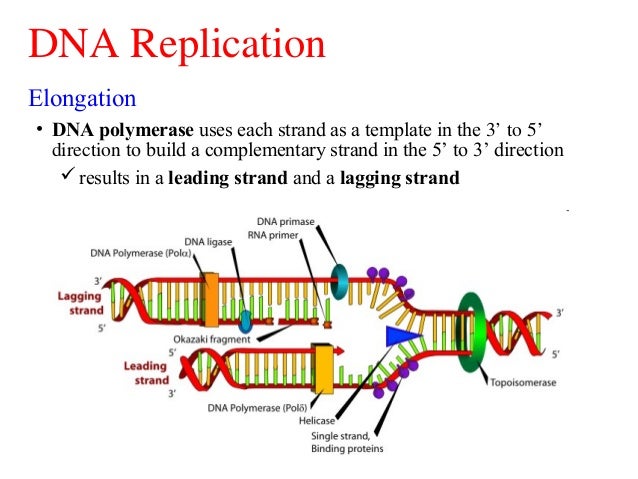 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
O a helicase o b. It begins at a site called the origin of replication, and it creates a replication fork by separating the two sides of the parental dna. Which enzyme catalyzes the elongation of a new dna strand?
 Source: quia.com
Source: quia.com
Which enzyme catalyzes the elongation of a dna strand in the 5� 3� direction? Which enzyme catalyzes the elongation of a dna strand in the 5� 3� direction? 12) what determines the nucleotide sequence of the newly synthesized strand during dna replication?
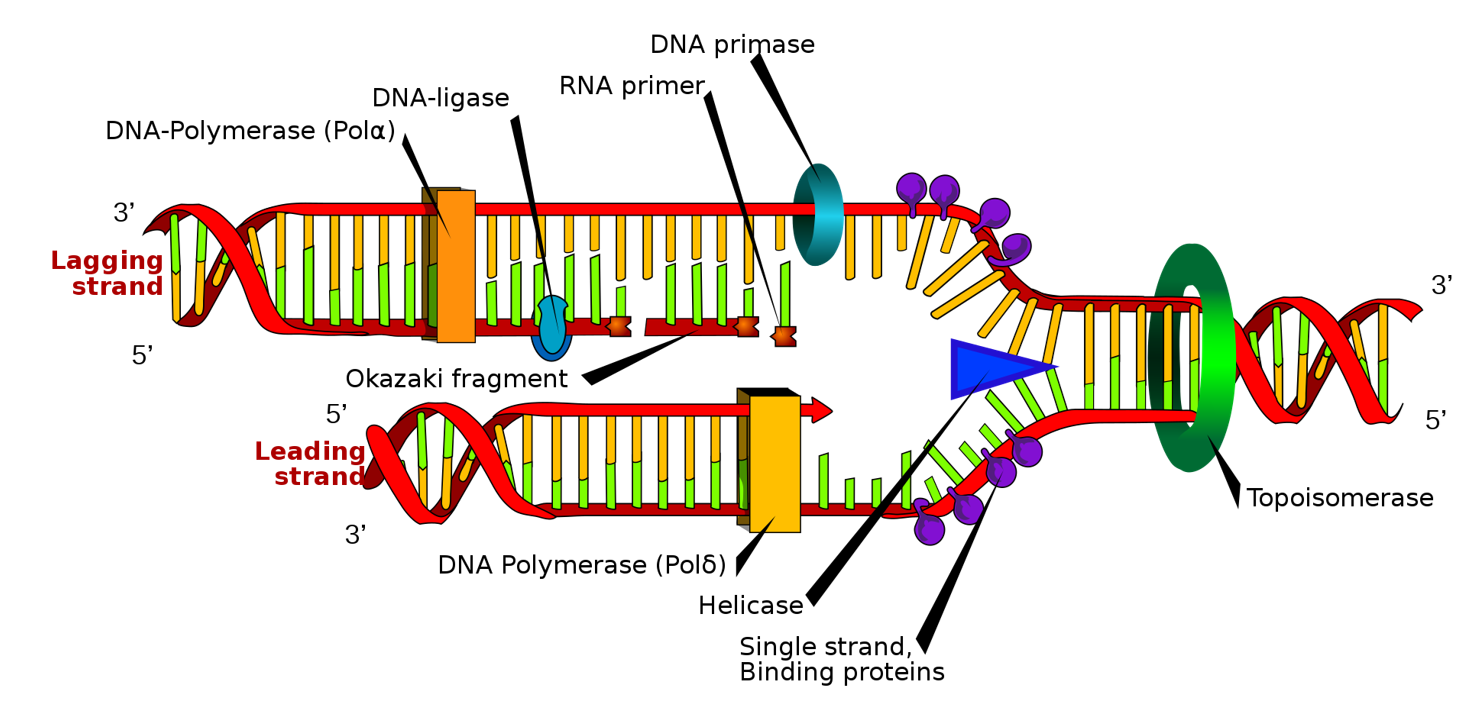 Source: clutchprep.com
Source: clutchprep.com
It begins at a site called the origin of replication, and it creates a replication fork by separating the two sides of the parental dna. O a helicase o b. It begins at a site called the origin of replication, and it creates a replication fork by separating the two sides of the parental dna.
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
B) it catalyzes the lengthening of telomeres. O a helicase o b. 27) what is the role of dna ligase in the elongation of the lagging strand during dna replication?
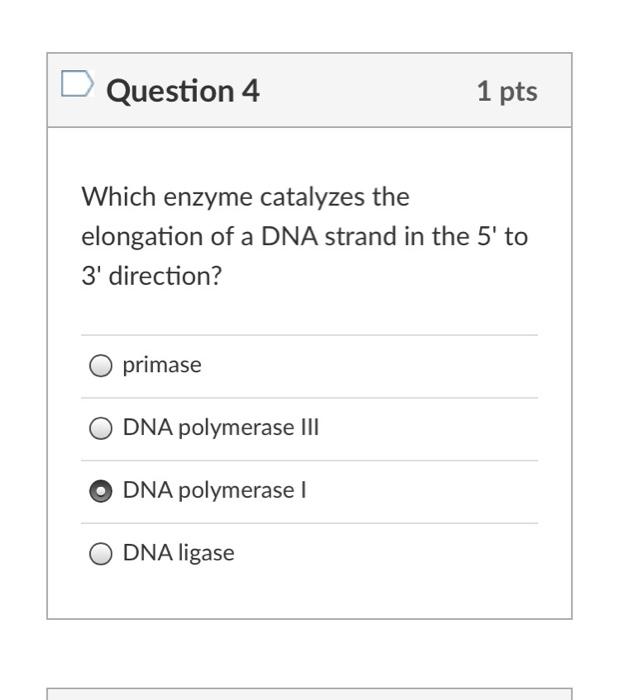
Which enzyme catalyzes the elongation of a dna strand. A) dna polymerase can add nucleotides only to the free 3� end b) the polarity of the dna molecule prevents addition of nucleotides at the 3� end c) dna polymerase begins adding nucleotides at the 5� end of the template d) replication must progress toward the replication fork The ribosome’s peptidyl transferase catalyses the transfer of the growing polypeptide chain from the p site trna to the amino group of the a site amino acid.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
What determines the nucleotide sequence of the newly synthesized strand during dna replication? Furthermore, why does a new dna strand elongates in. D) it unwinds the parental double helix.
 Source: quizlet.com
Source: quizlet.com
This enzyme is very important to dna elongation and it works by creating two pairs of identical dna strands from from a single strand of the parent dna. Dna helicase continues to unwind the dna forming a structure called the replication fork, which is named for the forked appearance of the two strands of dna as they are unzipped apart. Furthermore, why does a new dna strand elongates in.
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
Which is the complementary strand of rna? Which enzyme catalyzes the elongation of a dna strand in the 5� → 3� direction? Dna polymerase during elongation, an enzyme called dna polymerase adds dna nucleotides to the 3′ end of the newly synthesized polynucleotide strand.
 Source: quia.com
Source: quia.com
C ) dna polymerase iii. Which enzyme catalyzes the elongation of a dna strand in the 5� 3� direction? Which enzyme catalyzes the elongation of a dna strand in the 5� + 3� direction?
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
C) it joins okazaki fragments together. Which enzyme catalyzes the elongation of a dna strand in the 5� 3� direction? During elongation, an enzyme called dna polymerase adds dna nucleotides to the 3′ end of the newly synthesized polynucleotide strand.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
Which enzyme recognizes a specific nucleotide sequence (~4 to 8 nucleotides in length) and catalyzes the digestion of the nucleic acid at that site, causing a break in the dna strand? Askedsep 26, 2015in biology & microbiologyby roxxy. The particular dna polymerase catalyzing the reaction
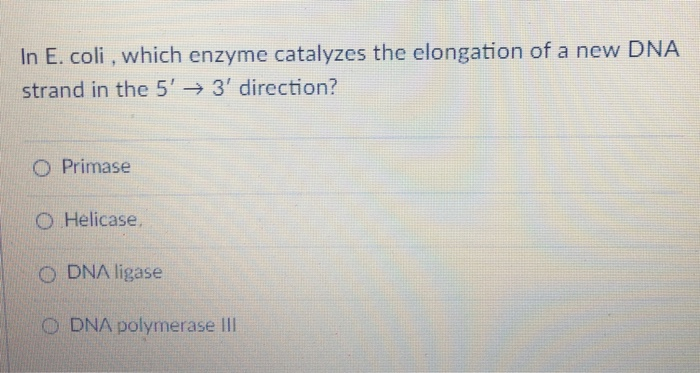 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
- what is the role of dna ligase in the elongation of the lagging strand during dna replication? Dna polymerase enzyme catalyses the reaction of adding nucleotide to growing complementary daughter strand of dna in the direction of 5�. Which enzymes is unwinding dna helix?

A) primase b) dna ligase c) dna polymerase iii d) topoisomerase e) helicase. The enzyme that catalyzes the dna strand elongation is the dna polymerase iii. 27) what is the role of dna ligase in the elongation of the lagging strand during dna replication?
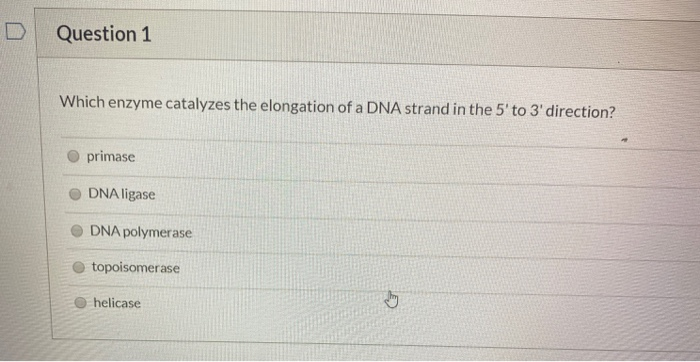 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
A) dna polymerase can add nucleotides only to the free 3� end b) the polarity of the dna molecule prevents addition of nucleotides at the 3� end c) dna polymerase begins adding nucleotides at the 5� end of the template d) replication must progress toward the replication fork A) it synthesizes rna nucleotides to make a primer. The particular dna polymerase catalyzing the reaction
 Source: studylib.net
Source: studylib.net
The two separated strands will act as templates for making the new strands of dna. B) it catalyzes the lengthening of telomeres. Which enzyme catalyzes the elongation of a new dna strand?
Also Read :





