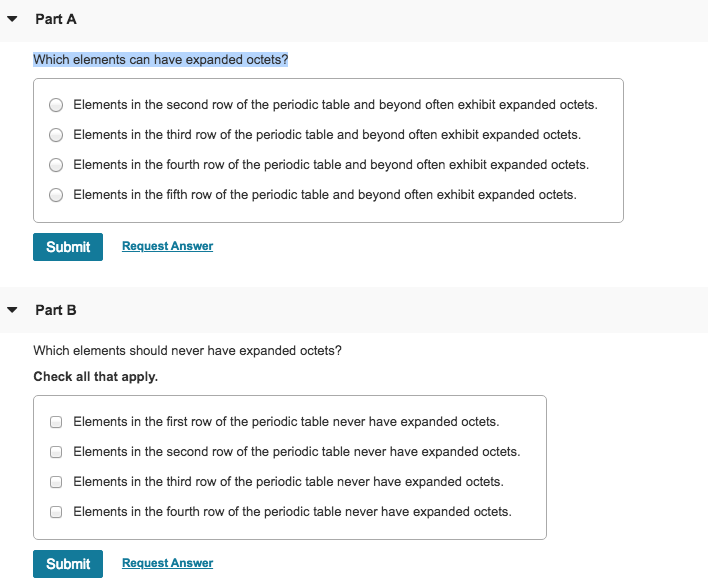
Elements in the first row of the periodic table never have expanded octets. Because sulfur is far less electronegative than oxygen.
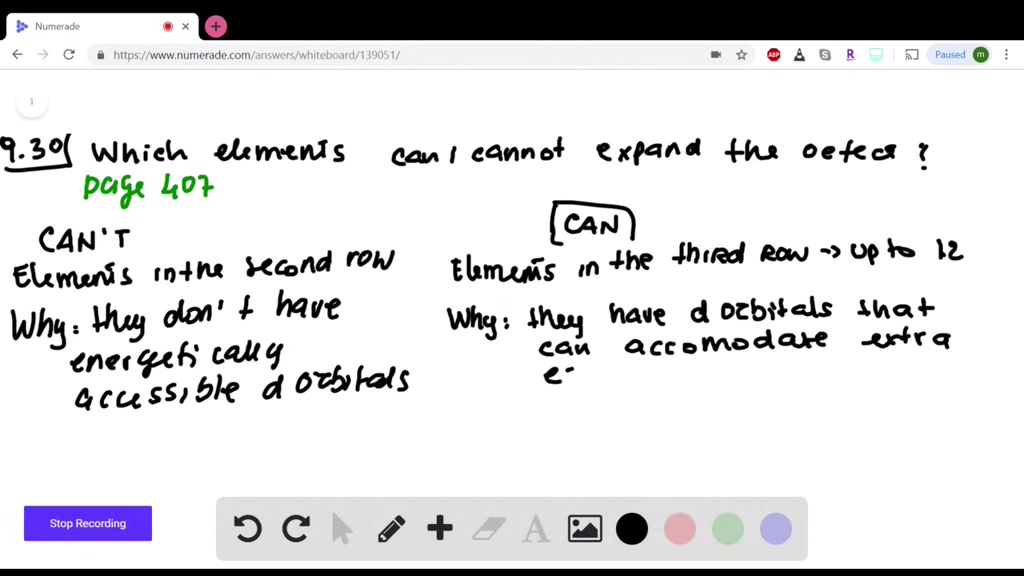
Which Elements Can Have Expanded Octets. Typically, the atoms with the greatest electronegativity have complete octets, and those with the lowest electronegativity have the unpaired electron. Which elements can have expanded octets? Elements in period 3 and beyond. Which elements cannot have expanded octets?
 Chemical Bonding Chapter Ppt Video Online Download From slideplayer.com
Chemical Bonding Chapter Ppt Video Online Download From slideplayer.com
Related Post Chemical Bonding Chapter Ppt Video Online Download :
Elements in the third row of the periodic table and beyond often exhibit expanded octets. An expanded octet cannot occur with atoms less than atomic number 10 (neon) because there are no d orbitals. Sulfur and phosphorus are common examples of this behavior. Notice that “expanded octets” only occur in compounds in which the central atom has low electronegativity relative to the ligands.
In the case of octet expansion, the rule is broken.
Which elements cannot have expanded octets? The university of alabama 01:22. • there is an odd number of electrons, like in radicals • there are less than 8 electrons or incomplete octet • there are more than 8 electrons or expanded octet. Recall that the octet rule states that an element is surrounded by eight electrons in the lewis structure. Periodic table can or cannot expand the oct it. Typically, the atoms with the greatest electronegativity have complete octets, and those with the lowest electronegativity have the unpaired electron.
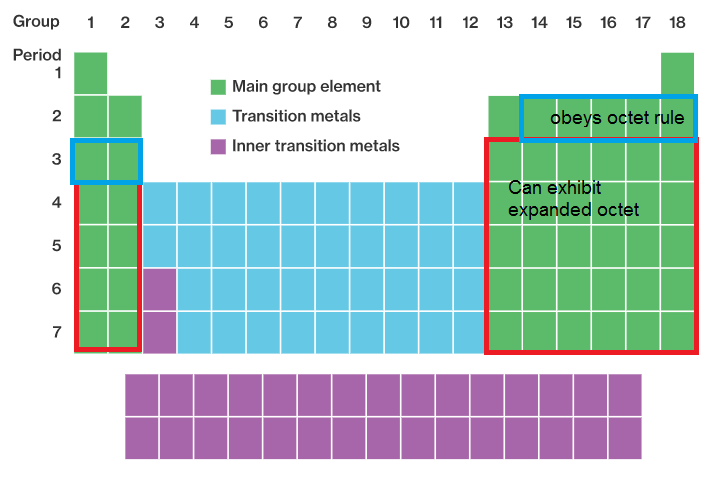 Source: clutchprep.com
Source: clutchprep.com
Elements in the third row of the periodic table and beyond often exhibit expanded octets. As per octet rule, atoms bond in a way that they have eight electrons in their valence shell. The elements that typically have less than an octet are hydrogen, helium, lithium, and beryllium.
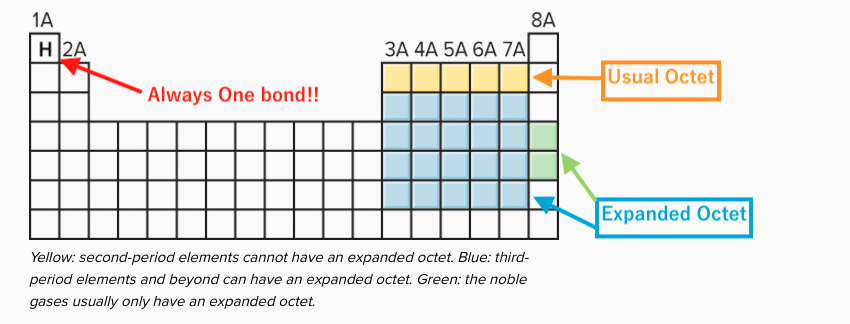 Source: myweb.liu.edu
Source: myweb.liu.edu
- odd octets, seen in electron species, molecules, or ions with an odd number of valence electrons (no). For example, s f 6 is a stable compound, but s h 6 is not. Elements in the second row of the periodic table never have expanded octets.
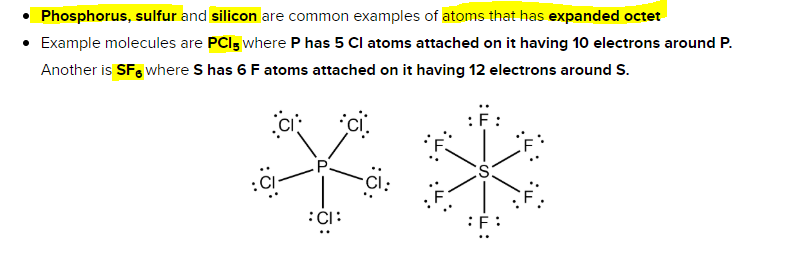 Source: clutchprep.com
Source: clutchprep.com
- odd octets, seen in electron species, molecules, or ions with an odd number of valence electrons (no). I believe br is the only one with an atomic number larger than 10. The university of alabama 01:22.

Elements in the third row of the periodic table and beyond often exhibit expanded octets. Boron also may form molecules where it only has 6 electrons. As per octet rule, atoms bond in a way that they have eight electrons in their valence shell.
 Source: chemistryguru.com.sg
Source: chemistryguru.com.sg
Sulfur and phosphorus are common examples of this behavior. Problem 13 what is bond energy? I brought up p and s but those elements are greater than 10 and since they are in the third period, they contain 3d orbitals and extra electrons can.
 Source: studylib.net
Source: studylib.net
Recall that the octet rule states that an element is surrounded by eight electrons in the lewis structure. 1) odd octets, seen in electron species, molecules, or ions with an odd number of valence electrons (no). Main group elements that form more bonds than would be predicted by the octet rule are called hypervalent compounds, and have what is known as an ‘expanded octet,’ meaning that there are more than eight electrons around one atom.
 Source: itprospt.com
Source: itprospt.com
So you find the different categories that can or cannot expand the update. Part a which elements can have expanded octets? 2) incomplete octets, seen in molecules or ions with fewer than 8 electrons surrounding an atom (bfsub3).
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
Elements in the third row of the periodic table and beyond often exhibit expanded octets. Typically, the atoms with the greatest electronegativity have complete octets, and those with the lowest electronegativity have the unpaired electron. Elements in period 3 and beyond.
 Source: numerade.com
Source: numerade.com
The page for all seven of your book elements in the third row and beyond can expand the opted upto, usually 12 or even 14 in some cases, electrons. As per octet rule, atoms bond in a way that they have eight electrons in their valence shell. For example, s f 6 is a stable compound, but s h 6 is not.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
O all of the noble gases. Argon compounds have been synthesised and have expanded octets. Boron also may form molecules where it only has 6 electrons.
 Source: numerade.com
Source: numerade.com
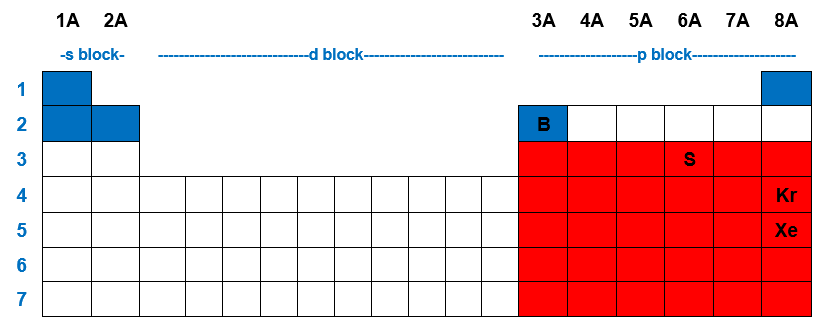
Element with eight number of electrons in its valance shell shows octet. When an element�s valence shell has enough orbitals to accommodate more than 8 valence electrons, they can form an expanded octet. Elements in group 3a and beyond.
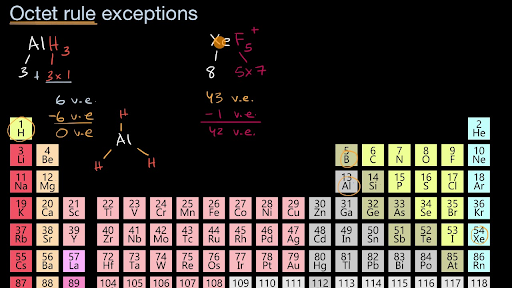
So you find the different categories that can or cannot expand the update. Sulfur and phosphorus are common examples of this behavior. Molecules or ions with more than 8 electrons around atom (ex.
 Source: numerade.com
Source: numerade.com
O all of the noble gases. Electron species, molecules, or ions with off number of electrons (ex. Argon compounds have been synthesised and have expanded octets.
 Source: clutchprep.com
Source: clutchprep.com
Element with eight number of electrons in its valance shell shows octet. Fluorine is more electronegative than sulfur, but hydrogen is not. Because sulfur is far less electronegative than oxygen.
 Source: thoughtco.com
Source: thoughtco.com
Exceptions to this rule occur when: Third row elements can have an expanded octet. Exceptions to this rule occur when:
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
Which elements cannot have expanded octets? The university of alabama 01:22. Elements in the second row of the periodic table and beyond often exhibit expanded octets.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Which elements cannot have expanded octets? As per octet rule, atoms bond in a way that they have eight electrons in their valence shell. O only the transition metals.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Element with eight number of electrons in its valance shell shows octet. Expanded octet means that an element possesses more than eight electrons in its valance shell. So you find the different categories that can or cannot expand the update.
 Source: clutchprep.com
Source: clutchprep.com
So you find the different categories that can or cannot expand the update. Typically, the atoms with the greatest electronegativity have complete octets, and those with the lowest electronegativity have the unpaired electron. In the case of octet expansion, the rule is broken.
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
Notice that “expanded octets” only occur in compounds in which the central atom has low electronegativity relative to the ligands. Elements in the third row of the periodic table and beyond often exhibit expanded octets. Atoms in these periods may follow the octet rule, but there are conditions where they can expand their valence shells to accommodate more than eight electrons.
Also Read :





