Tertiary carbocations are more stable than primary or secondary carbocations because they have three methyl groups to distribute it's positive charge rather than only one or two methyl groups. Before we start talking about carbocation stability, we should have a starting discussion about some carbocation basics.
Which Carbocation Is The Most Stable. What this means is that, in general, more substituted carbocations are more stable: Within the carbocations, a tertiary carbocation is more stable than a secondary one which in turn is more stable than a primary one. Primary allyl carbocation is stabilised only by resonance effect whereas secondary and tertiary allyl carbocations are stabilised by resonance, hyperconjugation and inductive effect. The increasing order of stability of carbocation is:
 Which Of The Following Is Most Stable Carbocation And Why? | Socratic From socratic.org
Which Of The Following Is Most Stable Carbocation And Why? | Socratic From socratic.org
Related Post Which Of The Following Is Most Stable Carbocation And Why? | Socratic :
$3^\circ > 2^\circ > 1^\circ $ complete step by step answer: But carbocation #5 is vinylic carbocation (positively charged carbon is sp 2 hybridized, i.e. Carbon of the double bond) and this is the. Allylic carbocation is more stable than the substituted alkyl carbocation due to the delocalization relation of the resonance interaction between the carbon bearing the positive charge and the pie bond present next to it.
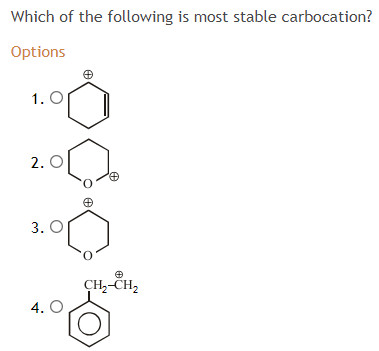
I have read that resonance is the biggest deciding factor about the stability of a carbocation but some argue that (a) would be most stable as it is farthest away from a highly electronegative chlorine atom.
The order of stability of carbocations can be explained based on the following factors: >>fundamental concepts in organic reaction mechanism. Which carbocation is most reactive? The most stable version is the tertiary benzylic carbocation. The stability of the carbocation. Of course, the more the positive charge is spread out, the more stable your carbocation will be!
 Source: wegglab.com
Source: wegglab.com
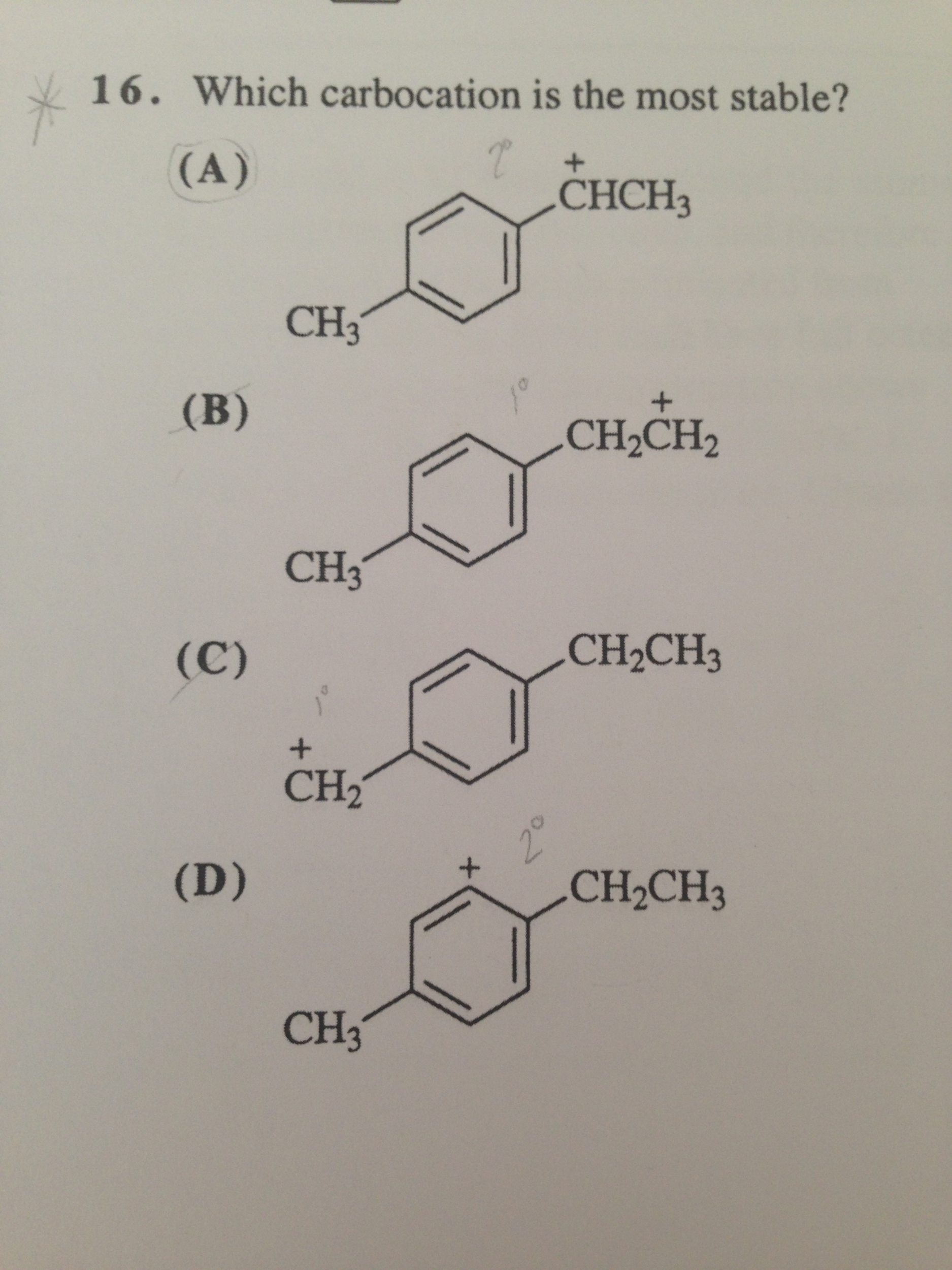
Carbocation (a), (b) and _ (d) are all secondary but (d) and (b) are aromatic. This module covers the factors that influence the stability of carbocations. But carbocation #5 is vinylic carbocation (positively charged carbon is sp 2 hybridized, i.e.
 Source: socratic.org
Source: socratic.org
Beside this, which is more stable carbocation? Benzylic carbocations are very stable because they can go for four kind of resonance structure which gives more stability with more. $3^\circ > 2^\circ > 1^\circ $ complete step by step answer:
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Primary allyl carbocation is stabilised only by resonance effect whereas secondary and tertiary allyl carbocations are stabilised by resonance, hyperconjugation and inductive effect. Please log in or register to add a comment. Tertiary carbocations are more stable than primary or secondary carbocations because they have three methyl groups to distribute it�s positive charge rather than only one or two methyl groups.
 Source: toppr.com
Source: toppr.com
I have read that resonance is the biggest deciding factor about the stability of a carbocation but some argue that (a) would be most stable as it is farthest away from a highly electronegative chlorine atom. Of course, the more the positive charge is spread out, the more stable your carbocation will be! All carbocations are very reactive, so their relative reactivity doesn�t matter much for the rate of a reaction.
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
Carbocation (a), (b) and _ (d) are all secondary but (d) and (b) are aromatic. Carbon of the double bond) and this is the. C 2 h + 3:
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
Carbocation (a), (b) and _ (d) are all secondary but (d) and (b) are aromatic. >>which allylic carbocation is the most st. The stability of the carbocation.

A carbocation, also sometimes referred to as the carbonium ion, is an sp2 hybridized carbon atom with three groups bonded to it and a empty orbital. Which carbocation is most reactive? Allylic carbocation is more stable than the substituted alkyl carbocation due to the delocalization relation of the resonance interaction between the carbon bearing the positive charge and the pie bond present next to it.
 Source: toppr.com
Source: toppr.com
Therefore (d) and (b) are more stable than (a). C 6 h + 5: Because the hydride took the bond electrons, the carbon where the h migrated from becomes the new carbocation.
 Source: toppr.com
Source: toppr.com
Of course, the more the positive charge is spread out, the more stable your carbocation will be! Carbocation (c) is antiaromatic and hence is least stable. What this means is that, in general, more substituted carbocations are more stable:

Overall 1o has been rearranged to 3o. The product is then formed by nucleophilic attack at the new, more stable carbocation. C 6 h + 5:

Beside this, which is more stable carbocation? Ch + 3 (least stable). Carbocation (c) is antiaromatic and hence is least stable.
 Source: digital.aakash.ac.in
Source: digital.aakash.ac.in
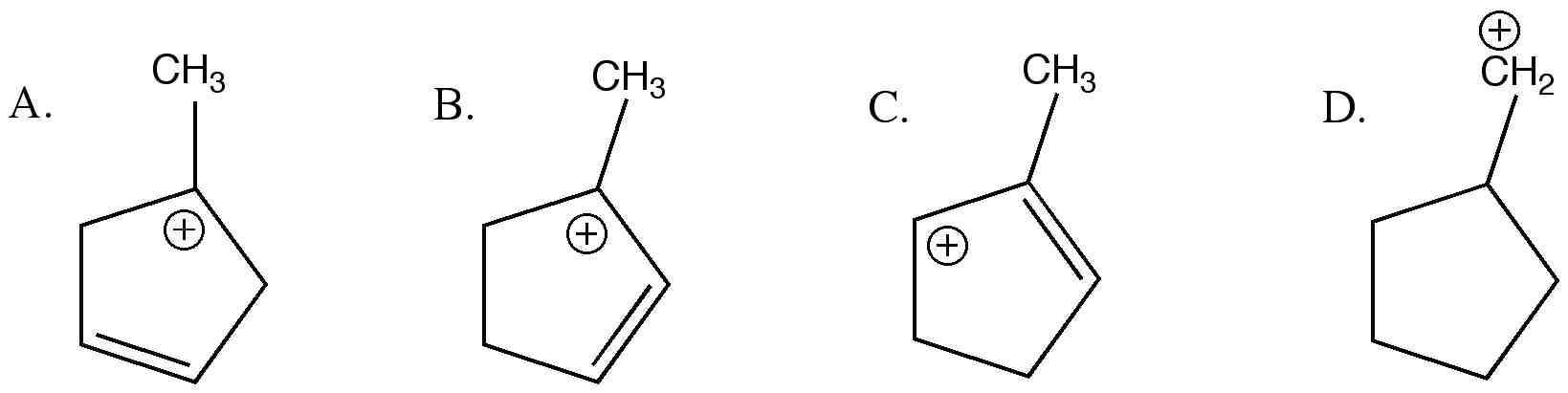
We have one more case in this example with primary carbocations (1 and 5). In the first question, the most stable carbocation is the one in which the positive charge is on a tertiary carbon atom, because a tertiary carbocation is more stable than primary or secondary carbocation, because of the electron donatind tendency of the methyl groups. What this means is that, in general, more substituted carbocations are more stable:
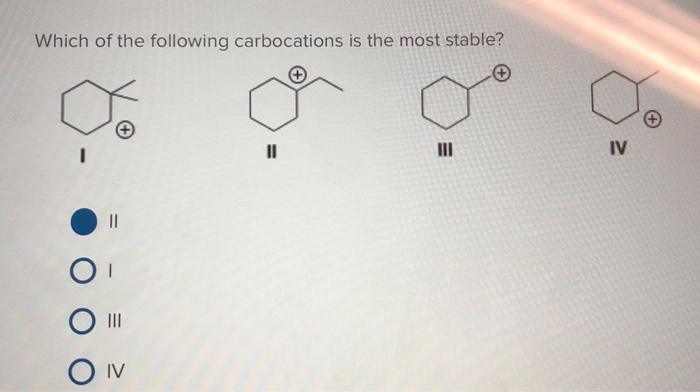 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
Within the carbocations, a tertiary carbocation is more stable than a secondary one which in turn is more stable than a primary one. Ch + 3 (least stable). The order of stability of carbocation is :
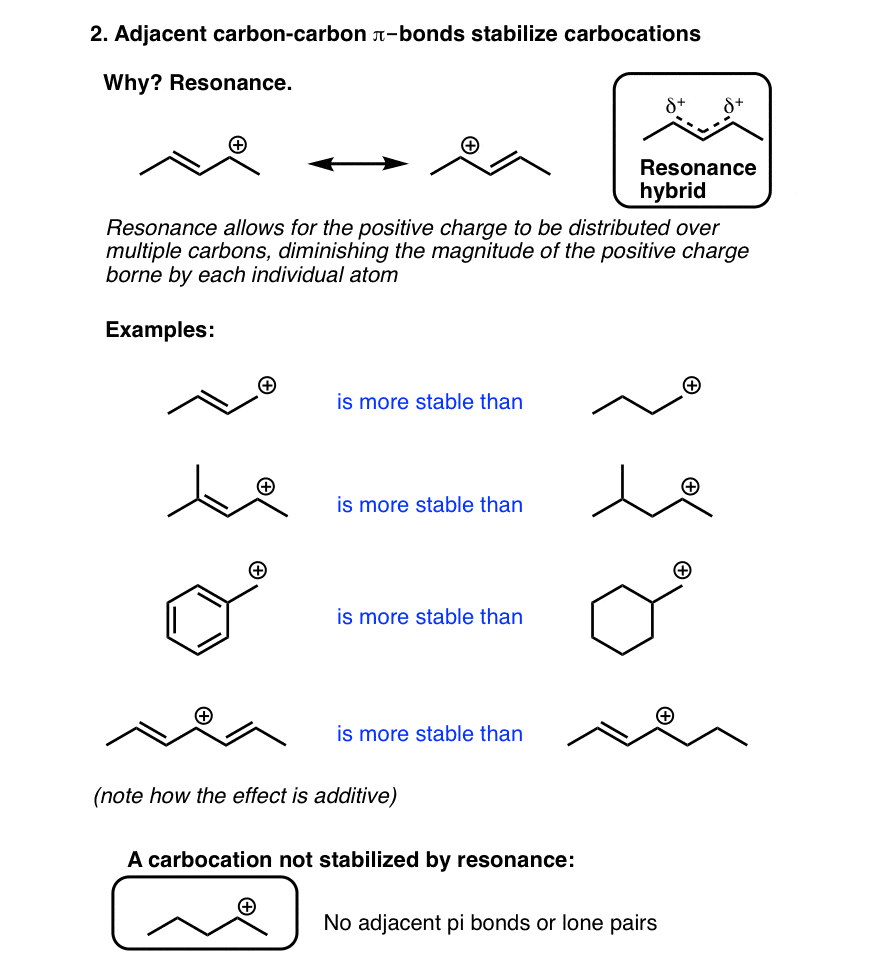 Source: masterorganicchemistry.com
Source: masterorganicchemistry.com
Carbon of the double bond) and this is the. I have read that resonance is the biggest deciding factor about the stability of a carbocation but some argue that (a) would be most stable as it is farthest away from a highly electronegative chlorine atom. Hydride ion affinity (hia) as a measure of carbocation stability carbocation:
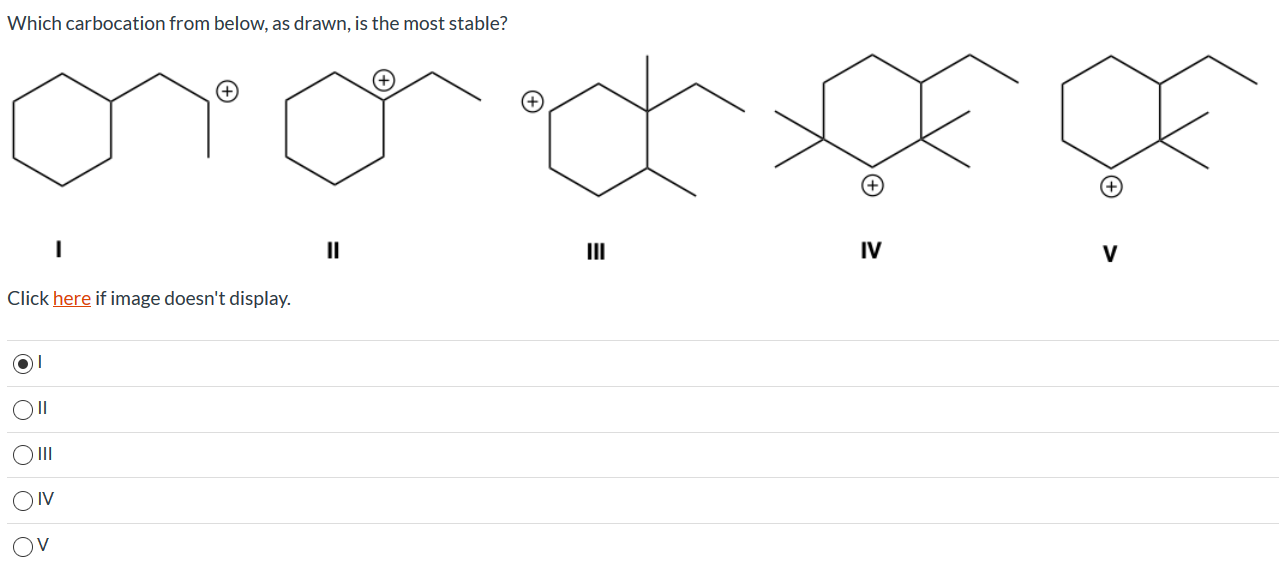 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
Some students fall into the trap of thinking that the system with the less stable carbocation will react fastest, but they are forgetting that it is the generation of. The stability of carbocations follows the order: Further out of (b) and (d), (d) has less angular strain and as such is more stable.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Overall 1o has been rearranged to 3o. Some students fall into the trap of thinking that the system with the less stable carbocation will react fastest, but they are forgetting that it is the generation of. Of course, the more the positive charge is spread out, the more stable your carbocation will be!
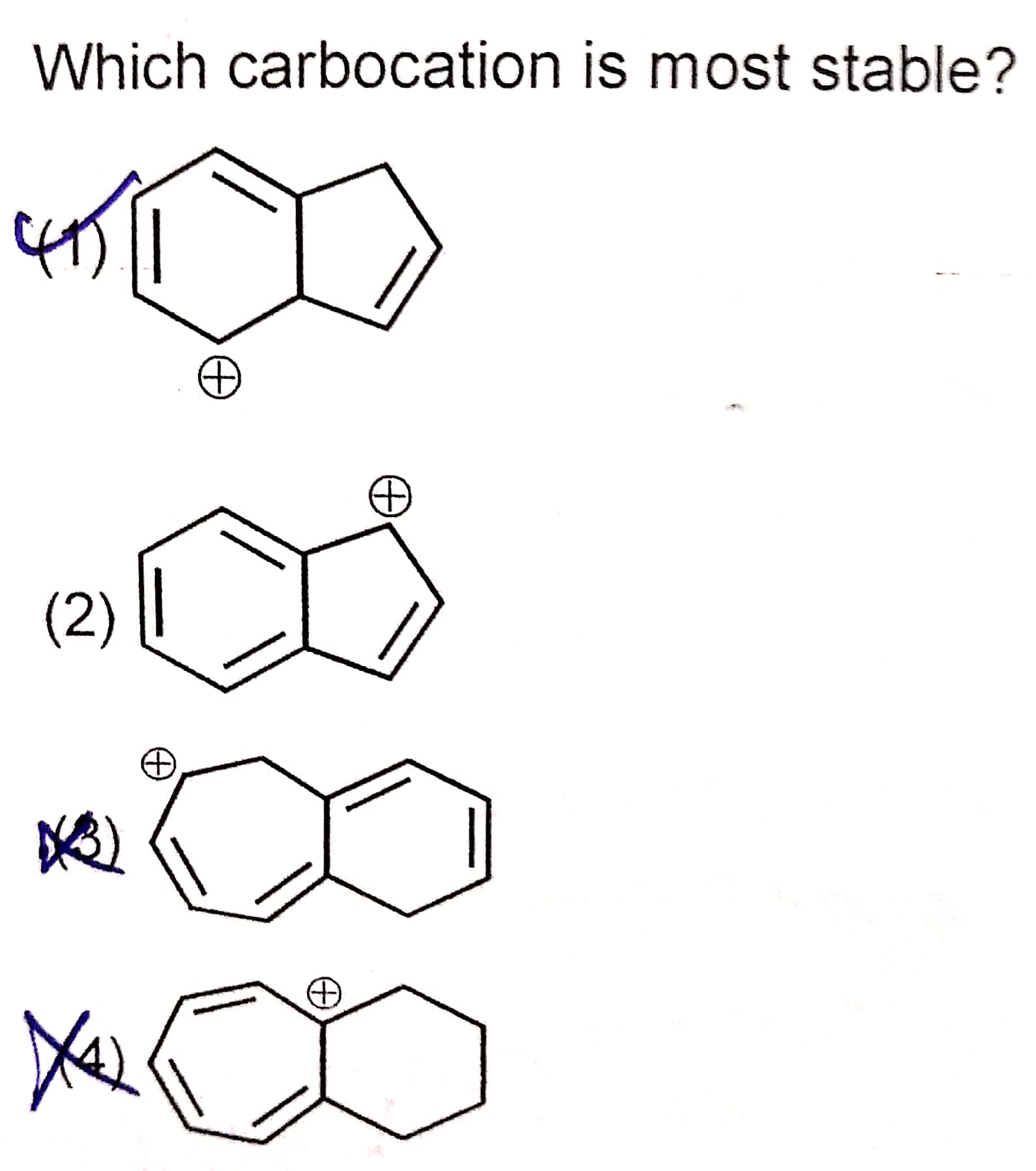 Source: embibe.com
Source: embibe.com
Overall 1o has been rearranged to 3o. Which allylic carbocation is the most stable carbocation? Carbocation (c) is antiaromatic and hence is least stable.
 Source: study.com
Source: study.com
In our example, the carbocation #4 is more stable than the carbocation #3. Carbon of the double bond) and this is the. I have read that resonance is the biggest deciding factor about the stability of a carbocation but some argue that (a) would be most stable as it is farthest away from a highly electronegative chlorine atom.
 Source: toppr.com
Source: toppr.com
Because the hydride took the bond electrons, the carbon where the h migrated from becomes the new carbocation. Hydride ion affinity (hia) as a measure of carbocation stability carbocation: A tertiary carbocation forms the most quickly because it is the most stable.
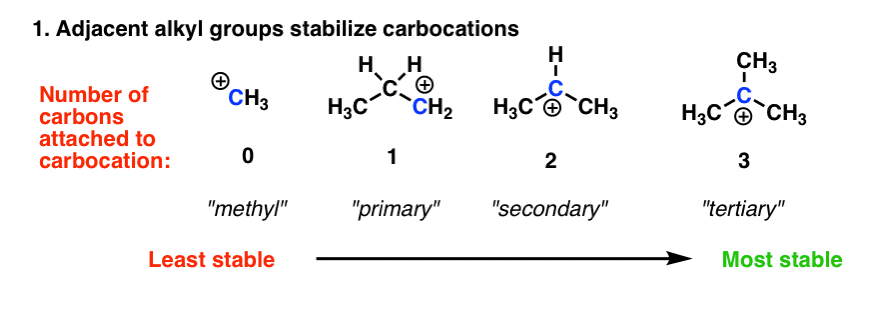 Source: masterorganicchemistry.com
Source: masterorganicchemistry.com
Therefore a primary vinylic carbocation is less stable than a primary alkyl carbocation. C 2 h + 3: C 6 h 5 ch + 2:
Also Read :