Examples include supraorbital foramen, infraorbital foramen, and mental foramen on the cranium. Omnivore teeth are a mix of.
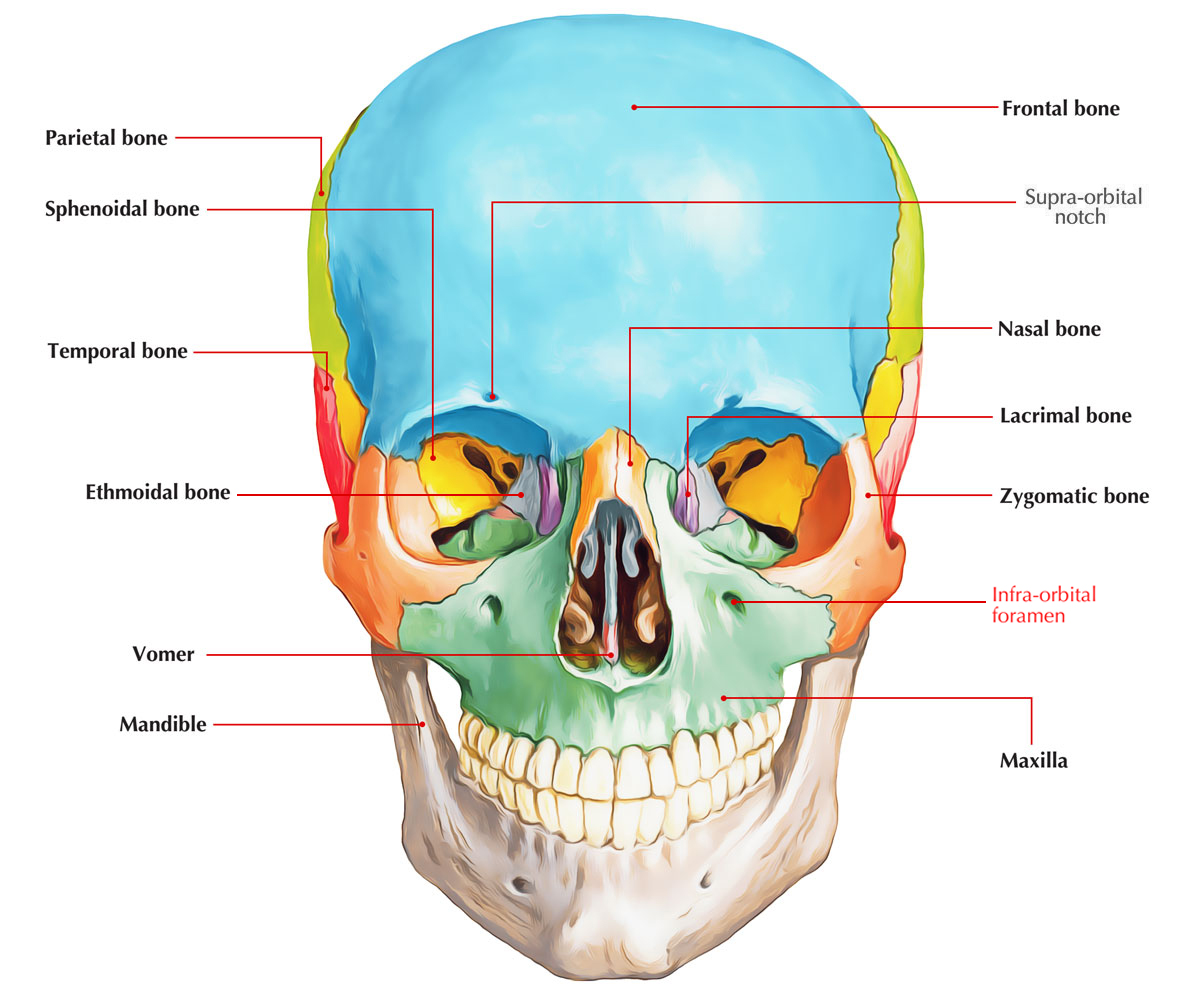
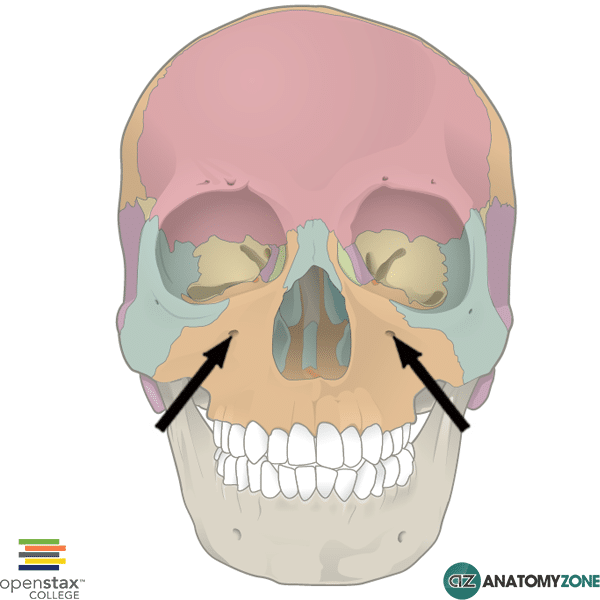
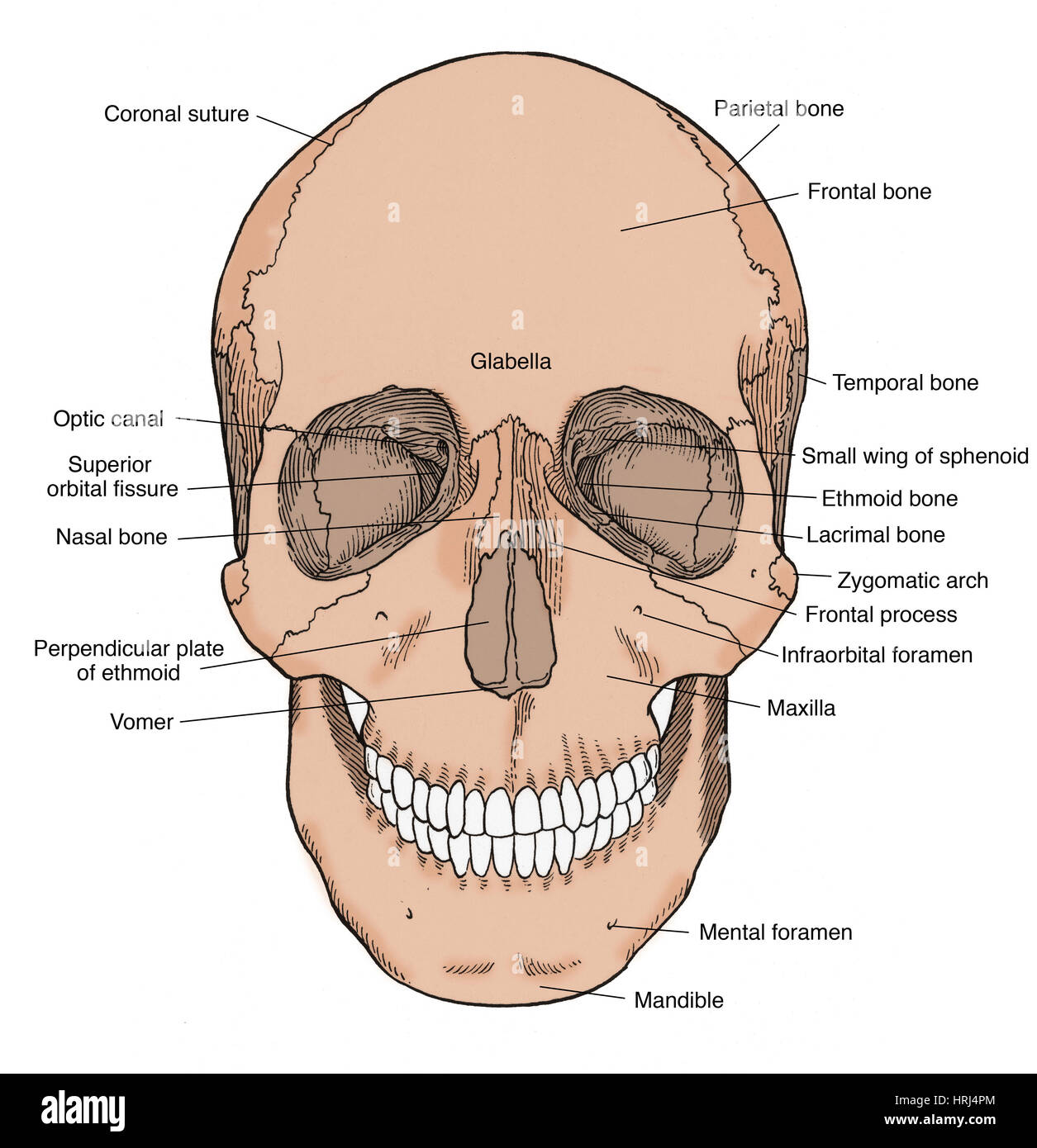
Which Bone Bears The Infraorbital Foramen. It is situated at the upper and lateral part of the face and forms the prominence of the cheek , part of the lateral wall and floor of the orbit , and parts of the temporal fossa and the infratemporal. Frontal temporal mandible maxilla zygomatic It transmits the infraorbital artery and vein, and the infraorbital nerve, a branch of the maxillary nerve. In human anatomy, the infraorbital foramen is an opening in the maxillary bone of the skull located below the infraorbital margin of the orbit.
 Osteology And Radiological Anatomy Of Skull And Cervical Bones (Part … From slideshare.net
Osteology And Radiological Anatomy Of Skull And Cervical Bones (Part … From slideshare.net
Related Post Osteology And Radiological Anatomy Of Skull And Cervical Bones (Part … :
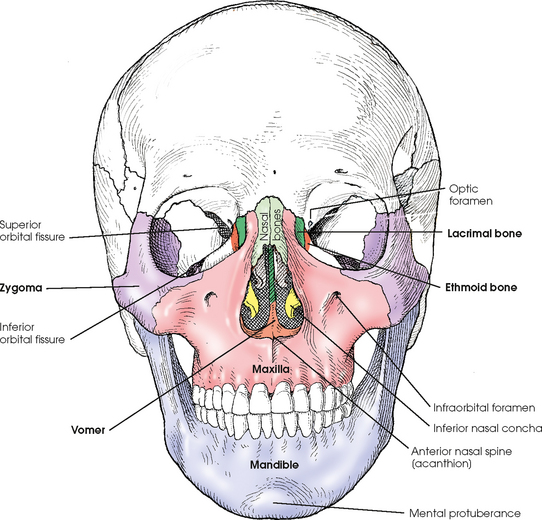
Though it does not articulate with any other bone, the hyoid bone is considered to be part of the axial skeleton. Transcutaneous approach involves injecting directly into the subcutaneous space inferior to the infraorbital rim just beneath the foramen utilizing the. David j terris, manoj kumar, in sleep apnea and snoring, 2009. The seven bones that form the orbit are the maxilla, frontal, nasal, ethmoid, sphenoid, palatine, and zygomatic bones.
Though it does not articulate with any other bone, the hyoid bone is considered to be part of the axial skeleton.
Here it may receive another articulating bone. The condyles are located at the distal end of the bone. Here it may receive another articulating bone. In anatomic position, the femur is angled medially. It is situated at the upper and lateral part of the face and forms the prominence of the cheek , part of the lateral wall and floor of the orbit , and parts of the temporal fossa and the infratemporal. Temporal which bone comprise each pectoral girdle?
 Source: earthslab.com
Source: earthslab.com
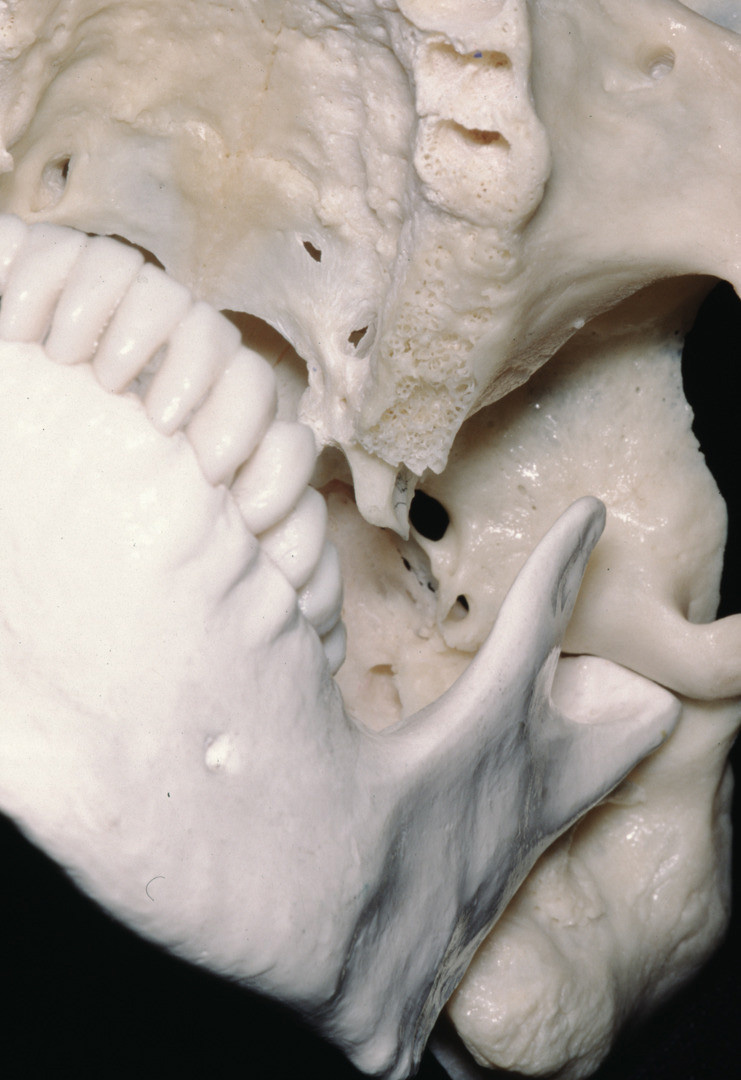
Maxillary (anteroinferior) border articulates with the maxilla, tapers just above the infraorbital foramen; David j terris, manoj kumar, in sleep apnea and snoring, 2009. Which bone bears the infraorbital foramen?
 Source: radiologykey.com
Source: radiologykey.com
Omnivore teeth are a mix of. Infraorbital foramen (opening below eye socket) oval, larger than foramen magnum. Irregular opening just medial to the styloid process of the temporal bone is the.
 Source: alamy.com
Source: alamy.com
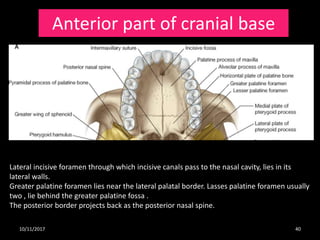
Frontal temporal mandible maxilla zygomatic The waters and waldron (1915) semiaxial occipitomental projection is indispensable for assessing the condition of the anterior portions of the medial wall, the roof and floor of the orbit, the zygomatic bones, the lesser wing of the sphenoid bone, the infraorbital foramen, as well as the maxillary sinuses and the ethmoidal labyrinth (figs. The lateral (exterior) surface bears the nasal foramen.
 Source: wikiwand.com
Source: wikiwand.com
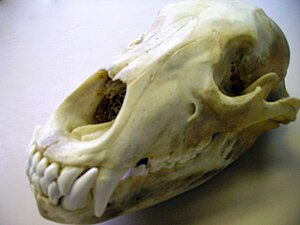
(1) articulations, (2) projections, and (3) holes. In the human skull, the zygomatic bone (cheekbone or malar bone) is a paired irregular bone which articulates with the maxilla, the temporal bone, the sphenoid bone and the frontal bone. Foxes, coyotes, raccoons, bears, and skunks.
 Source: anatomyzone.com
Source: anatomyzone.com
(1) articulations, (2) projections, and (3) holes. Examples include supraorbital foramen, infraorbital foramen, and mental foramen on the cranium. Though it does not articulate with any other bone, the hyoid bone is considered to be part of the axial skeleton.
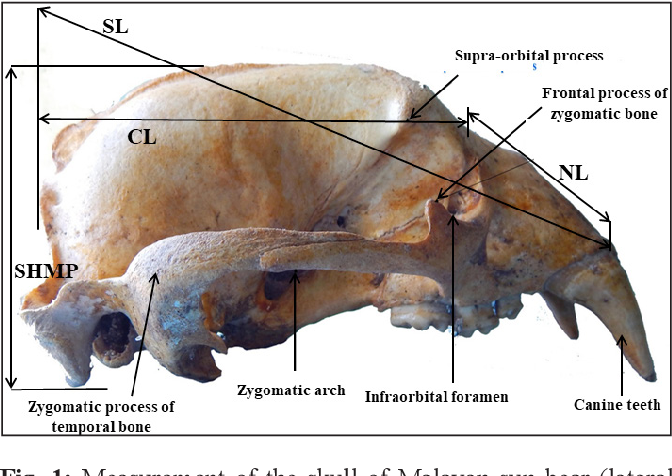 Source: semanticscholar.org
Source: semanticscholar.org
The ___ of a vertebra bears the most weight. Temporal which bone comprise each pectoral girdle? Which is not a correct pairing of a bone and a feature?
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
It is situated at the upper and lateral part of the face and forms the prominence of the cheek , part of the lateral wall and floor of the orbit , and parts of the temporal fossa and the infratemporal. In the human skull, the zygomatic bone (cheekbone or malar bone) is a paired irregular bone which articulates with the maxilla, the temporal bone, the sphenoid bone and the frontal bone. Middle nasal concha of ethmoid 23.

Though it does not articulate with any other bone, the hyoid bone is considered to be part of the axial skeleton. In anatomic position, the femur is angled medially. → the intercondylar fossa is located on the anterior surface of the bone.
![Infraorbital_Foramen [Operative Neurosurgery] Infraorbital_Foramen [Operative Neurosurgery]](https://operativeneurosurgery.com/lib/exe/fetch.php?w=400&tok=d74a66&media=infraorbitalforamen.png) Source: operativeneurosurgery.com
Source: operativeneurosurgery.com
A process (projection) on one bone may fit with a depression on a second bone to form a joint. There are three general classes of bone markings: It transmits the infraorbital artery and vein, and the infraorbital nerve, a branch of the maxillary nerve.
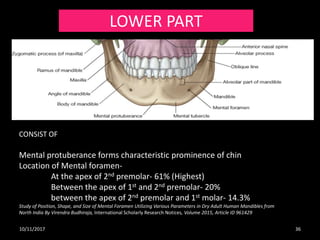 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
It is situated at the upper and lateral part of the face and forms the prominence of the cheek , part of the lateral wall and floor of the orbit , and parts of the temporal fossa and the infratemporal. Though it does not articulate with any other bone, the hyoid bone is considered to be part of the axial skeleton. The waters and waldron (1915) semiaxial occipitomental projection is indispensable for assessing the condition of the anterior portions of the medial wall, the roof and floor of the orbit, the zygomatic bones, the lesser wing of the sphenoid bone, the infraorbital foramen, as well as the maxillary sinuses and the ethmoidal labyrinth (figs.
 Source: en.wikipedia.org
Source: en.wikipedia.org
The seven bones that form the orbit are the maxilla, frontal, nasal, ethmoid, sphenoid, palatine, and zygomatic bones. The infraorbital vessels are found in the inferior orbital fissure, and travel down the infraorbital groove into the infraorbital canal and exit through the infraorbital foramen. Examples include supraorbital foramen, infraorbital foramen, and mental foramen on the cranium.
 Source: alamy.com
Source: alamy.com
In human anatomy, the infraorbital foramen is an opening in the maxillary bone of the skull located below the infraorbital margin of the orbit. The surfaces of bones bear projections, depressions, ridges, and various other features. Interparietal bone fused to parietal in adult, indistinct;
 Source: alamy.com
Source: alamy.com
→ the intercondylar fossa is located on the anterior surface of the bone. In human anatomy, the infraorbital foramen is an opening in the maxillary bone of the skull located below the infraorbital margin of the orbit. The infraorbital vessels are found in the inferior orbital fissure, and travel down the infraorbital groove into the infraorbital canal and exit through the infraorbital foramen.
 Source: en.wikipedia.org
Source: en.wikipedia.org
Frontal temporal mandible maxilla zygomatic In anatomic position, the femur is angled medially. It transmits the infraorbital artery and vein, and the infraorbital nerve, a branch of the maxillary nerve.
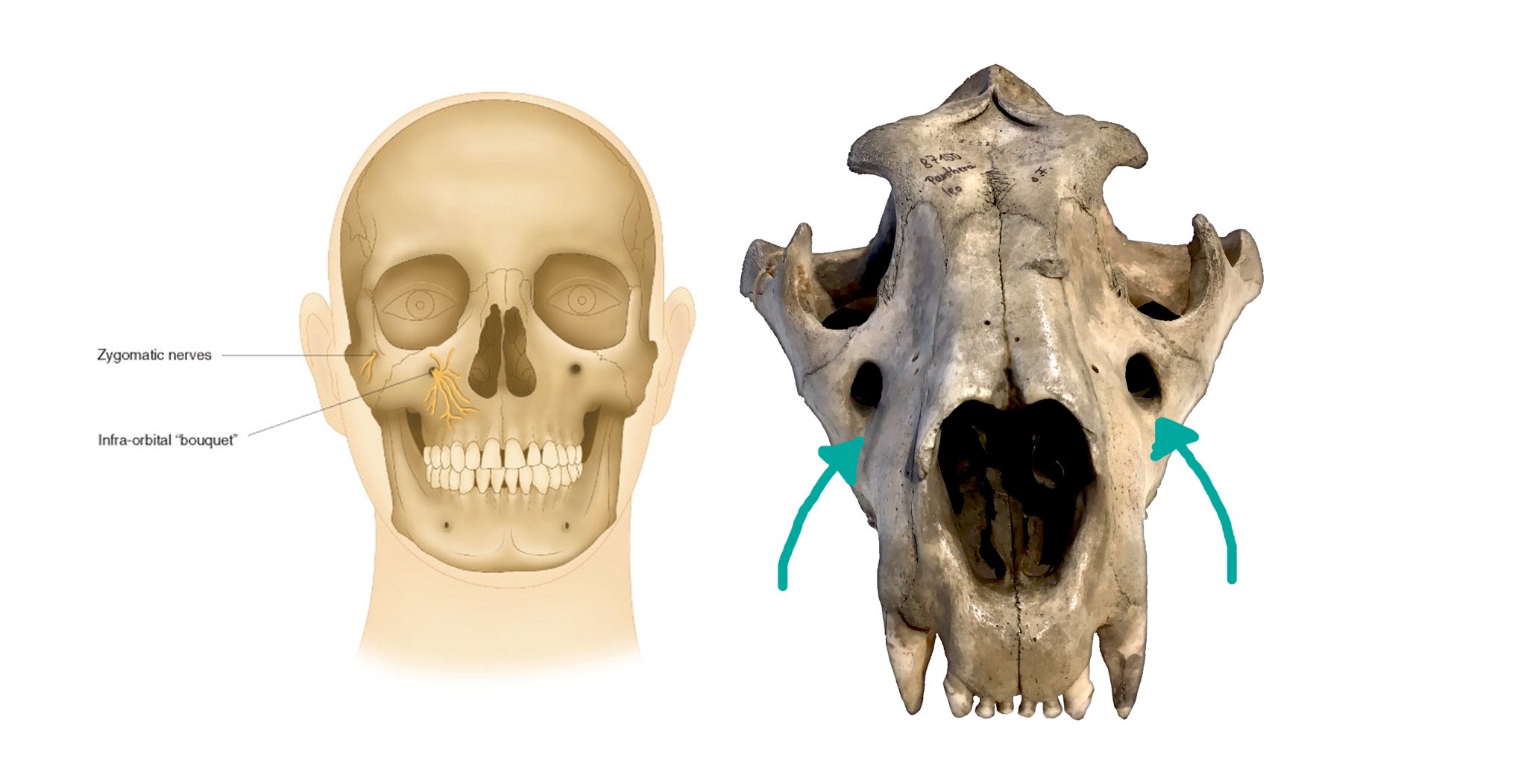
The head of the femur articulates with the acetabulum. Maxillary (anteroinferior) border articulates with the maxilla, tapers just above the infraorbital foramen; It transmits the infraorbital artery and vein, and the infraorbital nerve, a branch of the maxillary nerve.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
The seven bones that form the orbit are the maxilla, frontal, nasal, ethmoid, sphenoid, palatine, and zygomatic bones. The head of the femur articulates with the acetabulum. It transmits the infraorbital artery and vein, and the infraorbital nerve, a branch of the maxillary nerve.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
There are three general classes of bone markings: Mandible supports the lower teeth and provides attachment for muscles of mastication and facial expression. Maxillary (anteroinferior) border articulates with the maxilla, tapers just above the infraorbital foramen;
 Source: neurosurgicalatlas.com
Source: neurosurgicalatlas.com
(1) articulations, (2) projections, and (3) holes. It transmits the infraorbital artery and vein, and the infraorbital nerve, a branch of the maxillary nerve. Here it may receive another articulating bone.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
The head of the femur articulates with the acetabulum. The lacrimals are tiny rectangular paired bones that contribute to the medial wall of the eye orbit. The zygomatic process of the temporal bone and the ___ process of the zygomatic bone form the zygomatic arch.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
The mandible articulates with the neurocranium at the temporomandibular joints (tmjs). Examples include supraorbital foramen, infraorbital foramen, and mental foramen on the cranium. There are three general classes of bone markings:
Also Read :