The myelin sheet of myelinated nerve fiber was varied in thickness and diameter. Unmyelinated nerve fibres is enveloped by a schwann cell that doesn't form a myelin sheath around the axon, and found in autonomous and the somatic neural systems.
Where Are Unmyelinated Nerve Fibers Surrounded By Schwann Cells. Blood vessels run longitudinally within compartments formed by epineurium and perineurium. [ nerv ] a macroscopic cordlike structure of the body, comprising a collection of nerve fibers that convey impulses between a part of the central nervous system and some other body region. Similarly to the organization of the cns tracts, both myelinated and unmyelinated fibers occur peripherally too. An increase in proliferating schwann cells and in total schwann cells might reflect one of the following three mechanisms:
 Biology And Pathology Of Nonmyelinating Schwann Cells - Griffin - 2008 - Glia - Wiley Online Library From onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Biology And Pathology Of Nonmyelinating Schwann Cells - Griffin - 2008 - Glia - Wiley Online Library From onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Related Post Biology And Pathology Of Nonmyelinating Schwann Cells - Griffin - 2008 - Glia - Wiley Online Library :
Lymphocyte adhered to a endothelial cell wall. Describe the myelinated and unmyelinated nerve fibers. The myelin sheet of myelinated nerve fiber was varied in thickness and diameter. In unmyelinated fibers, the nerve impulse is like a grasshopper walking while in a myelinated fiber, the nerve impulse is like grasshopper jumping.
Describe the myelinated and unmyelinated nerve fibers.
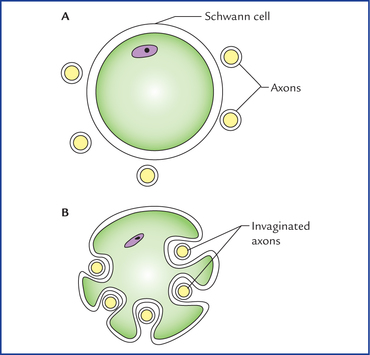
Usually several axons are surrounded by a single schwann cell in the unmyelinated nerve fibers. Similarly to the organization of the cns tracts, both myelinated and unmyelinated fibers occur peripherally too. [ nerv ] a macroscopic cordlike structure of the body, comprising a collection of nerve fibers that convey impulses between a part of the central nervous system and some other body region. One schwann cell does not wrap two or more myelinated nerve fibers; Within the perineurium, nerve fibers and their ensheathing schwann cells are surrounded by endoneurium, a delicate layer of connective tissue with a capillary network, separated from the schwann cell by a basement membrane. Usually several axons are surrounded by a single schwann cell in the unmyelinated nerve fibers.

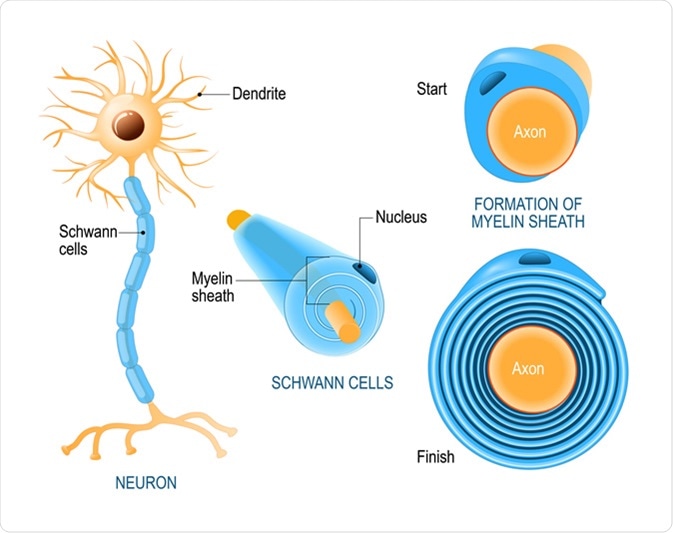
The spaces between adjacent schwann cells, where the axon is exposed are known as nodes of ranvier. Axons or nerve fibers may be myelinated or unmyelinated. The plasma membrane spirals around the axon arranging the membranes in concentric layers.
 Source: getbodysmart.com
Source: getbodysmart.com
Due to presence of nodes of ranvier on myelinated nerve fibers, the speed of transmission of nerve impulses is high in myelinated nerve fibers. Therefore, each unmyelinated fiber is not completely covered by the myelin sheath formed by the schwann cell. The schwann cells wrap tightly around the nerve axon and form the myelin sheath.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
- (kanda et ai., 1991b). They represent the majority of peripheral sensory and autonomic fibers. They lack the myelin envelope completely, with schwann cells surrounding them forming the remak fibers in bundles within peripheral nerves.

Due to presence of nodes of ranvier on myelinated nerve fibers, the speed of transmission of nerve impulses is high in myelinated nerve fibers. Unmyelinated nerve fibres is enveloped by a schwann cell that doesn�t form a myelin sheath around the axon, and found in autonomous and the somatic neural systems. Abutting schwann cells are tightly joined and nodes of ranvier do not form.
 Source: getbodysmart.com
Source: getbodysmart.com
Sympathetic nervous system is part of autonomous nervous system. In the pns and cns d. Sympathetic nervous system is part of autonomous nervous system.
 Source: neupsykey.com
Source: neupsykey.com
Unmyelinated nerve fibers surrounded by one layer of myelin from the schwann cell. In the pns and cns d. In the peripheral nervous system, schwann cells form the sheath around axons, and each schwann cell forms the sheath for just one neuron.
 Source: doubtnut.com
Source: doubtnut.com
Lymphocyte adhered to a endothelial cell wall. Myelinated nerve fibers are nerve fibers that are insulated by a myelin sheath. [ nerv ] a macroscopic cordlike structure of the body, comprising a collection of nerve fibers that convey impulses between a part of the central nervous system and some other body region.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
4 myelinated nerve fibers tend to be larger than unmyelinated nerve fibers, with myelin typically found in those greater than 2 µm and absent in those smaller than 2 µm; Similarly to the organization of the cns tracts, both myelinated and unmyelinated fibers occur peripherally too. In central nervous system the myelin is formed by oligodendrocytes and in peripheral nervous sytem by schwann cells.
 Source: nysora.com
Source: nysora.com
An increase in proliferating schwann cells and in total schwann cells might reflect one of the following three mechanisms: Each axon has a thin lamina of schwann cell sheets enveloping both myelinated and unmyelinated nerve fibers (figs. Inner aspect of a cell showing a nucleus, golgi complex and a centrioles.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
Unmyelinated nerve fibers conduct impulses at low velocities. The myelinated nerve fibres are enveloped with schwann cells, it form a myelin sheath around the axon. The schwann cells wrap tightly around the nerve axon and form the myelin sheath.
 Source: intechopen.com
Source: intechopen.com
Where are unmyelinated nerve fibers surrounded by schwann cells? Each schwann cell typically contains several axons (up to 20), which are often brought into the cell by. The nonmyelinating schwann cells (nmscs) include the schwann cells of remak fibers, the specialized terminal schwann cells (tscs) at neuromuscular junctions, and those in some sensory transducers, including in pacinian corpuscles and meissner�s corpuscles.
 Source: quora.com
Source: quora.com
Note basal lamina (arrows) outlining the cell membrane of each schwann cell. Due to presence of nodes of ranvier on myelinated nerve fibers, the speed of transmission of nerve impulses is high in myelinated nerve fibers. Explore the role of all three in the development of ms and the action.
 Source: doctorlib.info
Source: doctorlib.info
The basement membrane of perineural cell was noted (fig. Therefore, each unmyelinated fiber is not completely covered by the myelin sheath formed by the schwann cell. They are also found in the spinal cord.
 Source: study.com
Source: study.com
Abutting schwann cells are tightly joined and nodes of ranvier do not form. On the contrary, one to four unmyelinated axons are normally included in one schwann cell subunit. The axon, its sheath of schwann cells and the surrounding basal lamina form the impulse conducting structures, the nerve fibres, classified in myelinated.
 Source: intechopen.com
Source: intechopen.com
[ nerv ] a macroscopic cordlike structure of the body, comprising a collection of nerve fibers that convey impulses between a part of the central nervous system and some other body region. Depending on their function, nerves are known as sensory, motor, or mixed. Similarly to the organization of the cns tracts, both myelinated and unmyelinated fibers occur peripherally too.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Unmyelinated nerve fibers surrounded by one layer of myelin from the schwann cell. One schwann cell does not wrap two or more myelinated nerve fibers; Myelinated nerve fibers usually range 2 to 14 µm while unmyelinated fibers range 0.2 to 3.
 Source: news-medical.net
Source: news-medical.net
- are enveloped by perineural cell cytoplasmic laminae. The plasma membrane spirals around the axon arranging the membranes in concentric layers. They are also found in the spinal cord.
 Source: onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Source: onlinelibrary.wiley.com
The plasma membrane spirals around the axon arranging the membranes in concentric layers. Unmyelinated nerve fibres is enveloped by a schwann cell that doesn�t form a myelin sheath around the axon, and found in autonomous and the somatic neural systems. Where are unmyelinated nerve fibers surrounded by schwann cells?

Usually several axons are surrounded by a single schwann cell in the unmyelinated nerve fibers. 5) are enveloped by perineural cell cytoplasmic laminae. 3) (kanda et ai., 1991b).
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
They represent the majority of peripheral sensory and autonomic fibers. The plasma membrane spirals around the axon arranging the membranes in concentric layers. In the pns and cns d.
Also Read :