Site now thought to have normal microbiota or their dna (4) 1. In kernel, as the microbe acquires a stable part of foods, stable environment, protection and involvement, the host besides obtains single nutritionary and digestive additions every bit good as the development and natural action of the immune system which protects it against the infective infection by the bugs.
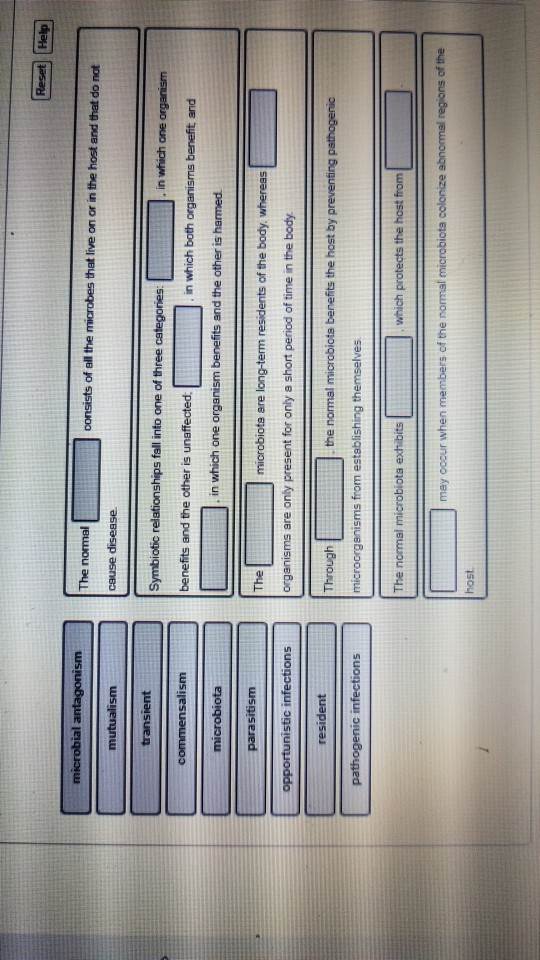
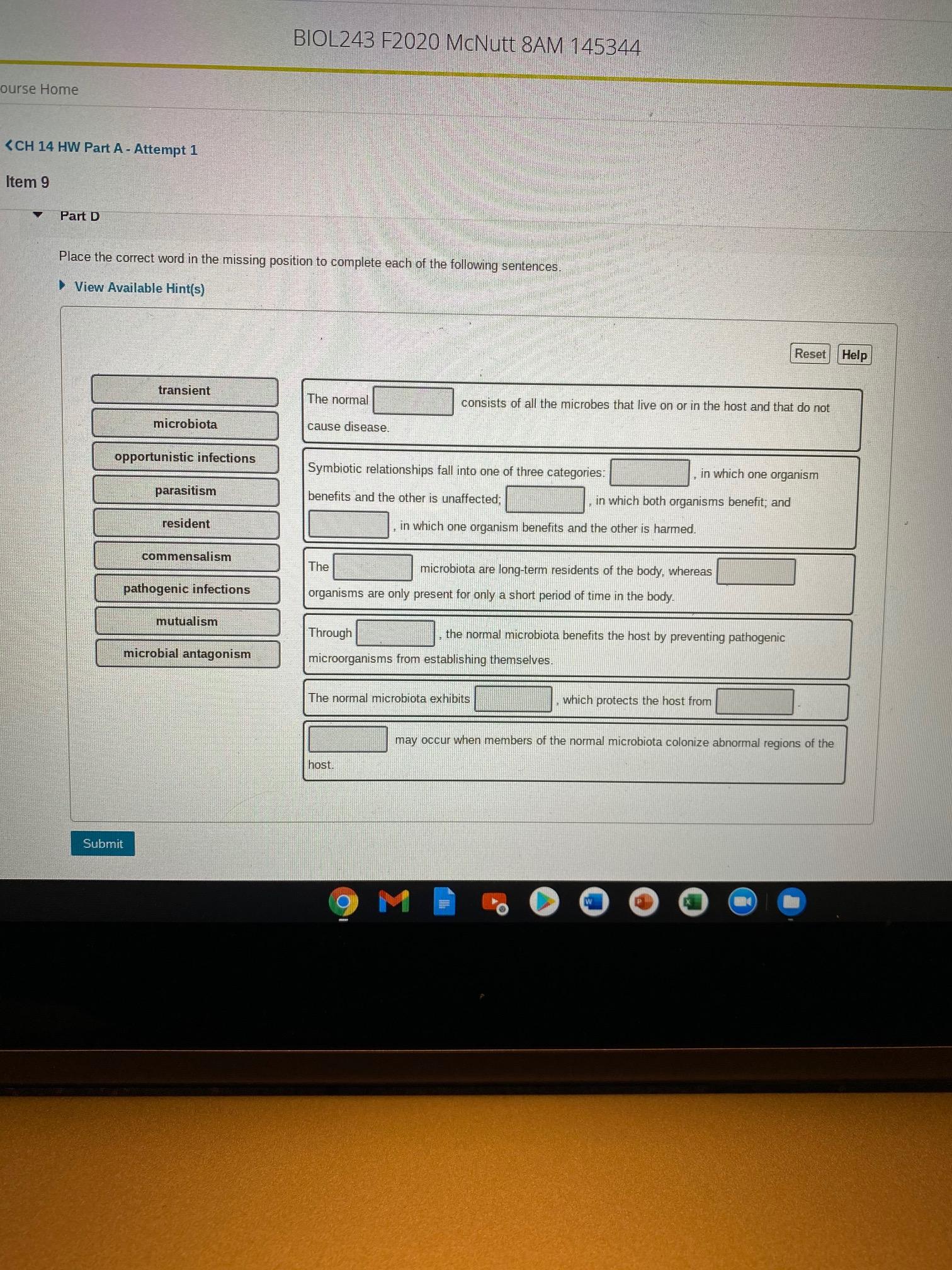
The Normal Microbiota Exhibits Which Protects The Host From. 9 a seminal discovery by markle et al. Which of the following represents an instance of commensalism? A vaginal microbiome dominated by lactobacillus species benefits the host, whereas a dysbiotic vaginal microbiome consisting of anaerobic bacteria is linked to numerous gynaecological and. System protects the host 2.
 Frontiers | Mechanism Of The Gut Microbiota Colonization Resistance And Enteric Pathogen Infection | Cellular And Infection Microbiology From frontiersin.org
Frontiers | Mechanism Of The Gut Microbiota Colonization Resistance And Enteric Pathogen Infection | Cellular And Infection Microbiology From frontiersin.org
Related Post Frontiers | Mechanism Of The Gut Microbiota Colonization Resistance And Enteric Pathogen Infection | Cellular And Infection Microbiology :
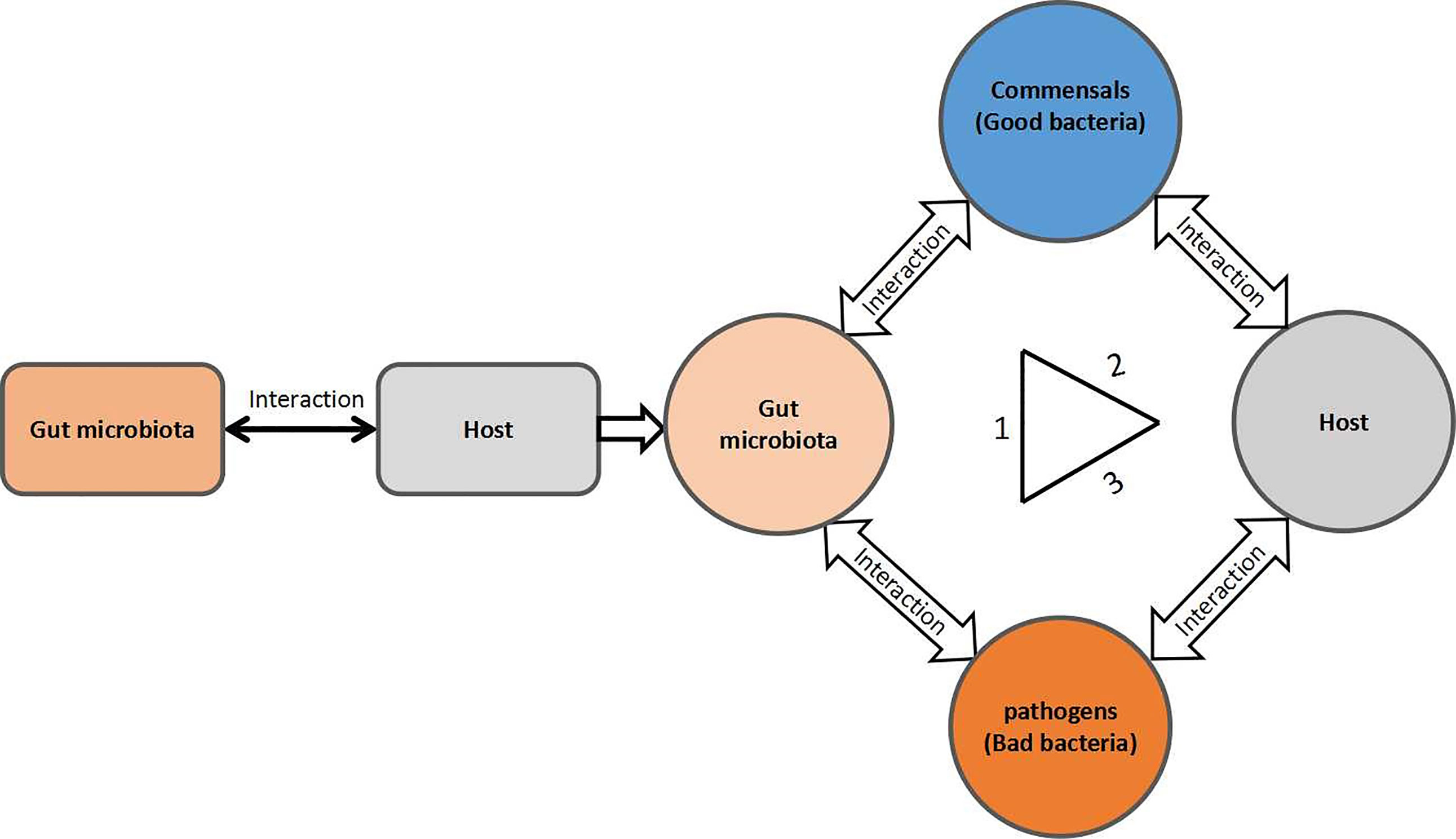
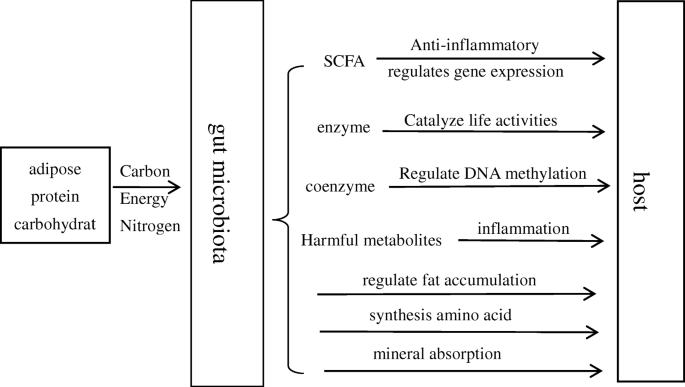
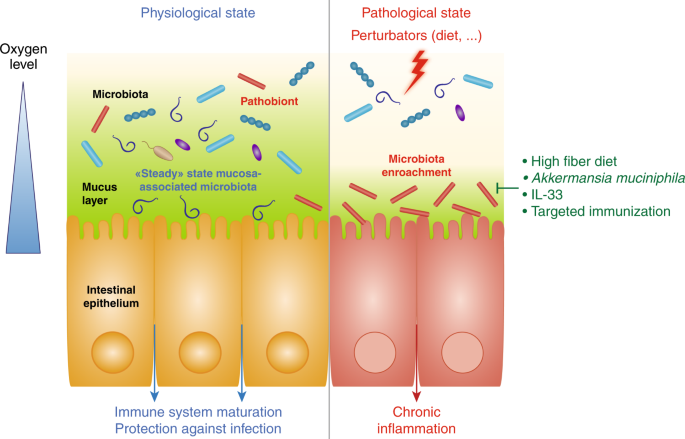
The microbiota offers many benefits to the host, through a range of physiological functions such as strengthening gut integrity or shaping the intestinal epithelium , harvesting energy , protecting against pathogens and regulating host immunity. The microbiota has emerged as a key regulator of metabolism within the mammalian host, and the composition of the microbiota in obese individuals is sufficient to confer metabolic defects when transferred into mice. In essence, as the microbe acquires a stable contribution of nutrients, stable environment, protection and interest, the host also obtains individual nutritional and digestive gains as well as the development and natural action of the immune system which protects it against the pathogenic infection by the microbes. Infectious pathogens can disrupt the microbiome in addition to directly affecting the host.
The integral roles of the gut microbiota in resisting colonization of enteric pathogens, educating and promoting the maturation of the host immune system, and host metabolism, as shown by numerous studies in the past few years, underscore the need to understand mechanisms underlying the myriad of supportive roles of the gut microbiota in human health.
The role of microbiota and gender in autoimmune development. Additionally, other aspects of host physiology, such as gut anatomy and function, may also act as filters for large proportions of the microbiota. Which of the following represents an instance of commensalism? Modulation of the gut microbiota has become a promising and important approach to improve host health as it protects the host from infections and diseases and produces important vitamins and scfas. The skin hosts a wide diversity of beneficial microbes that provide physical and immunological protection from. It has been widely known that gut microbiota modulates the host response to protect against influenza infection, but mechanistic details remain largely unknown.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
Recently, several studies have begun to elucidate the molecular mechanisms underlying how the gut microbiota regulates host innate immunity against pathogens (16, 17), including a role in helping the host resist pathogen colonization. However, there is potential for these mechanisms to be disrupted as a result of an altered microbial composition, known. In essence, as the microbe acquires a stable contribution of nutrients, stable environment, protection and interest, the host also obtains individual nutritional and digestive gains as well as the development and natural action of the immune system which protects it against the pathogenic infection by the microbes.
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
The normal microbiota exhibits which protects the host from may occur when members of the normal microbiota colonize abnormal regions of the host submit 9 m 9 a seminal discovery by markle et al. Phagocytes ____________ refers to the process by which microbes gain a more stable foothold at the portal of entry through interaction of their molecules with host cell receptors.
 Source: jlr.org
Source: jlr.org
Influenza is a severe respiratory illness that continually threatens global health. Phagocytes ____________ refers to the process by which microbes gain a more stable foothold at the portal of entry through interaction of their molecules with host cell receptors. Impacts of disease may be dependent on the ability of.
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
Which of the following represents an instance of commensalism? 9 a seminal discovery by markle et al. Site now thought to have normal microbiota or their dna (4) 1.
 Source: microbiologynote.com
Source: microbiologynote.com
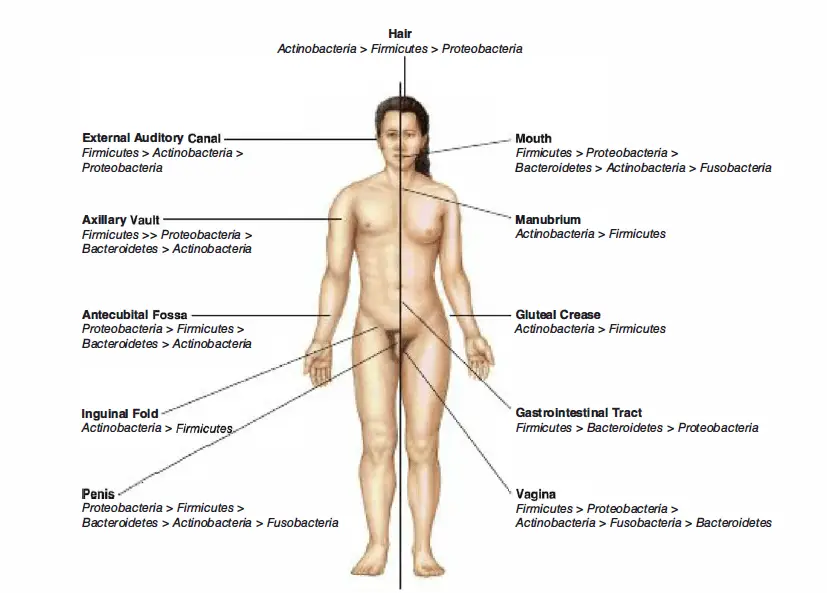
Sites previously known to harbor normal microbiota (7) 1. In kernel, as the microbe acquires a stable part of foods, stable environment, protection and involvement, the host besides obtains single nutritionary and digestive additions every bit good as the development and natural action of the immune system which protects it against the infective infection by the bugs. In this review, we summarize the main mechanisms by which commensal bacteria, including certain probiotic species, actively.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
Sites in which dna from microbiota has been detected (2) 1. The microbiota has emerged as a key regulator of metabolism within the mammalian host, and the composition of the microbiota in obese individuals is sufficient to confer metabolic defects when transferred into mice. The normal microbiota prevents a pathogen from establishing an infection by both taking up space and producing toxic substances.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Impacts of disease may be dependent on the ability of. It stimulates immune reactivity and blocks the spread of an infectious agent. 9 a seminal discovery by markle et al.
 Source: link.springer.com
Source: link.springer.com
Sites previously known to harbor normal microbiota (7) 1. In this review, the interactions between gut microbiota and the host have been focused on, to provide an overview of the role of gut microbiota and their unique metabolites in conferring host protection against invading pathogen, regulation of diverse host physiological functions including metabolism, development and homeostasis of immunity and the nervous system. The normal microbiota prevents a pathogen from establishing an infection by both taking up space and producing toxic substances.
 Source: nature.com
Source: nature.com
9 a seminal discovery by markle et al. However, there is potential for these mechanisms to be disrupted as a result of an altered microbial composition, known. In particular, reductions in the gene richness of the microbiota have been reported during metabolic disease, including decreased.
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
In kernel, as the microbe acquires a stable part of foods, stable environment, protection and involvement, the host besides obtains single nutritionary and digestive additions every bit good as the development and natural action of the immune system which protects it against the infective infection by the bugs. It has been widely known that gut microbiota modulates the host response to protect against influenza infection, but mechanistic details remain largely unknown. There is no normal microbiota because microbes are moved by the continuous stream of mucous generated by ciliated epithelial cells (cilliary escalator), phagocytic action of alveolar macrophages, and lysozyme in mucus.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
In this review, the interactions between gut microbiota and the host have been focused on, to provide an overview of the role of gut microbiota and their unique metabolites in conferring host protection against invading pathogen, regulation of diverse host physiological functions including metabolism, development and homeostasis of immunity and the nervous system. The normal microbiota can benefit the host by preventing the overgrowth of harmful microorganisms what is a consequence of competitive exclusion? 9 a seminal discovery by markle et al.
 Source: frontiersin.org
Source: frontiersin.org
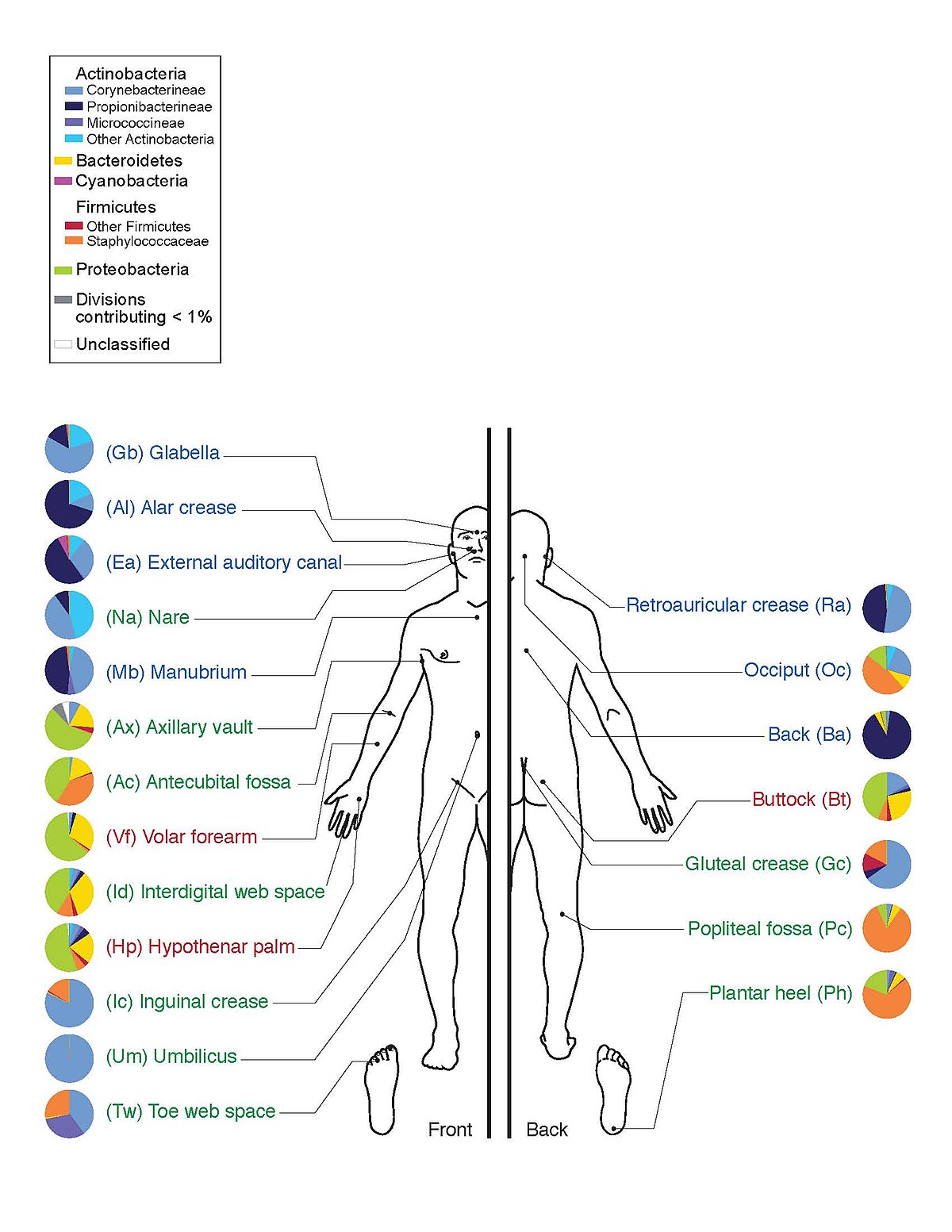
Normal microbiota of the lower respiratory tract. The microbiota has emerged as a key regulator of metabolism within the mammalian host, and the composition of the microbiota in obese individuals is sufficient to confer metabolic defects when transferred into mice. In kernel, as the microbe acquires a stable part of foods, stable environment, protection and involvement, the host besides obtains single nutritionary and digestive additions every bit good as the development and natural action of the immune system which protects it against the infective infection by the bugs.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
The normal microbiota protect the host against colonization by potentially pathogenic microbes by competing for nutrients, producing substances harmful to the invading microbes and affection conditions such as. System protects the host 2. Recently, several studies have begun to elucidate the molecular mechanisms underlying how the gut microbiota regulates host innate immunity against pathogens (16, 17), including a role in helping the host resist pathogen colonization.
 Source: onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Source: onlinelibrary.wiley.com
The normal microbiota exhibits which protects the host from may occur when members of the normal microbiota colonize abnormal regions of the host submit 9 m Host resistance overview • most pathogens (disease causing microbes). The microbiota, consisting of the community of bacterial, viral, fungal, and protozoa organisms that inhabit a mammalian host, can impact susceptibility to a range of diseases including cancer.
Gut microbiota gut microbiota (gm) is also called as “forgotten organ” which harbours 100 trillion bacteria, (fungi, archaea, and viruses) which are 10 times greater than the number of cells present in human body 41. 9 a seminal discovery by markle et al. In this review, the interactions between gut microbiota and the host have been focused on, to provide an overview of the role of gut microbiota and their unique metabolites in conferring host protection against invading pathogen, regulation of diverse host physiological functions including metabolism, development and homeostasis of immunity and the nervous system.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
In this review, we summarize the main mechanisms by which commensal bacteria, including certain probiotic species, actively. Here, we took advantage of the phenomenon of lethal dose 50 (ld50) and metagenomic sequencing analysis to identify. Coli lives in the host�s intestine and releases vitamins that are.
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
Infectious pathogens can disrupt the microbiome in addition to directly affecting the host. Influenza is a severe respiratory illness that continually threatens global health. Normal microbiota of the lower respiratory tract.
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
The normal microbiota prevents a pathogen from establishing an infection by both taking up space and producing toxic substances. Recently, several studies have begun to elucidate the molecular mechanisms underlying how the gut microbiota regulates host innate immunity against pathogens (16, 17), including a role in helping the host resist pathogen colonization. The role of microbiota and gender in autoimmune development.
 Source: en.wikipedia.org
Source: en.wikipedia.org
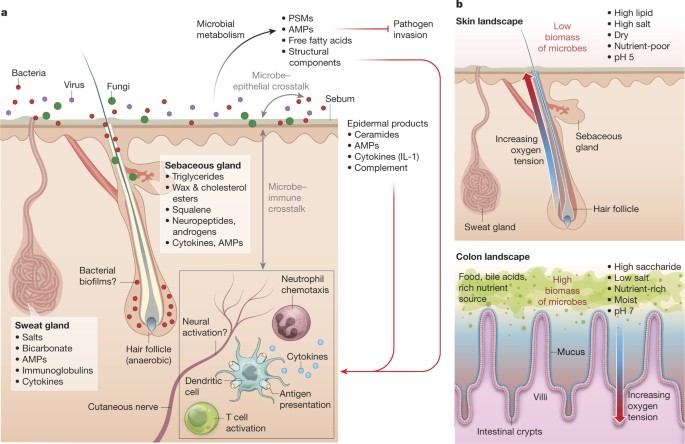
Modulation of the gut microbiota has become a promising and important approach to improve host health as it protects the host from infections and diseases and produces important vitamins and scfas. The skin hosts a wide diversity of beneficial microbes that provide physical and immunological protection from. The normal microbiota can benefit the host by preventing the overgrowth of harmful microorganisms what is a consequence of competitive exclusion?
 Source: nature.com
Source: nature.com
Here, we took advantage of the phenomenon of lethal dose 50 (ld50) and metagenomic sequencing analysis to identify. The normal microbiota protect the host against colonization by potentially pathogenic microbes by competing for nutrients, producing substances harmful to the invading microbes and affection conditions such as. A category of white blood cells called _____ are most likely to be the first defense encountered upon entering the host by a microbe that is not part of the normal biota.
Also Read :