These muscle fibers originate the chordae tendineae that inserts in the atrioventricular valv e margin. The true chordae tendineae emerge from the apical third of the papillary muscles or (less frequently) from the base of the papillary muscles.
Structure From Which Chordae Tendineae Originate. The chordae originate from the fibrous heads of the papillary muscles and may be classified according to their site of insertion on the leaflet. Prevents blood movement from the right ventricle to right atrium tricuspid valve. The mitral valve (mv) is a very complex structure composed of the anterior (aml) and posterior (pml) leaflets, the chordae tendineae (ct), and the papillary muscles (ppmm), all of which work on a very harmonious basis to ensure an appropriate opening and closing of the left atrioventricular orifice. Pericardial sac _____double layered membrane around heart;
 Solved (Chamber) (Chamber) Epicardium Myocardium Endocardium | Chegg.com From chegg.com
Solved (Chamber) (Chamber) Epicardium Myocardium Endocardium | Chegg.com From chegg.com
Related Post Solved (Chamber) (Chamber) Epicardium Myocardium Endocardium | Chegg.com :
Membranes around heart (j, pericardial sac) d. As observed with the scanning Prevents blood movement from the right ventricle to right atrium tricuspid valve. Structure from which chordae tendineae originate (h, papillary muscle) b.
Moreover, the fibers that constitute the chordae tendineae form bundles arranged in layers with a predominantly longitudinal disposition.
After their origin and before their insertion, they split in numerous branches and interconnections that ensure a balanced distribution of the mechanical forces among chordae. They have central function by allowing coaptation and preventing leaflet prolapse or flail into the left atrium. The chordae originate from the fibrous heads of the papillary muscles and may be classified according to their site of insertion on the leaflet. These muscle fibers originate the chordae tendineae that inserts in the atrioventricular valv e margin. 41,46 after their origin and before their insertion, they split in numerous branches and interconnections that ensure a balanced distribution of the mechanical forces among chordae. Membranes around the heart pericardial sac.
 Source: en.wikipedia.org
Source: en.wikipedia.org
The true chordae tendineae emerge from the apical third of the papillary muscles or (less frequently) from the base of the papillary muscles. The chordae tendineae make up the leaflet suspension system that ultimately determine and maintain the position and tension on the valve leaflets at end of systole. Prevents blood movement from right ventricle to right atrium.
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
After their origin and before their insertion, they split in numerous branches and interconnections that ensure a balanced distribution of the mechanical forces among chordae. The true chordae tendineae emerge from the apical third of the papillary muscles or (less frequently) from the base of the papillary muscles. As observed with the scanning

Prevents blood movement from right ventricle to right atrium (l, tricuspid valve) c. These issues originate from papillary muscles. They arise from the tips of the papillary muscles on the inside of the wall of the ventricles and extend into the hollow lumen.
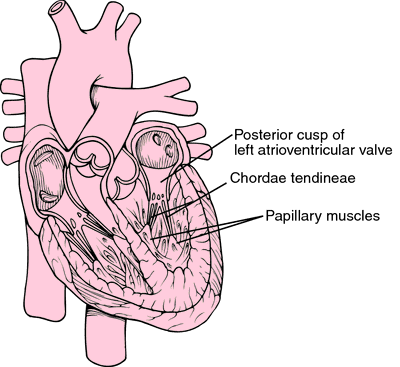 Source: knowyourbody.net
Source: knowyourbody.net
After their origin and before their insertion, they split in numerous branches and interconnections that ensure a balanced distribution of the mechanical forces among chordae. The simplest and perhaps most effective classification of chordae tendineae. Structure from which chordae tendineae originate papillary muscle.
 Source: socratic.org
Source: socratic.org
Membranes around the heart pericardial sac. They anchor the cusps to the papillary muscles of the ventricular walls. The mitral valve (mv) is a very complex structure composed of the anterior (aml) and posterior (pml) leaflets, the chordae tendineae (ct), and the papillary muscles (ppmm), all of which work on a very harmonious basis to ensure an appropriate opening and closing of the left atrioventricular orifice.
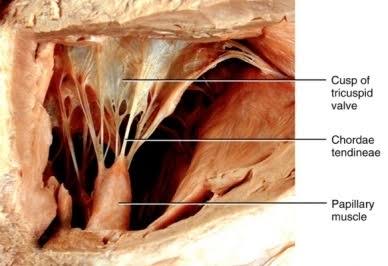
 Source: clinicalanatomy.com
Source: clinicalanatomy.com
The chordae tendineae make up the leaflet suspension system that ultimately determine and maintain the position and tension on the valve leaflets at end of systole. Describe the function of the chordae tendineae and the papillary muscles. They anchor the cusps to the papillary muscles of the ventricular walls.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
After their origin and before their insertion, they split in numerous branches and interconnections that ensure a balanced distribution of the mechanical forces among chordae. They have central function by allowing coaptation and preventing leaflet prolapse or flail into the left atrium. Where connective tis sue originate
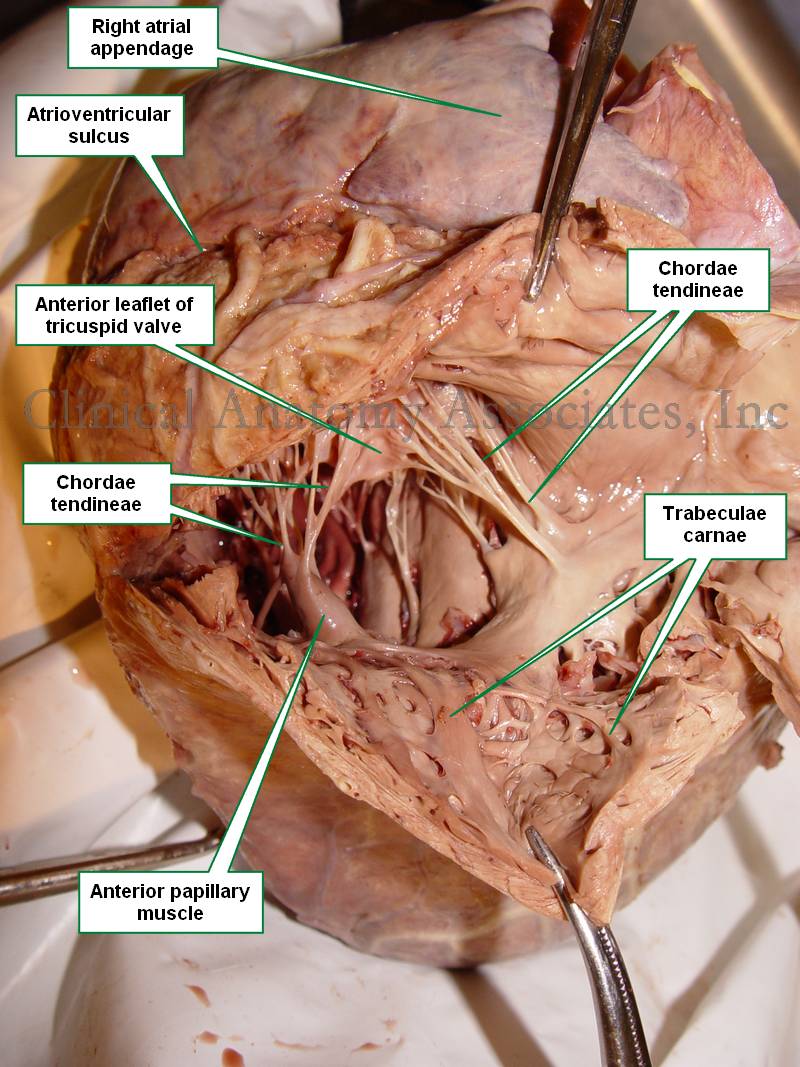
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
After their origin and before their insertion, they split in numerous branches and interconnections that ensure a balanced distribution of the mechanical forces among chordae. They anchor the cusps to the papillary muscles of the ventricular walls. The tricuspid valve moves up and closes the opening between the right atrium and right ventricle.
 Source: coursehero.com
Source: coursehero.com
Pericardial cavity _____space containing serous fluid. These muscles project inwardly from the walls of the ventricle of the heart. False chordae tendineae are irregular and more commonly are attached either between papillary muscles or from the papillary muscles to the walls of the ventricles.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
Are part of the subvalvular apparatus, the chordae tendinae are composed of fibrous strings that originate from the papillary muscles or the ventricle wall and that its insertion is into the ventricle, the anterior leaflet, posterior leaflet, and commissural leaflet. They anchor the cusps to the papillary muscles of the ventricular walls. The tricuspid valve is large and has chordae tendinaea and papillary muslces.
 Source: heartviews.org
Source: heartviews.org
The tricuspid valve moves up and closes the opening between the right atrium and right ventricle. Although the anatomy and function A(n) _____ is the structure from which chordae tendineae originate.
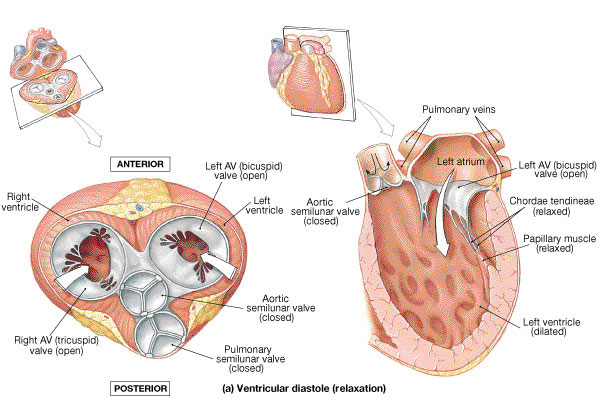 Source: knowyourbody.net
Source: knowyourbody.net
They have central function by allowing coaptation and preventing leaflet prolapse or flail into the left atrium. Structure from which chordae tendineae originate papillary muscle. These tissue bands originate from papillary tissue that.
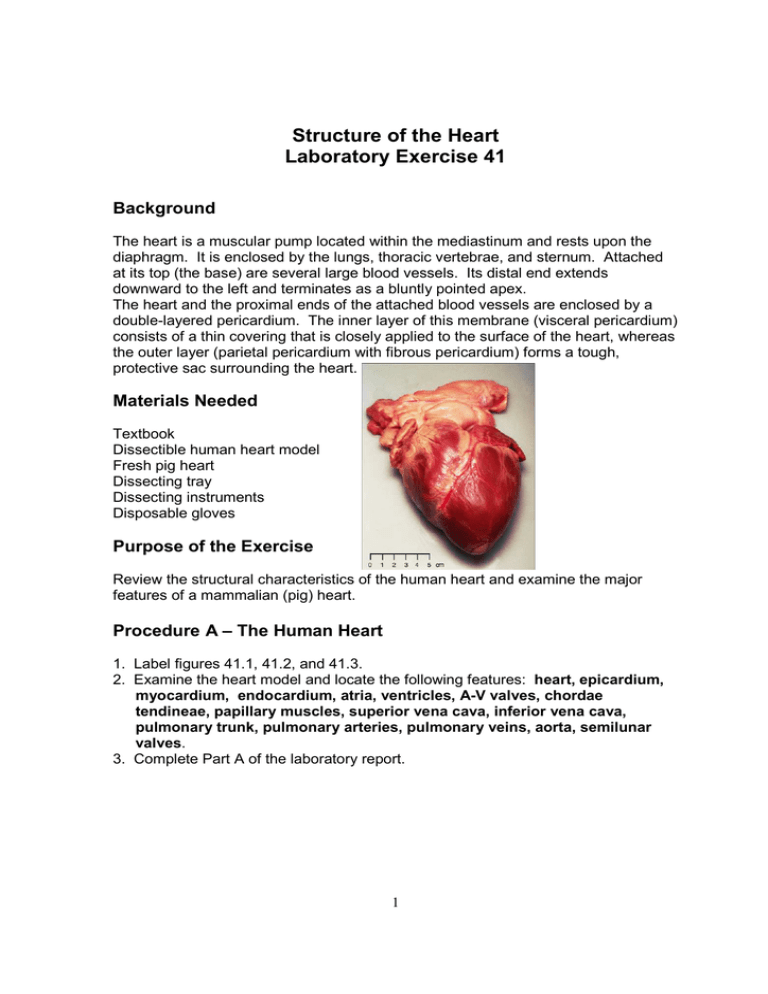 Source: studylib.net
Source: studylib.net
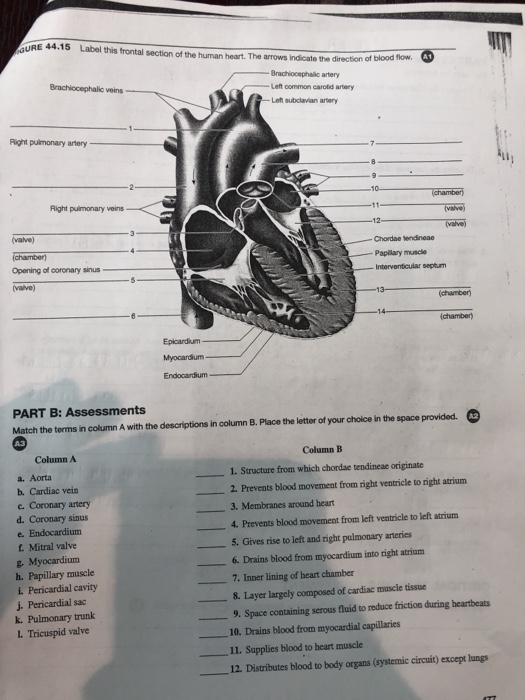
Papillary muscle identify the features on this anterior view of the heart region of a cadaver by clicking and dragging the labels to the correct location. The chordae originate from the fibrous heads of the papillary muscles and may be classified according to their site of insertion on the leaflet. Prevents blood movement from the right ventricle to right atrium tricuspid valve.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
They arise from the tips of the papillary muscles on the inside of the wall of the ventricles and extend into the hollow lumen. Moreover, the fibers that constitute the chordae tendineae form bundles arranged in layers with a predominantly longitudinal disposition. Prevents blood movement from right ventricle to right atrium (l, tricuspid valve) c.
 Source: studylib.net
Source: studylib.net
Prevents blood movement from left ventricle to left atrium mitral valve. Yes, there are chordae tendineae in the right ventricle. These muscles project inwardly from the walls of the ventricle of the heart.
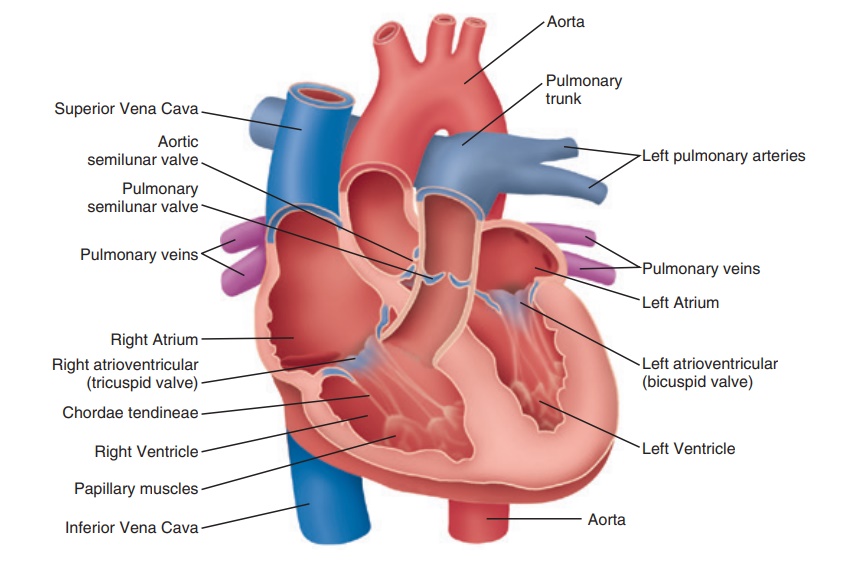 Source: pharmacy180.com
Source: pharmacy180.com
False chordae tendineae are irregular and more commonly are attached either between papillary muscles or from the papillary muscles to the walls of the ventricles. The other part was fixed in 2.5% morphogenesis of chordae tendineae in human [9] gluteraldehyde for transmission electrone microscopy lymphatic capillary in chordae [10] structure of chordae (tem. Pulmonary trunk_____ gives rise to left and right pulmonary arteries
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Prevents blood movement from the right ventricle to right atrium tricuspid valve. Click to see full answer. Are part of the subvalvular apparatus, the chordae tendinae are composed of fibrous strings that originate from the papillary muscles or the ventricle wall and that its insertion is into the ventricle, the anterior leaflet, posterior leaflet, and commissural leaflet.
 Source: study.com
Source: study.com
A single papillary muscle in swine and human hearts may originate several chordae tendineae which after that may divide in several branches as described previously (lam et al.; Structure from which chordae tendineae originate papillary muscle. Click to see full answer.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Where connective tis sue originate After their origin and before their insertion, they split in numerous branches and interconnections that ensure a balanced distribution of the mechanical forces among chordae. Where connective tis sue originate
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
The mitral valve (mv) is a very complex structure composed of the anterior (aml) and posterior (pml) leaflets, the chordae tendineae (ct), and the papillary muscles (ppmm), all of which work on a very harmonious basis to ensure an appropriate opening and closing of the left atrioventricular orifice. The mitral valve (mv) is a very complex structure composed of the anterior (aml) and posterior (pml) leaflets, the chordae tendineae (ct), and the papillary muscles (ppmm), all of which work on a very harmonious basis to ensure an appropriate opening and closing of the left atrioventricular orifice. A single papillary muscle may originate multiple chordae tendineae which can divide into branches in swine and human hearts.
Also Read :





