This area is free of ribosomes and most other cell organelles, with the exception of cytoskeletal elements and organelles that are being transported down the axon. Region of the cell body from which the axon originates.
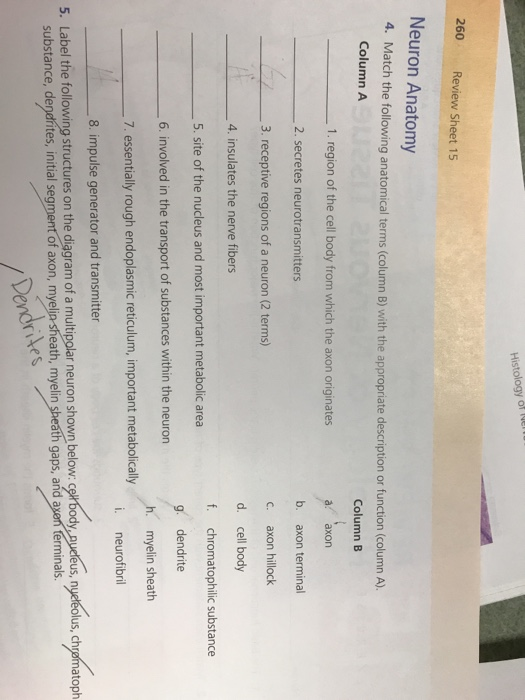
Region Of The Cell Body From Which The Axon Originates. Involved in the transport of substances within the neuron 7. The axon hillock is generally the site of action potential initiation. Region of the cell body from which the axon originates a. Region of the cell body from which the axon originates.
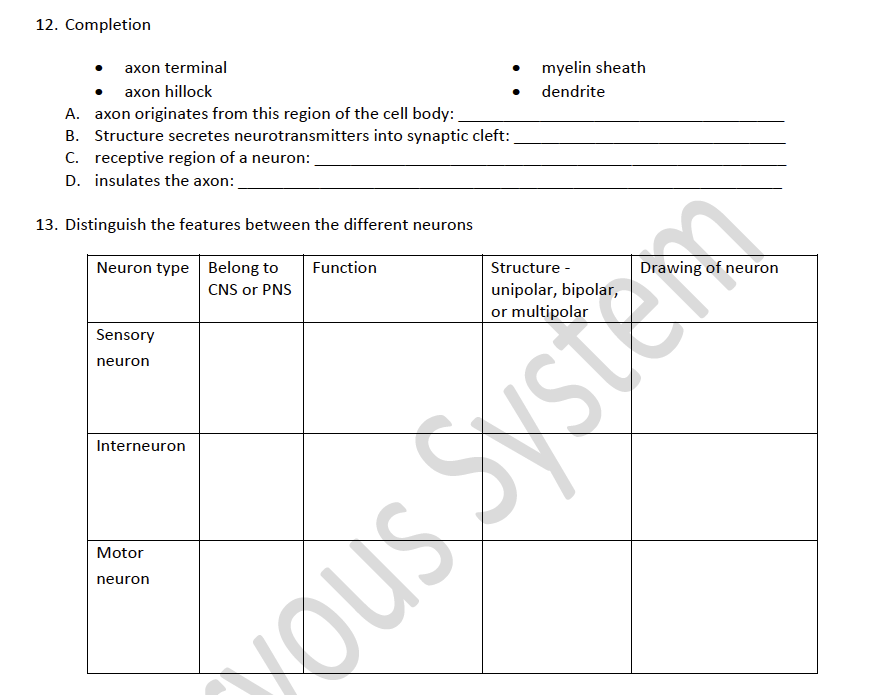 Solved 12. Completion Axon Terminal Myelin Sheath Axon | Chegg.com From chegg.com
Solved 12. Completion Axon Terminal Myelin Sheath Axon | Chegg.com From chegg.com
Related Post Solved 12. Completion Axon Terminal Myelin Sheath Axon | Chegg.com :
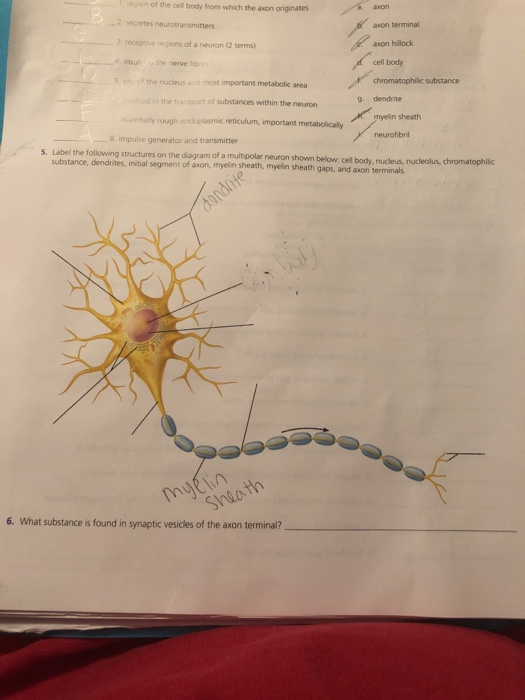
Receptive region of a neuron. Slightly enlarged region of the cell body from which the axon originates axonal terminal form synapses, or junctions with neurons (effector cells).; The region of the neuron cell body from which the axon originates. Eon of the cell body from which the axon originates 9 receptive regions of a neuron (2 tems) insulthe nerve 5 cf the nudeus and most important metabolic area axon terminal axon hillock cell body d in the transport of substances within the neuron 9 dendrite myelin sheath neurofibril ssintaly rough endoplasmic reticulum, important.
Axons connect with other cells in the body including other neurons, muscle cells, and organs.
The axon (in motor neurons) begins just distal to a slightly enlarged cell body structure called the axon hillock. Column a column b a. These connections occur at junctions known as synapses. Glial cells of the pns, found surrounding neuron cell bodies within ganglia. Receptive regions of a neuron (2 terms) 4. This area is free of ribosomes and most other cell organelles, with the exception of cytoskeletal elements and organelles that are being transported down the axon.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
Region of the cell body from which the axon originates axon b. Region of the cell body from which the axon originates. Region of the cell body from which the axon originates:
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
Schwann cell bodies wrap around the axon forming the myelin sheath. Axons connect with other cells in the body including other neurons, muscle cells, and organs. Region of the cell body from which the axon originates, it is the area of the cell that generates atp.
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
The axon hillock is generally the site of action potential initiation. May be involved in the transport of substances within the neuron f. Receptive region of a neuron.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
Receptive region of a neuron, as it depolarizes it delivers graded potential to. Receptive region of a neuron, as it depolarizes it delivers graded potential to. Region of the cell body from which the axon originates.
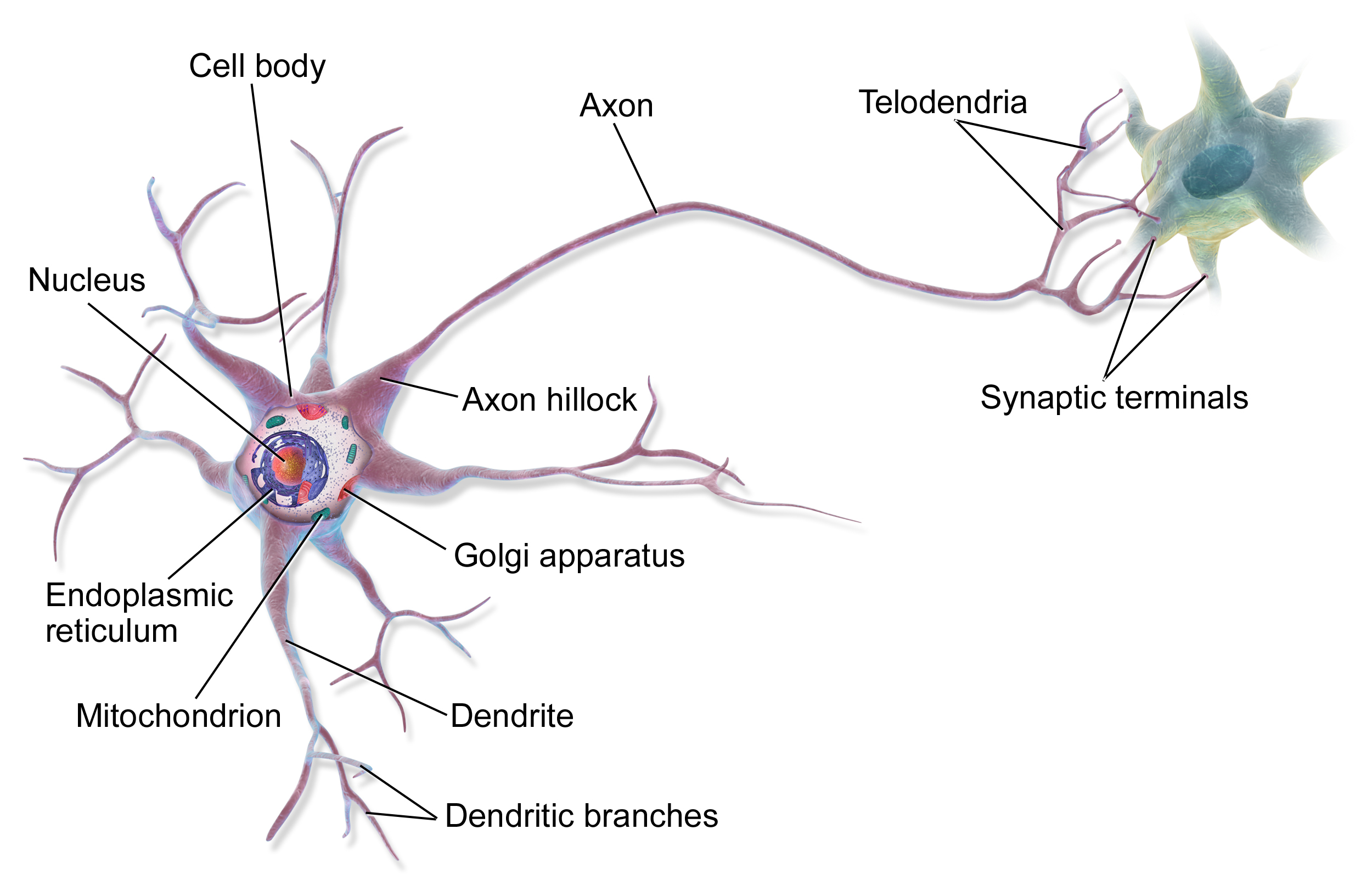 Source: en.wikipedia.org
Source: en.wikipedia.org
Slightly enlarged region of the cell body from which the axon originates axonal terminal form synapses, or junctions with neurons (effector cells).; Region of the cell body from which the axon originates: The axon hillock is generally the site of action potential initiation.

32 related question answers found The neurofilaments in the axon hillock become clustered together as fascicles. Receptive regions of a neuron (2 terms) 4.
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
32 related question answers found May be involved in the transport of substances within the neuron f. Site of the nucleus and most important metabolic area 6.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
Region of the cell body from which the axon originates: Region of the cell body from which the axon originates b axon terminal 2. Receptive region of a neuron.
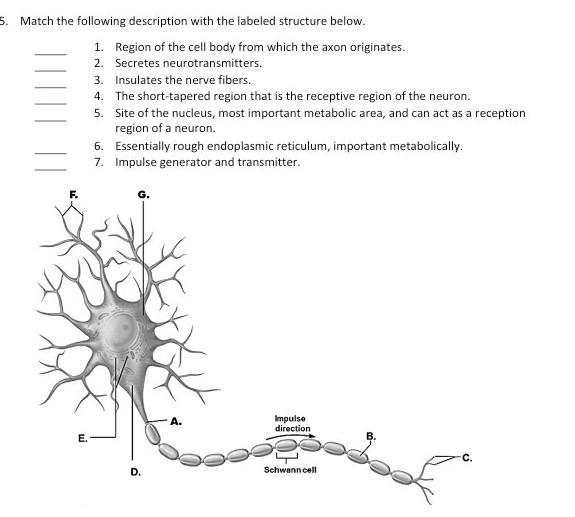
It is also referred to as the initial segment. In many cases, an axon originates at an axon hillock on the soma; The neurofilaments in the axon hillock become clustered together as fascicles.
 Source: en.wikipedia.org
Source: en.wikipedia.org
Region of the cell body from which the axon originates. This area is free of ribosomes and most other cell organelles, with the exception of cytoskeletal elements and organelles that are being transported down the axon. Receptive regions of a neuron (2 terms) d.
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
These connections occur at junctions known as synapses. Describe how the schwann cells form the myelin sheath encasing nerve fibers. Involved in the transport of substances within the neuron.
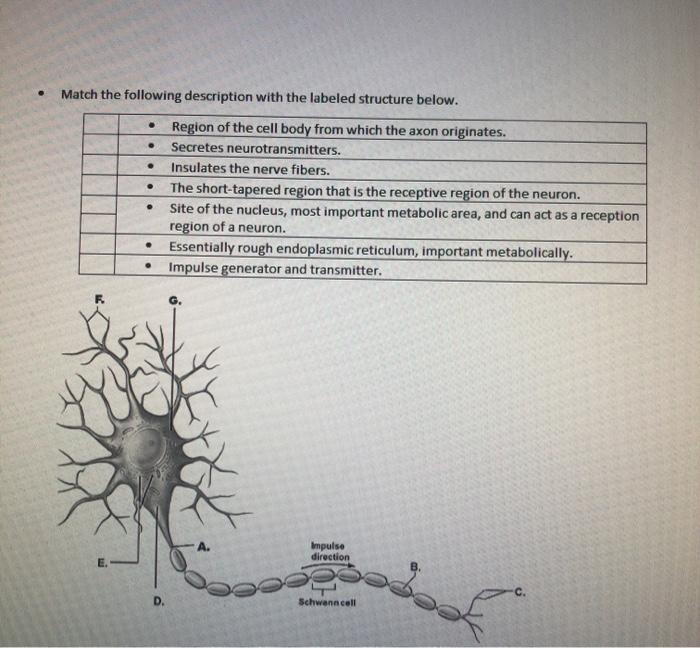
Slightly enlarged region of the cell body from which the axon originates axonal terminal form synapses, or junctions with neurons (effector cells).; This area is free of ribosomes and most other cell organelles, with the exception of cytoskeletal elements and organelles that are being transported down the axon. Atomy following anatomical terms (column b) with the appropriate description or function (column a) column b a axon 1.
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
Match each anatomical term in column b with its description or function in column a. Involved in the transport of substances within the neuron 7. Receptive region of a neuron, as it depolarizes it delivers graded potential to.

Slightly enlarged region of the cell body from which the axon originates axonal terminal form synapses, or junctions with neurons (effector cells).; This area is free of ribosomes and most other cell organelles, with the exception of cytoskeletal elements and organelles that are being transported down the axon. Site of the nucleus and is the most important metabolic area.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
Glial cells of pns that surround nerve fibers and form myelin sheath. The axon (in motor neurons) begins just distal to a slightly enlarged cell body structure called the axon hillock. This area is free of ribosomes and most other cell organelles, with the exception of cytoskeletal elements and organelles that are being transported down the axon.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
Schwann cell bodies wrap around the axon forming the myelin sheath. The region of the neuron cell body from which the axon originates. Insulates the nerve fibers d.
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
Insulates the nerve fibers 5. Receptive region of a neuron. Glial cells of the pns, found surrounding neuron cell bodies within ganglia.
 Source: biologyonline.com
Source: biologyonline.com
The neurofilaments in the axon hillock become clustered together as fascicles. This area is free of ribosomes and most other cell organelles, with the exception of cytoskeletal elements and organelles that are being transported down the axon. Receptive regions of a neuron (2 terms) 4.
 Source: biologyonline.com
Source: biologyonline.com
Glial cells of the cns that wrap around neuron fibers forming myelin sheaths. Involved in the transport of substances within the neuron. Glial cells of pns that surround nerve fibers and form myelin sheath.
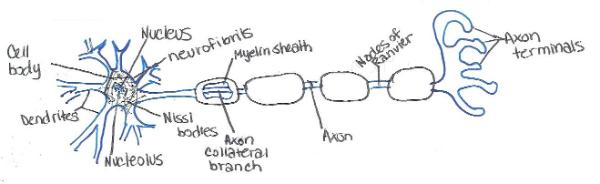 Source: easynotecards.com
Source: easynotecards.com
Site of the nucleus and is the most important metabolic area. Axons connect with other cells in the body including other neurons, muscle cells, and organs. Receptive region of a neuron.
Also Read :





