Sympatric speciation can occur in ways other than polyploidy, as well. A) xyy males b) some plants alternate between haploid and diploid phases c) xo females d) a normal watermelon has 22 chromosomes but seedless watermelons have 33 chromosomes.
Polyploidy Is Involved In Which Of The Following Examples. A genetic divergence that results in nonviable offspring. The definition of allopolyploidy is. Polyploidy is involved in which of the following examples? Although polyploidy has been involved in speciation in both animals and plants, the general perception is often that it is too rare to have been a significant factor in animal evolution and its role in plant diversification has been questioned.
 Polyploidy Control In Hepatic Health And Disease - Journal Of Hepatology From journal-of-hepatology.eu
Polyploidy Control In Hepatic Health And Disease - Journal Of Hepatology From journal-of-hepatology.eu
Related Post Polyploidy Control In Hepatic Health And Disease - Journal Of Hepatology :
Polyploidy is involved in which of the following examples? Such polyploidy is obtained by doubling of chromosome number by colchicine treatment. Although polyploidy has been involved in speciation in both animals and plants, the general perception is often that it is too rare to have been a significant factor in animal evolution and its role in plant diversification has been questioned. Chromosomal mutations are any alterations or errors that occur on a chromosome.
Miscellus has extensive chromosomal variability (lim et al., 2008;
The examples of allopolyploids are cultivated forms of wheat, cotton, and tobacco plants. Polyploidy is involved in which of the following examples? Such polyploidy is obtained by doubling of chromosome number by colchicine treatment. Although polyploidy is less common in mammals than in plants, polyploid cells are generated in different tissues. The examples of allopolyploids are cultivated forms of wheat, cotton, and tobacco plants. A decrease in chromosome number within a single species.
 Source: cell.com
Source: cell.com
This is also known as hybrid polyploidy or bispecies or multispecies polyploidy depending upon the species involved. Which of the following is an example of a beneficial mutation inherited polyploidy. Polyploidy is involved in which of the following examples?
 Source: nph.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Source: nph.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Miscellus has extensive chromosomal variability (lim et al., 2008; Red crosses represent extinction, while orange circles represent successful polyploidy coinciding with environmental stress, and light orange triangles represent successful polyploidy following delayed rediploidization [responsible for lag times between the wgd event and its exerted effects {schranz et al., 2012; A genetic divergence that results in nonviable offspring.
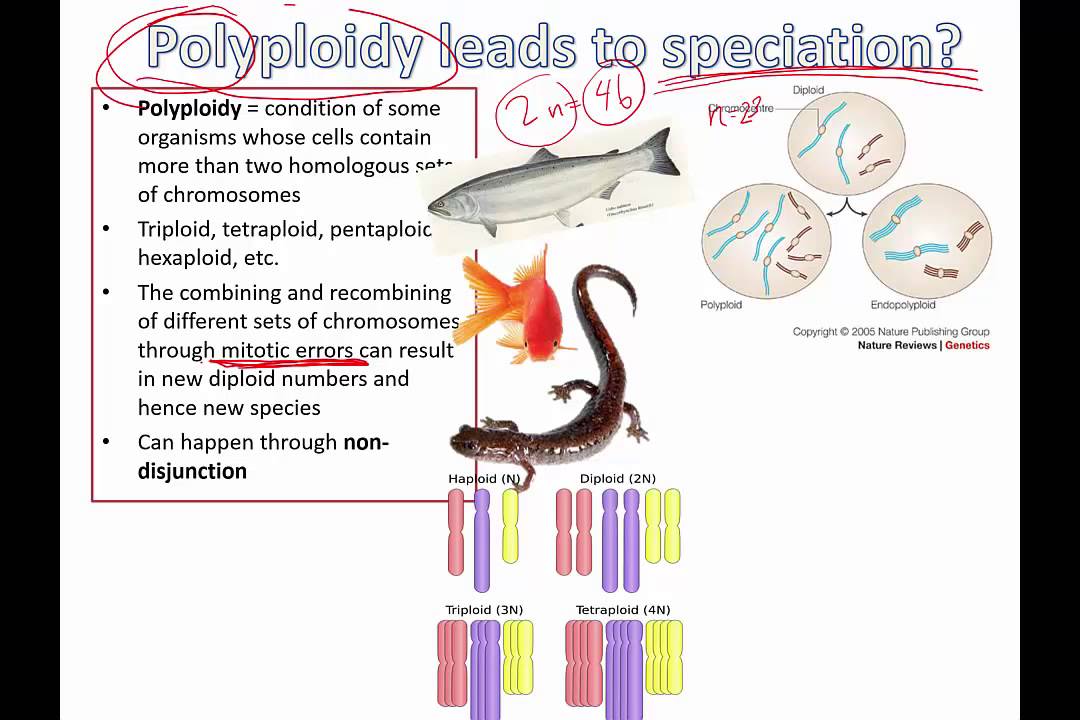 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Which one of the following examples does not come under the particular group? They are separated from the parent species by a reproductive isolating mechanism. Each schwann cell forms a single myelin sheath around an axon.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
In plants, researchers are just beginning to understand how polyploidy in some tissues leads to increased adaptation and evolutionary and agronomic success; Learn pros and cons of chromosomal mutations. A) xyy males b) some plants alternate between haploid and diploid phases c) xo females d) a normal watermelon has 22 chromosomes but seedless watermelons have 33 chromosomes.
 Source: journal-of-hepatology.eu
Source: journal-of-hepatology.eu
This is also known as hybrid polyploidy or bispecies or multispecies polyploidy depending upon the species involved. In prokaryotes, polyploidy can contribute to the direct survival of the individual (for example, by serving as a phosphate reserve or by protecting against highly mutational environments) but can. Learn more about polyploidy in this article.
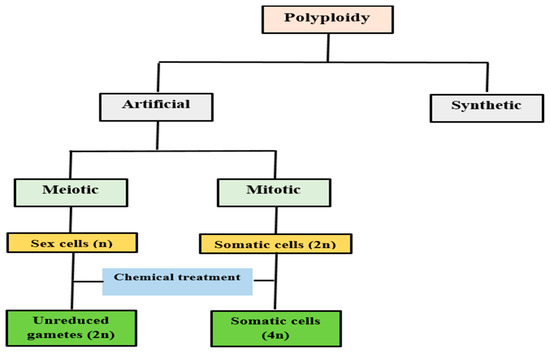 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
Chromosomal mutations are any alterations or errors that occur on a chromosome. Chromosomal mutations are any alterations or errors that occur on a chromosome. Such polyploidy is obtained by doubling of chromosome number by colchicine treatment.
 Source: wikiwand.com
Source: wikiwand.com
Ornamental crops such as snapdragons and marigolds have been bred through chromosome doubling to improve the quality and size of their blossoms (emsweller and ruttle,. A normal watermelon has 22 chromosomes but seedless watermelons have 33 chromosomes polyploidy is involved in which of the following examples? None of the populations examined was fixed for a particular.
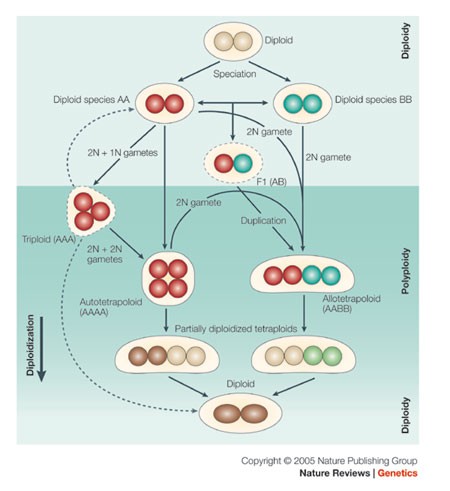 Source: nature.com
Source: nature.com
Explain three of the following processes or phenomena, using an appropriate example for each. Allopolyploidy has been more instrumental in evolution of crop plants, because 50% of the crop plants are alloployploids. Polyploidy, the condition in which a normally diploid cell or organism acquires one or more additional sets of chromosomes.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
For example, polyploid cells are important in the development of structures such. Polyploidy refers to a condition in which a diploid cell or organism acquires additional sets of chromosomes. For each process or phenomenon you selected in a., discuss its impact on the diversity of life on earth.
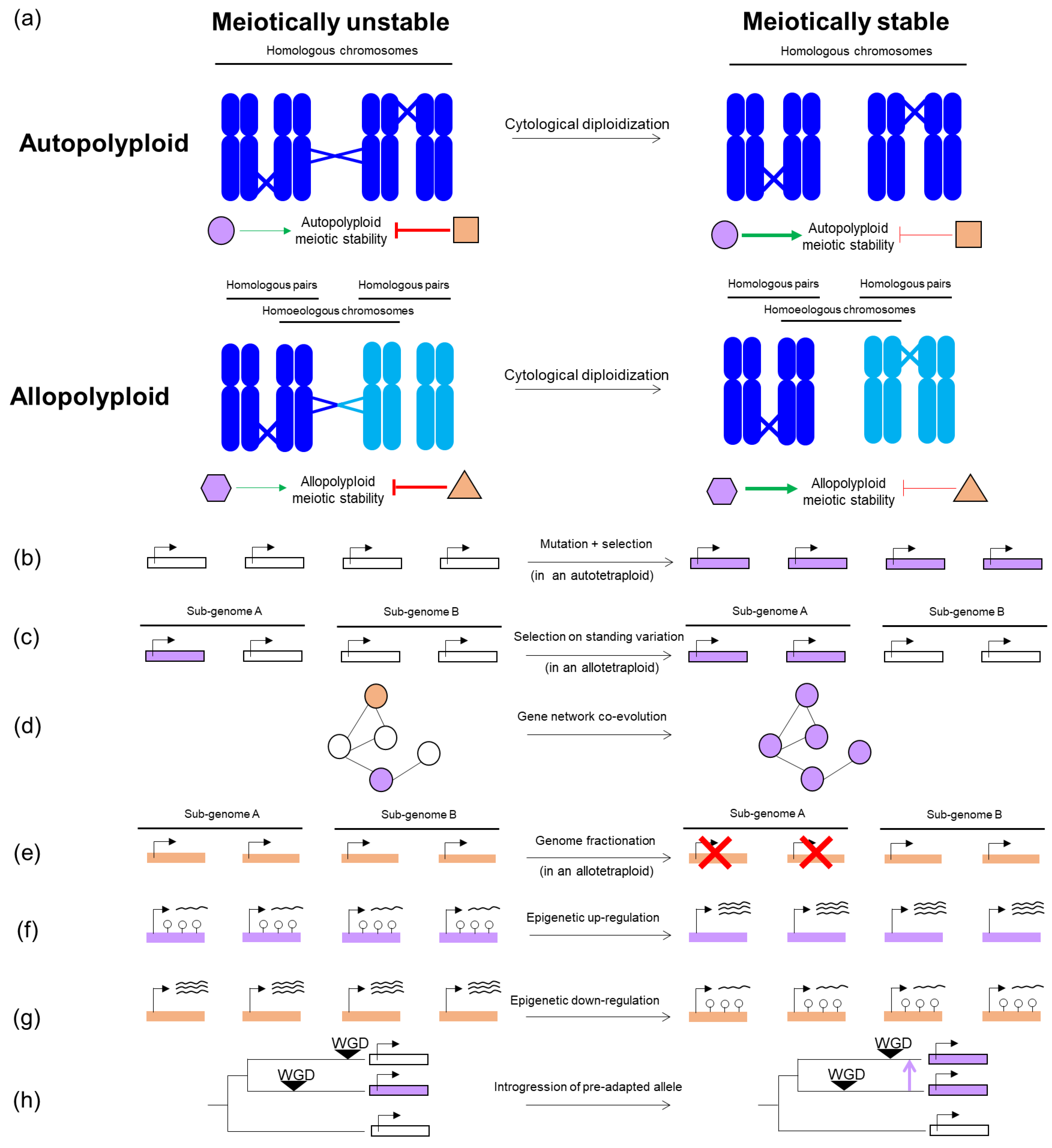 Source:
Source:
Polyploidy of individual cells or cell types (endopolyploidy), arising from chromosome replication without cell division, is involved in the normal (e.g., secretory cells) or abnormal (e.g., many cancers) development of organisms. Allopolyploidy has been more instrumental in evolution of crop plants, because 50% of the crop plants are alloployploids. Polyploidy of individual cells or cell types (endopolyploidy), arising from chromosome replication without cell division, is involved in the normal (e.g., secretory cells) or abnormal (e.g., many cancers) development of organisms.
 Source: wikiwand.com
Source: wikiwand.com
Learn pros and cons of chromosomal mutations. Learn pros and cons of chromosomal mutations. Ornamental crops such as snapdragons and marigolds have been bred through chromosome doubling to improve the quality and size of their blossoms (emsweller and ruttle,.

How many generations does it take to develop a new plant species by polyploidy? An increase in chromosome number due to hybridization of different species. A normal watermelon has 22 chromosomes but seedless watermelons have 33 chromosomes polyploidy is involved in which of the following examples?
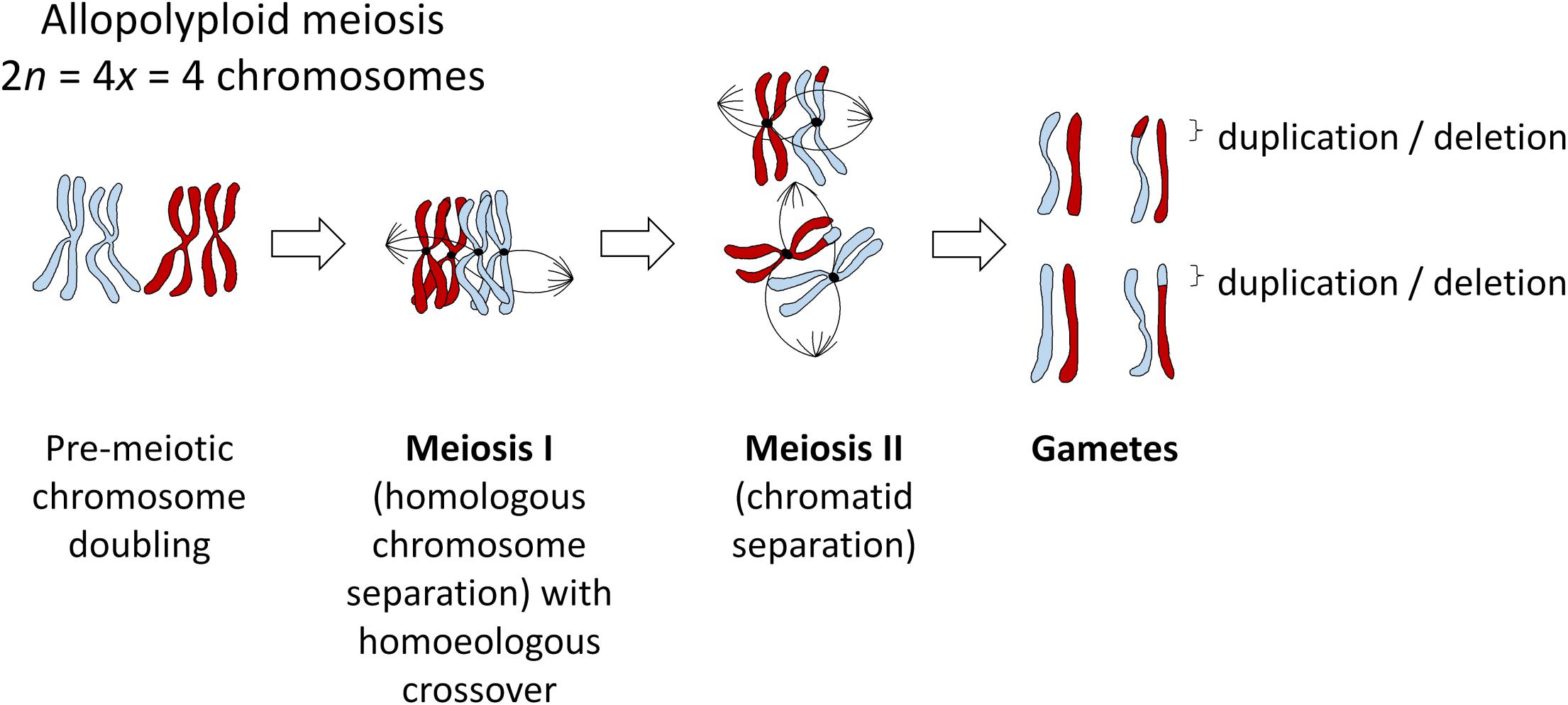 Source: frontiersin.org
Source: frontiersin.org
Allopolyploidy is the other form of polyploidy where individuals of two different species reproduce to yield a fertile offspring. The definition of allopolyploidy is. Polyploidy refers to a condition in which a diploid cell or organism acquires additional sets of chromosomes.
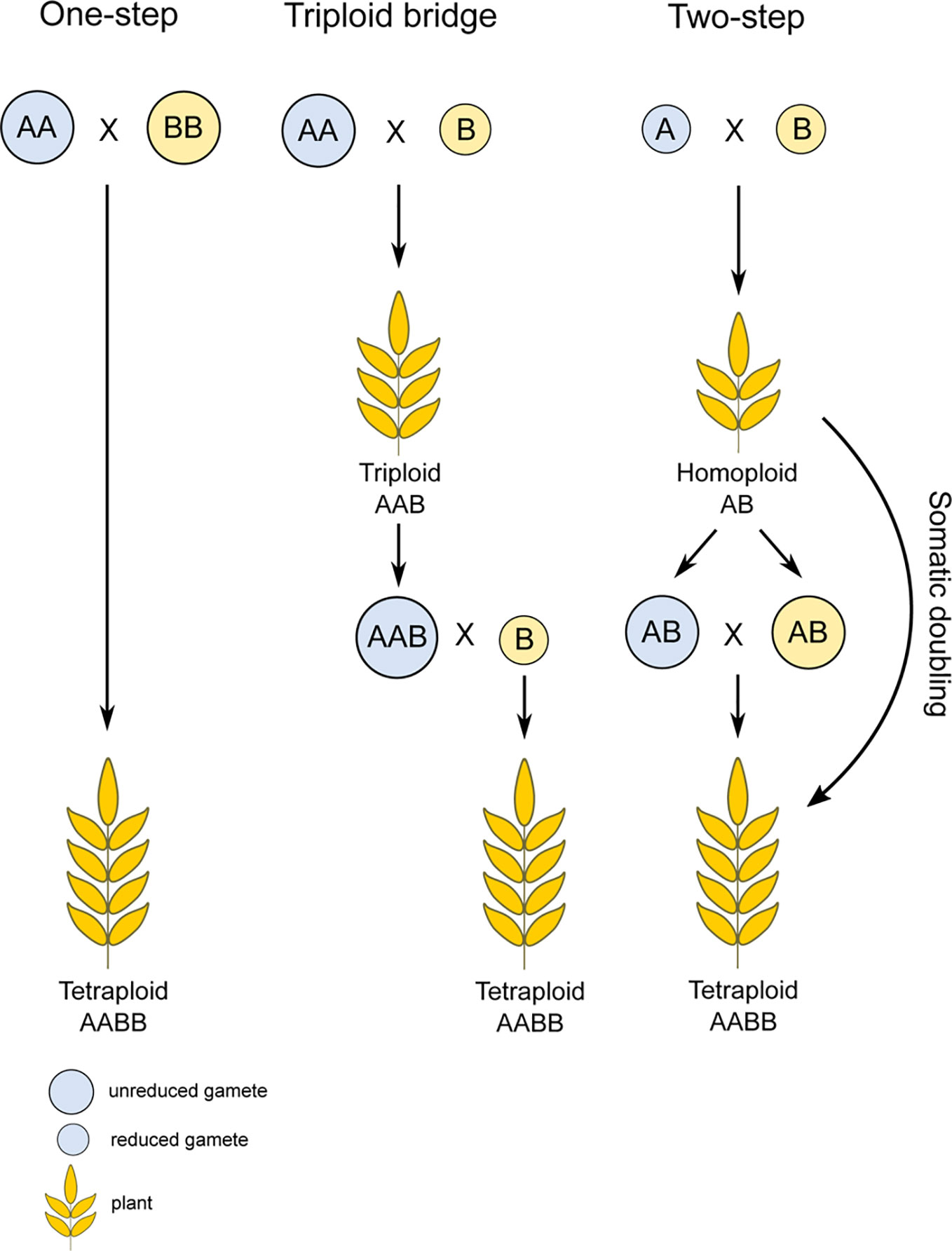 Source: frontiersin.org
Source: frontiersin.org
Sympatric speciation can occur in ways other than polyploidy, as well. Polyploidy, the condition in which a normally diploid cell or organism acquires one or more additional sets of chromosomes. A normal watermelon has 22 chromosomes but seedless watermelons have 33 chromosomes polyploidy is involved in which of the following examples?
 Source: nph.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Source: nph.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Allopolyploidy is the other form of polyploidy where individuals of two different species reproduce to yield a fertile offspring. The definition of allopolyploidy is. They are separated from the parent species by a reproductive isolating mechanism.
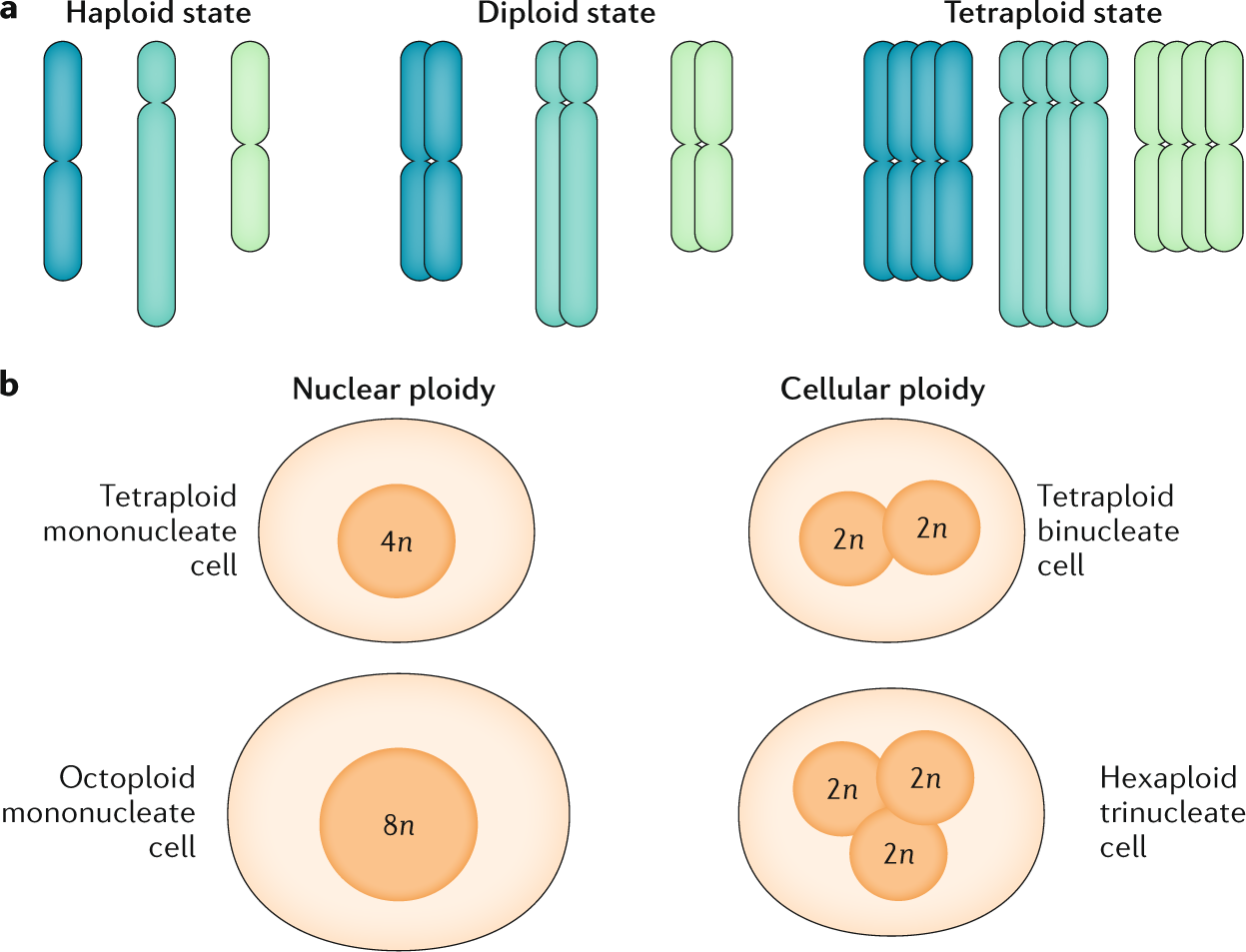 Source: nature.com
Source: nature.com
Polyploidy is involved in which of the following examples? This is also known as hybrid polyploidy or bispecies or multispecies polyploidy depending upon the species involved. Polyploidy of individual cells or cell types (endopolyploidy), arising from chromosome replication without cell division, is involved in the normal (e.g., secretory cells) or abnormal (e.g., many cancers) development of organisms.
 Source: gastrojournal.org
Source: gastrojournal.org
Myelin is formed by schwann cells in the peripheral nervous system (pns) and oligodendrocytes in the central nervous system (cns). A decrease in chromosome number within a single species. If we consider a species of fish residing in a lake.
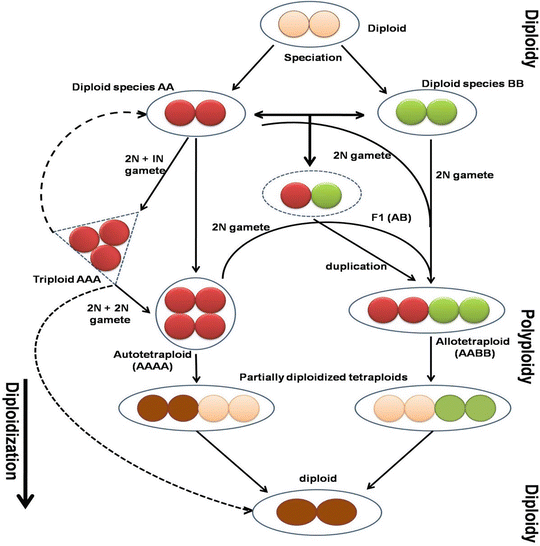 Source: link.springer.com
Source: link.springer.com
Explain three of the following processes or phenomena, using an appropriate example for each. In prokaryotes, polyploidy can contribute to the direct survival of the individual (for example, by serving as a phosphate reserve or by protecting against highly mutational environments) but can. Red crosses represent extinction, while orange circles represent successful polyploidy coinciding with environmental stress, and light orange triangles represent successful polyploidy following delayed rediploidization [responsible for lag times between the wgd event and its exerted effects {schranz et al., 2012;
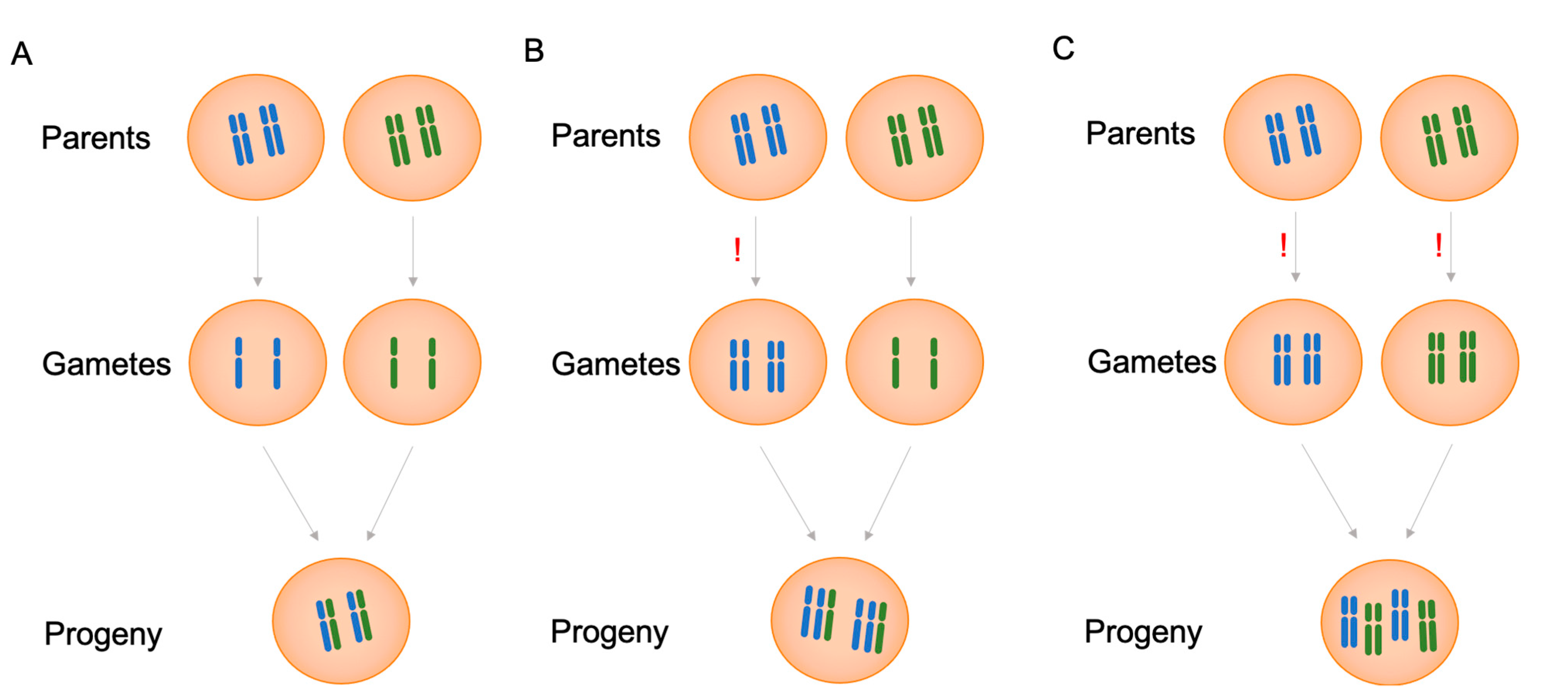 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
Explore as what happens when a chromosome encounters such changes in its structure, number, and type. A genetic divergence that results in nonviable offspring. Each schwann cell forms a single myelin sheath around an axon.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Match column i (taxonomic aids) column ii (definition/description)column icolumn iia.monographsi.aids in species identification in an areab.floraii.listing of species in. In prokaryotes, polyploidy can contribute to the direct survival of the individual (for example, by serving as a phosphate reserve or by protecting against highly mutational environments) but can. The examples of allopolyploids are cultivated forms of wheat, cotton, and tobacco plants.
Also Read :





