The insertion sequence isaba11 is mobile and replicative in atcc 19606. Insertion sequences are part of transposons (sequences of dna that can move around to different positions within the genome of a single cell in a process called transposition), which use insertion sequences to insert into another or another part of the genome.
Insertion Sequences Target Which Areas On A Target Dna Sequence. Insertion sequences target which areas on a target dna sequence? Is1, is2, is3, is10, is50, is911, is26 etc.); When the postion and/or the sequence of an inserted sequence has not been defined, a description may have a format like g.(100_150)ins(25) Attack of each dna strand at the target site by one of the two transposon ends in a staggered way during insertion provides an explanation for this observation.
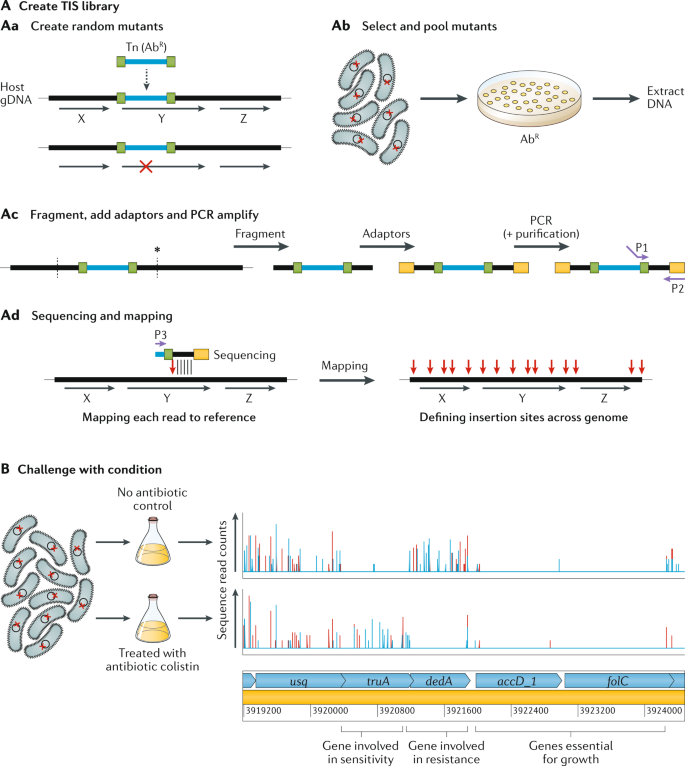 A Decade Of Advances In Transposon-Insertion Sequencing | Nature Reviews Genetics From nature.com
A Decade Of Advances In Transposon-Insertion Sequencing | Nature Reviews Genetics From nature.com
Related Post A Decade Of Advances In Transposon-Insertion Sequencing | Nature Reviews Genetics :
This is not the only naming scheme used, however. Preference for insertion into a site within the tnp recognition sequence would effectively inactivate one copy of the element and form clusters of the tn5 transposon. When the postion and/or the sequence of an inserted sequence has not been defined, a description may have a format like g.(100_150)ins(25) Insertion sequences are small (<2.5 kb) dna segments delimited by short terminal inverted repeats that contain one (or sometimes two) open reading frames that encode proteins specifically required for the mobility of the insertion sequence, that is, a transposase [104].
Although insertion sequences are usually discussed in the context of prokaryotic genomes , certain eukaryotic dna sequences belonging to the family of tc1/ mariner transposable.
The insertion of some specific insertion sequences had been associated with repetitive extragenic palindromic (rep) elements. Preference for insertion into a site within the tnp recognition sequence would effectively inactivate one copy of the element and form clusters of the tn5 transposon. Exponential megapriming pcr (emp) cloning requires two consecutive pcr steps and can be carried out in one day. Insertion sequences target which areas on a target dna sequence? Insertion sequences are part of transposons (sequences of dna that can move around to different positions within the genome of a single cell in a process called transposition), which use insertion sequences to insert into another or another part of the genome. Although insertion sequences are usually discussed in the context of prokaryotic genomes , certain eukaryotic dna sequences belonging to the family of tc1/ mariner transposable.

Insertion sequences target which areas on a target dna sequence? Probes that were used for targeted donor dna insertion are indicated as red bars. (2) the length and sequence of the short flanking direct target dna repeats (drs) (tsd, t arget s ite d uplication, in eukaryotes) often generated on insertion;
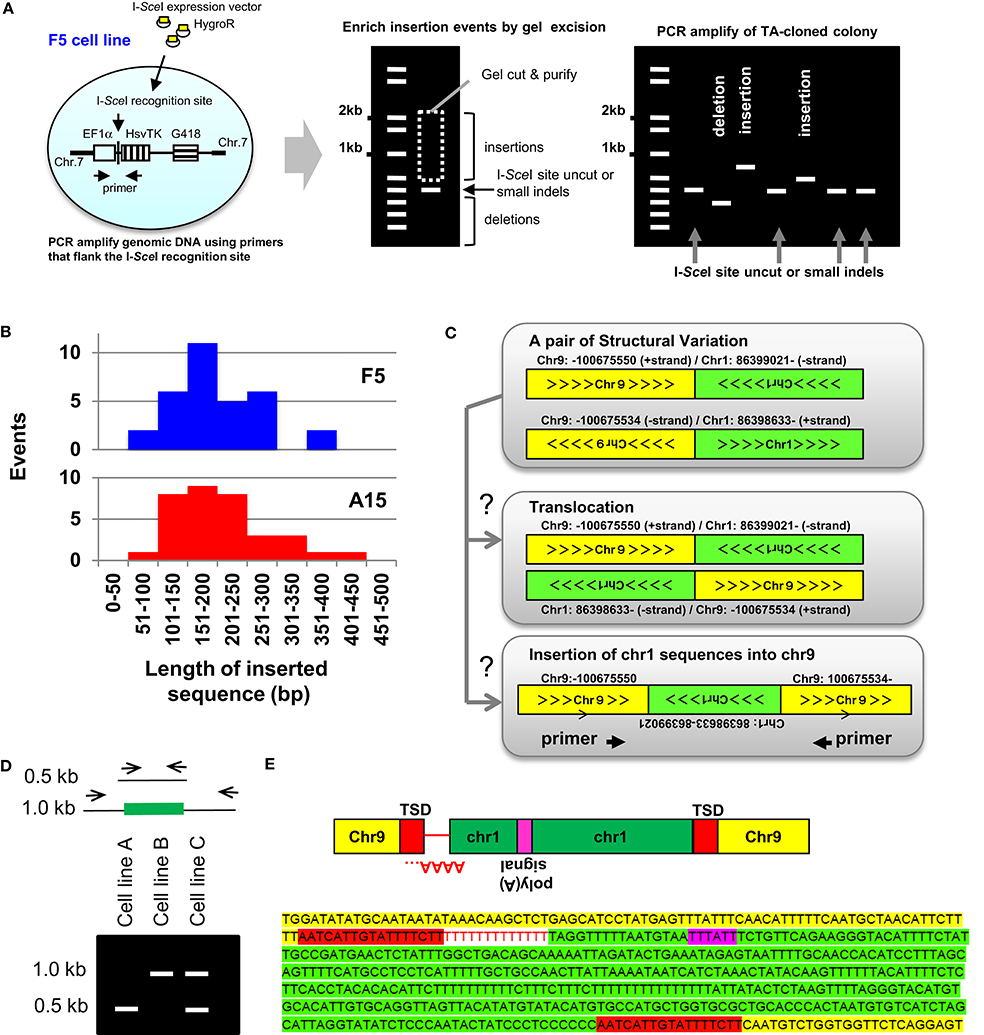 Source: frontiersin.org
Source: frontiersin.org
A variety of integrating vectors for gene delivery exist. (i) type 1 association, in which the percentage of association is 100% and each is copy is inserted in the same position of a rep sequence, making it possible to define the dna target consensus. It is directed to the target sequence by a short rna fragment known as a guide rna (grna).
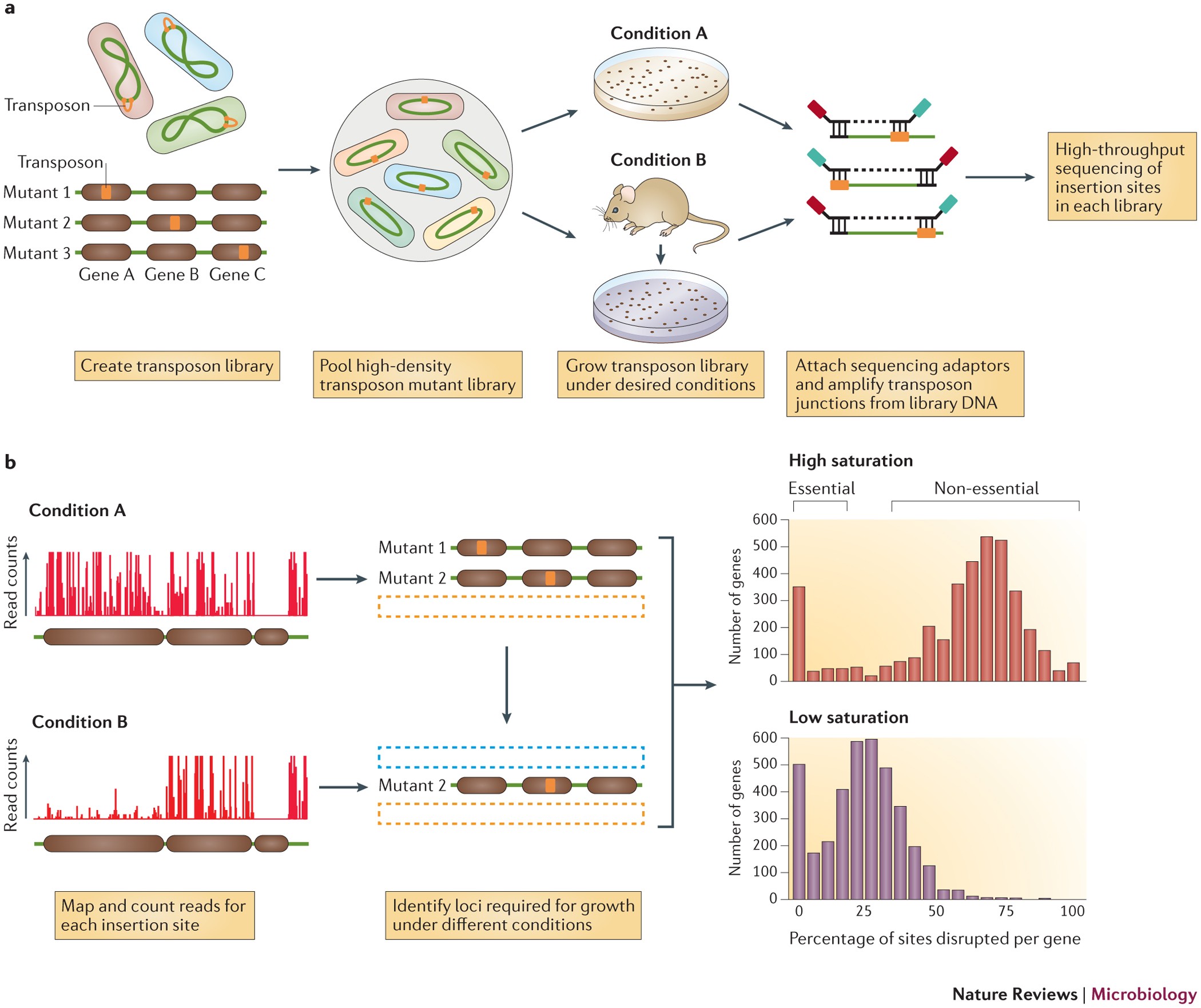 Source: nature.com
Source: nature.com
Insertion sequences are small (<2.5 kb) dna segments delimited by short terminal inverted repeats that contain one (or sometimes two) open reading frames that encode proteins specifically required for the mobility of the insertion sequence, that is, a transposase [104]. This includes (1) the length and sequence of the short imperfect terminal inverted repeat sequences (irs) carried by many iss at their ends (tirs or itrs in eukaryotes); When the postion and/or the sequence of an inserted sequence has not been defined, a description may have a format like g.(100_150)ins(25)
 Source: journals.asm.org
Source: journals.asm.org
A sequence of nucleotides identical to the inverted repeat sequence found on the insertion sequence itself. Insertion sequences target which areas on a target dna sequence? The inserted sequences were transmitted to the next generation and invite the possibility of future exploration of versatile genome editing by targeted dna insertion in plants.
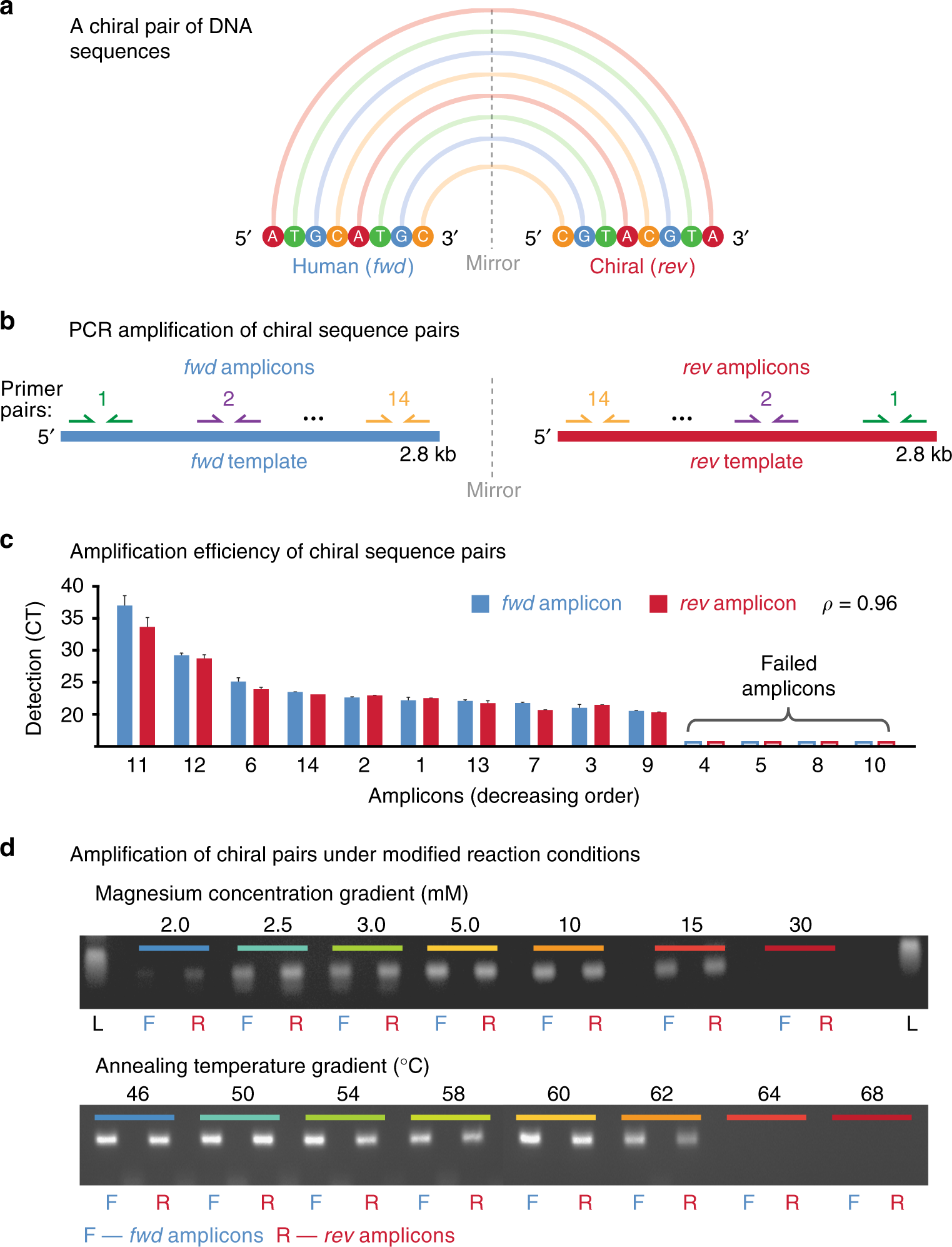 Source: nature.com
Source: nature.com
Insertion sequences are part of transposons (sequences of dna that can move around to different positions within the genome of a single cell in a process called transposition), which use insertion sequences to insert into another or another part of the genome. In all cases, gene disruption at the target site with large rearranged vector sequences without deletion of genomic dna sequences was observed (data not shown). When the postion and/or the sequence of an inserted sequence has not been defined, a description may have a format like g.(100_150)ins(25)
 Source: en.wikipedia.org
Source: en.wikipedia.org
Probes that were used for targeted donor dna insertion are indicated as red bars. Although insertion sequences are usually discussed in the context of prokaryotic genomes , certain eukaryotic dna sequences belonging to the family of tc1/ mariner transposable. The insertion of some specific insertion sequences had been associated with repetitive extragenic palindromic (rep) elements.
 Source: en.wikipedia.org
Source: en.wikipedia.org
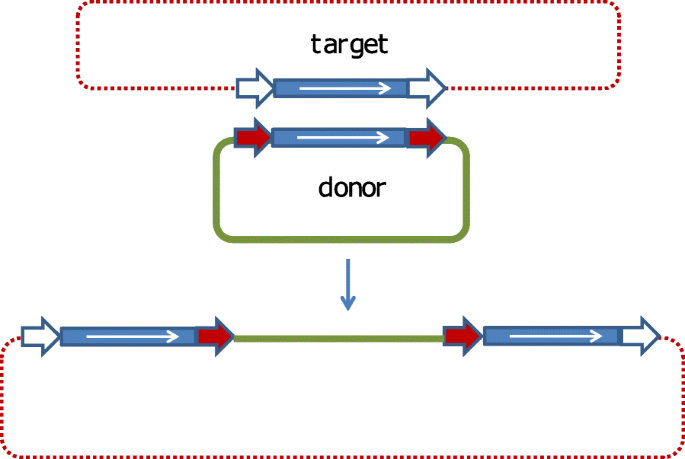
Primer pairs used for junction pcr are indicated as black arrows, and primers used to detect unmodified target dna are indicated as blue arrows. In all cases, gene disruption at the target site with large rearranged vector sequences without deletion of genomic dna sequences was observed (data not shown). A sequence of nucleotides identical to the inverted repeat sequence found on the insertion sequence itself.
 Source: jbc.org
Source: jbc.org
Residual insertion sequence elements (is elements) in escherichia coli strains that are commonly used for dna cloning are known to cause cloning artifacts by transposing themselves into the recombinant dna fragments.in such cases, chance insertion of is elements may occur at integration sites in the cloning targets, which in the case of the is10 element is a. Not only does that destroy the virus, but the fragment of foreign dna may be stored (3) the organisation of their open.
 Source: clutchprep.com
Source: clutchprep.com
Primer pairs used for junction pcr are indicated as black arrows, and primers used to detect unmodified target dna are indicated as blue arrows. Probes that were used for targeted donor dna insertion are indicated as red bars. This is not the only naming scheme used, however.
 Source: mobilednajournal.biomedcentral.com
Source: mobilednajournal.biomedcentral.com
Examination of flanking sequences revealed that insertion of is1001 occurs preferentially in stretches of t�s or a�s and results in a duplication of target sequences of 6 to 8 bases. Insertion sequences are small (<2.5 kb) dna segments delimited by short terminal inverted repeats that contain one (or sometimes two) open reading frames that encode proteins specifically required for the mobility of the insertion sequence, that is, a transposase [104]. A variety of integrating vectors for gene delivery exist.
 Source: clutchprep.com
Source: clutchprep.com
A sequence of nucleotides identical to the inverted repeat sequence found on the insertion sequence itself. When the postion and/or the sequence of an inserted sequence has not been defined, a description may have a format like g.(100_150)ins(25) In all cases, gene disruption at the target site with large rearranged vector sequences without deletion of genomic dna sequences was observed (data not shown).
 Source: journals.asm.org
Source: journals.asm.org
It is directed to the target sequence by a short rna fragment known as a guide rna (grna). Insertion sequences target which areas on a target dna sequence? Examination of flanking sequences revealed that insertion of is1001 occurs preferentially in stretches of t�s or a�s and results in a duplication of target sequences of 6 to 8 bases.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
(3) the organisation of their open. Is1, is2, is3, is10, is50, is911, is26 etc.); (2) the length and sequence of the short flanking direct target dna repeats (drs) (tsd, t arget s ite d uplication, in eukaryotes) often generated on insertion;
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
Sizes of dna fragments released upon spei/bamhi double digestion or saci digestion are indicated. (i) type 1 association, in which the percentage of association is 100% and each is copy is inserted in the same position of a rep sequence, making it possible to define the dna target consensus. Primer pairs used for junction pcr are indicated as black arrows, and primers used to detect unmodified target dna are indicated as blue arrows.
 Source: quizlet.com
Source: quizlet.com
A sequence of nucleotides identical to the inverted repeat sequence found on the insertion sequence itself. When the postion and/or the sequence of an inserted sequence has not been defined, a description may have a format like g.(100_150)ins(25) Preference for insertion into a site within the tnp recognition sequence would effectively inactivate one copy of the element and form clusters of the tn5 transposon.

Primer pairs used for junction pcr are indicated as black arrows, and primers used to detect unmodified target dna are indicated as blue arrows. Residual insertion sequence elements (is elements) in escherichia coli strains that are commonly used for dna cloning are known to cause cloning artifacts by transposing themselves into the recombinant dna fragments.in such cases, chance insertion of is elements may occur at integration sites in the cloning targets, which in the case of the is10 element is a. The insertion of some specific insertion sequences had been associated with repetitive extragenic palindromic (rep) elements.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
This event can result in gene inactivation as well as in. Sizes of dna fragments released upon spei/bamhi double digestion or saci digestion are indicated. The insertion sequence isaba11 is mobile and replicative in atcc 19606.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
(2) the length and sequence of the short flanking direct target dna repeats (drs) (tsd, t arget s ite d uplication, in eukaryotes) often generated on insertion; The direct consequence of is transposition is the insertion of one dna sequence into another. Probes that were used for targeted donor dna insertion are indicated as red bars.
 Source: mobilednajournal.biomedcentral.com
Source: mobilednajournal.biomedcentral.com
Insertion sequences target which areas on a target dna sequence? This is not the only naming scheme used, however. Prefix reference sequences accepted are g., m., c.
 Source: nature.com
Source: nature.com
(2) the length and sequence of the short flanking direct target dna repeats (drs) (tsd, t arget s ite d uplication, in eukaryotes) often generated on insertion; Primer pairs used for junction pcr are indicated as black arrows, and primers used to detect unmodified target dna are indicated as blue arrows. Insertion sequences are small (<2.5 kb) dna segments delimited by short terminal inverted repeats that contain one (or sometimes two) open reading frames that encode proteins specifically required for the mobility of the insertion sequence, that is, a transposase [104].
Also Read :





