I hope you find this lesson helpful. Lesson on coenzyme a biosynthesis and vitamin b5.
In Which Of The Following Metabolic Pathways Are Coenzymes Required. 3 the coenzyme after c=o bond formation Lesson on coenzyme a biosynthesis and vitamin b5. 2 oxidized form of flavin adenine dinucleotide e. As a cofactor of the acyl carrier protein, pantothenic acid participates in the synthesis of fatty acids.
 Coenzymes - An Overview | Sciencedirect Topics From sciencedirect.com
Coenzymes - An Overview | Sciencedirect Topics From sciencedirect.com
Related Post Coenzymes - An Overview | Sciencedirect Topics :
These reactions utilize several different enzymes at each step, producing intermediate products, on their way to the final product. 3 the coenzyme after c=o bond formation Coenzyme a is one of five crucial coenzymes that are necessary in the reaction mechanism of the citric acid cycle. However, as more and more are made, they
In both types of reactions, coenzymes are required to carry the hydrogen ions and electrons from or to the reacting substrate.
If internal cellular enzymes are denatured, it can lead to: Cofactors can be considered helper molecules that assist in biochemical transformations. The most common sources of coenzymes are dietary vitamins (figure 6.20). Energy management in a cell most often involves the making or breaking of. Feedback inhibition, where the end product of the pathway inhibits an upstream step, is an important regulatory mechanism in cells. The most common sources of coenzymes are dietary vitamins.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Coenzymes are organic helper molecules, with a basic atomic structure comprised of carbon and hydrogen, which are required for enzyme action. Cofactors can be considered helper molecules that assist in biochemical transformations. (see osteoporosis.) the coenzyme forms of vitamin b 12 are methylcobalamin (figure 2) and deoxyadenosylcobalamin.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
In both types of reactions, coenzymes are required to carry the hydrogen ions and electrons from or to the reacting substrate. The most common sources of coenzymes are dietary vitamins. Coenzyme small organic molecule, such as a vitamin or its derivative, which is required to enhance the activity of an enzyme cofactor inorganic ion, such as iron and magnesium ions, required for optimal regulation of enzyme activity

Enzymes bind their substrate but are not changed in the reaction; Metabolism is studied by looking at individual metabolic pathways, which are a series of biochemical reactions in which a given reactant is converted to a desired end product. The rates at which these happen are characterized in an area of study called enzyme kinetics.
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
Some vitamins are precursors to. In both types of reactions, coenzymes are required to carry the hydrogen ions and electrons from or to the reacting substrate. Some vitamins are precursors to coenzymes and.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
Not all coenzymes, however, are considered b vitamins. I hope you find this lesson helpful. Energy management in a cell most often involves the making or breaking of.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
The production of both amino acids and nucleotides is controlled through feedback inhibition. Cofactors typically differ from ligands in that they often derive their function. The most common sources of coenzymes are dietary vitamins.

If internal cellular enzymes are denatured, it can lead to: A) inhibit the enzyme and thus slow the rates of glycolysis and the citric acid cycle. The various metabolic pathways by which carbohydrates, fat and proteins are processed as metabolic fuels for energy supply or as precursors in the biosynthesis of compounds required by the cell for maintenance or growth are interrelated and well coordinated.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
Which of the following metabolic pathways are coenzymes required? Enzymes are not consumed in the reaction they catalyze. Coenzyme a is one of five crucial coenzymes that are necessary in the reaction mechanism of the citric acid cycle.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
3 the coenzyme after c=o bond formation Metabolic reactions a coenzyme that gains hydrogen ions and electrons is reduced, whereas a coenzyme that loses hydrogen ions and electrons to. Not all coenzymes, however, are considered b vitamins.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
Enzymes are not consumed in the reaction they catalyze. Enzymes bind their substrate but are not changed in the reaction; Some vitamins are precursors to.
 Source: onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Source: onlinelibrary.wiley.com
B vitamins are known to be coenzymes and assist with various bodily reactions and functions. Feedback inhibition, where the end product of the pathway inhibits an upstream step, is an important regulatory mechanism in cells. Coenzyme a is necessary for the metabolism of carbohydrates, amino acids, fatty acids, and other biomolecules.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
In both types of reactions, coenzymes are required to carry the hydrogen ions and electrons from or to the reacting substrate. Results of a long series of chemical reactions called metabolic pathways. Metabolic pathways are a series of reactions catalyzed by multiple enzymes.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
B vitamins are known to be coenzymes and assist with various bodily reactions and functions. As final products are produced in metabolic pathways, they are used. Metabolism is studied by looking at individual metabolic pathways, which are a series of biochemical reactions in which a given reactant is converted to a desired end product.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
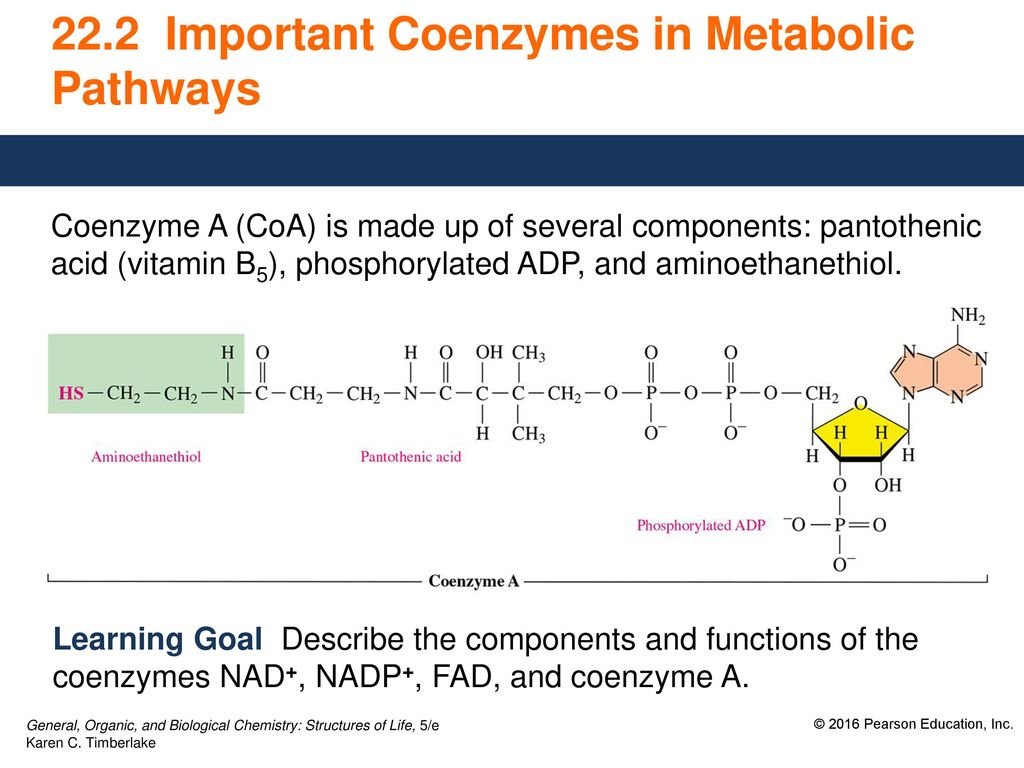
Coenzyme a is biosynthesized from pantothenic acid (vitamin b5), and also requires cysteine and atp. The rates at which these happen are characterized in an area of study called enzyme kinetics. Coenzyme a is required for a variety of processes including metabolism of fatty acids and degradation of some vitamins.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
Coenzymes are organic helper molecules, with a basic atomic structure comprised of carbon and hydrogen, which are required for enzyme action. (see osteoporosis.) the coenzyme forms of vitamin b 12 are methylcobalamin (figure 2) and deoxyadenosylcobalamin. These reactions utilize several different enzymes at each step, producing intermediate products, on their way to the final product.
 Source: transtutors.com
Source: transtutors.com
3 the coenzyme after c=o bond formation B vitamins are known to be coenzymes and assist with various bodily reactions and functions. Cofactors can be considered helper molecules that assist in biochemical transformations.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Some vitamins are precursors to coenzymes and others act directly as. Coenzyme small organic molecule, such as a vitamin or its derivative, which is required to enhance the activity of an enzyme cofactor inorganic ion, such as iron and magnesium ions, required for optimal regulation of enzyme activity In both types of reactions, coenzymes are required to carry the hydrogen ions and electrons from or to the reacting substrate.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
Some vitamins are precursors to coenzymes and others act directly as. Coenzymes are organic helper molecules, with a basic atomic structure comprised of carbon and hydrogen, which are required for enzyme action. B vitamins are known to be coenzymes and assist with various bodily reactions and functions.
 Source: jbc.org
Source: jbc.org
The production of both amino acids and nucleotides is controlled through feedback inhibition. Some vitamins are precursors to coenzymes and others act directly as. 3 the coenzyme after c=o bond formation
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
Energy management in a cell most often involves the making or breaking of. Lesson on coenzyme a biosynthesis and vitamin b5. Not all coenzymes, however, are considered b vitamins.
Also Read :





