The primary aim of recruitment and selection process is to; The primary active transport system uses atp to move a substance such as an ion into the cell and often at the same time a second substance is moved out of the cell.
A Primary Active Transport Process Is One In Which __________. Primary active transport, also called direct active transport, directly uses energy to transport molecules across a membrane. It involves using energy (usually atp) to directly pump a solute across a membrane against its electrochemical gradient. Which one of the following is a transport layer protocol; Primary active transport — active transport of small molecules that directly uses atp as an energy source
 Active Transport- Features, Types And Significance - Biology - Microbe Notes From microbenotes.com
Active Transport- Features, Types And Significance - Biology - Microbe Notes From microbenotes.com
Related Post Active Transport- Features, Types And Significance - Biology - Microbe Notes :
Active transport pumps molecules or substance against a concentration gradient using cellular energy. Primary active transport, also called direct active transport, directly uses energy to transport molecules across a membrane. With energy from atp, the pumps transport ions against their electrochemical gradients—a direction they would not normally travel by diffusion. The main three types of active transport are:
These charged ions require ion pumps/channels to cross membranes and.
It involves using energy (usually atp) to directly pump a solute across a membrane against its electrochemical gradient. An intracellular vesicle fuses with the plasma membrane and releases its contents to the extracellular fluid molecules move through transport proteins that have been activated by atp the plasma membrane folds inward to form a vesicle containing extracellular material molecules pass directly through the phospholipid bilayer of the plasma membrane molecules move. In main active transport process, the energy is obtained straight from the breakdown of atp or some other high energy phosphate substance. Primary active transport, also called direct active transport, directly uses metabolic energy to transport molecules across a membrane. Uptake of glucose in the human intestines is an example of primary active transport. A symporter carries two different ions or molecules, both in the same direction.
 Source: quizlet.com
Source: quizlet.com
In main active transport process, the energy is obtained straight from the breakdown of atp or some other high energy phosphate substance. Thus, this is an important process in cell biology that requires energy. Which one of the following is an active transducer;
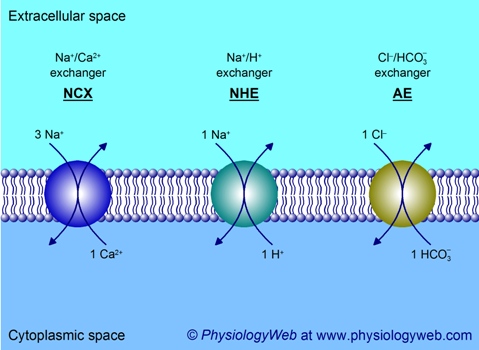 Source: physiologyweb.com
Source: physiologyweb.com
Which one of the following is a transport layer protocol; Active transport process is the movement of molecules across a cell membrane in the direction against their concentration gradient, i.e., moving from a lower to higher concentration. Thus, this is an important process in cell biology that requires energy.
 Source: quizlet.com
Source: quizlet.com
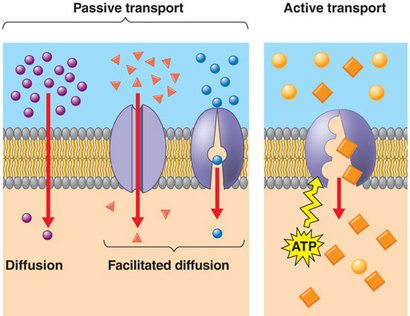
In these cases, active transport is required. In some cases, the movement of substances can be accomplished by passive transport, which uses no energy. The process of endocytosis and exocytosis are utilized by all the cells for transportation of molecules which cannot passively permeate via the membrane.
 Source: en.lifeder.com
Source: en.lifeder.com
Primary active transport, also called direct active transport, directly uses chemical energy (such as from adenosine triphosphate or atp in case of cell membrane) to transport all species of solutes across a membrane against their concentration gradient. In some cases, the movement of substances can be accomplished by passive transport, which uses no energy. Molecules move through transport proteins that have been activated by atp some transport processes use transport proteins in the plasma membrane, but do not require atp.
 Source: osmosisdiffusion.wordpress.com
Source: osmosisdiffusion.wordpress.com
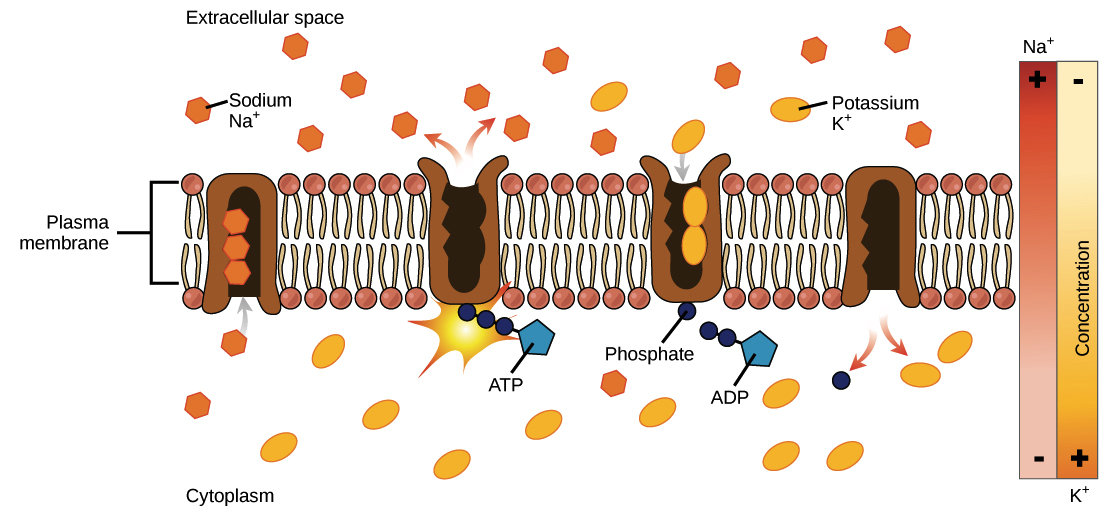
Substances that are transported across the cell membrane by primary active transport include metal ions, such as na + , k + , mg 2+ , and ca 2+. Primary active transport, also called direct active transport, directly uses metabolic energy to transport molecules across a membrane. The carrier proteins that facilitates this process are called as pumps.
 Source: quizlet.com
Source: quizlet.com
Primary active transport — active transport of small molecules that directly uses atp as an energy source Active transport pumps molecules or substance against a concentration gradient using cellular energy. In most cells, this is usually concerned with accumulating high concentrations of.
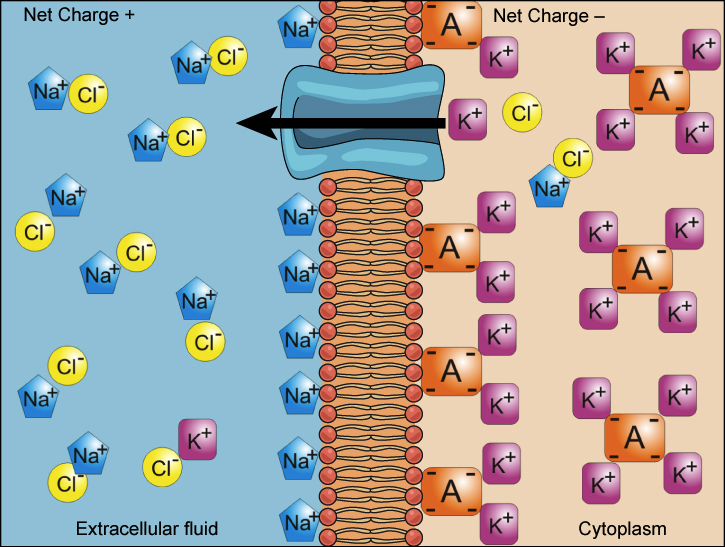 Source: khanacademy.org
Source: khanacademy.org
Molecules move through transport proteins that have been activated by atp some transport processes use transport proteins in the plasma membrane, but do not require atp. A primary active transport process is one in which _____. Primary active transport and secondary active transport.
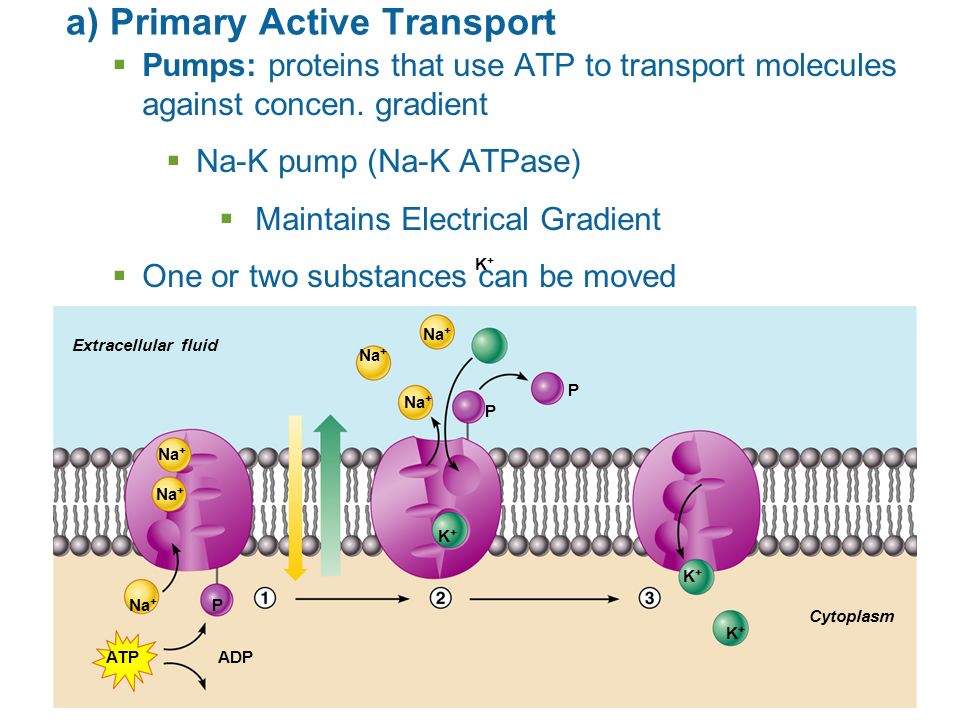 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
It involves using energy (usually atp) to directly pump a solute across a membrane against its electrochemical gradient. It involves using energy (usually atp) to directly pump a solute across a membrane against its electrochemical gradient. In main active transport process, the energy is obtained straight from the breakdown of atp or some other high energy phosphate substance.
 Source: brainly.com
Source: brainly.com
A few of the essential pumps associated with the main active transport processes are: Active transport process is the movement of molecules across a cell membrane in the direction against their concentration gradient, i.e., moving from a lower to higher concentration. In main active transport process, the energy is obtained straight from the breakdown of atp or some other high energy phosphate substance.
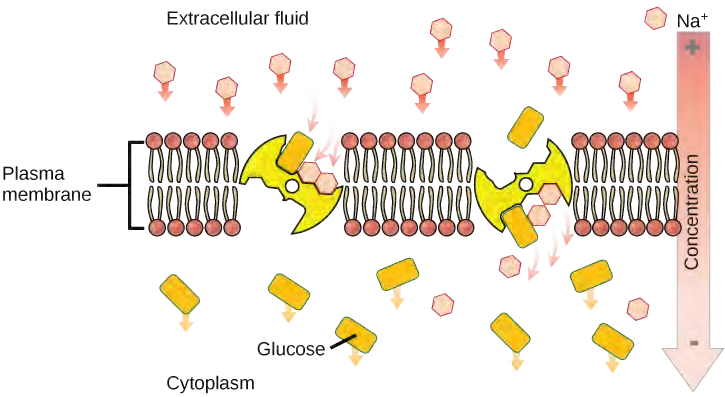 Source: slcc.pressbooks.pub
Source: slcc.pressbooks.pub
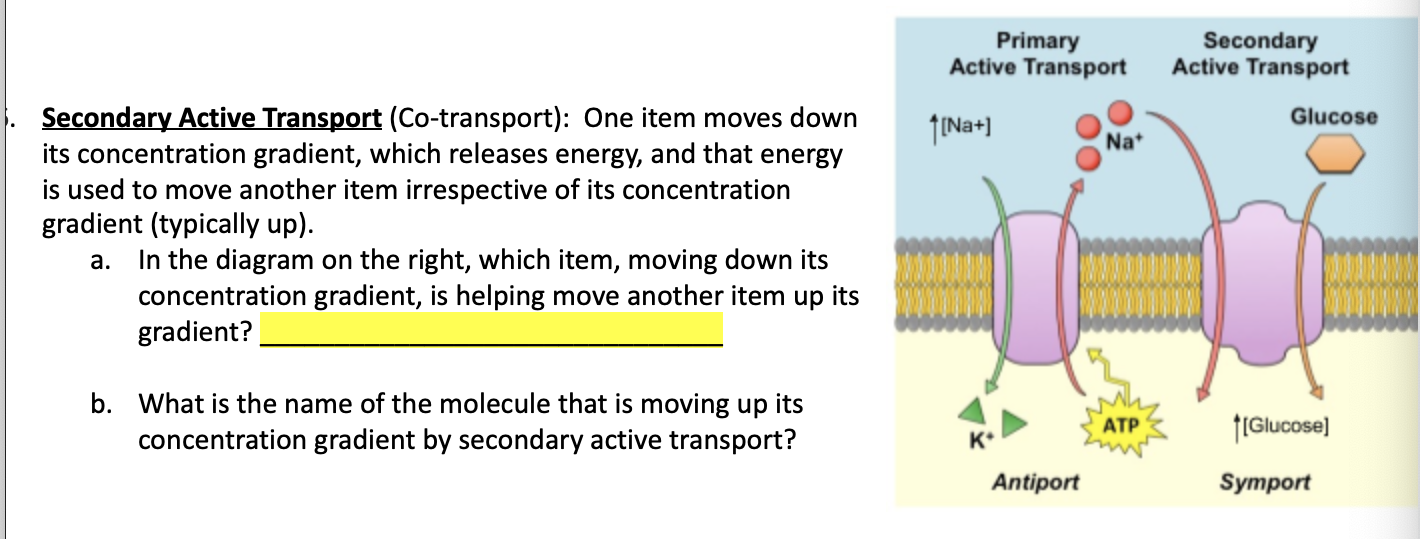
In secondary active transport, the electrochemical gradient is used to transport molecules across the membrane. The carrier proteins that facilitates this process are called as pumps. Secondary active transport is the transport of two different molecules across a transport membrane using energy in other forms than atp.
 Source: microbenotes.com
Source: microbenotes.com
Primary active transport, also known as direct active transport, carries molecules across a membrane using metabolic energy. Secondary active transport is the transport of two different molecules across a transport membrane using energy in other forms than atp. It involves using energy (usually atp) to directly pump a solute across a membrane against its electrochemical gradient.
 Source: nayturr.com
Source: nayturr.com
Examples of such substances that are carried across the cell membrane by primary active transport include metal ions, are na +, k +, mg 2 +, and ca 2 +. Which one of the following is a transport layer protocol; Thus, this is an important process in cell biology that requires energy.

Primary active transport utilizes chemical energy from atp to drive protein pumps that are embedded in the cell membrane. Primary active transport, also known as direct active transport, carries molecules across a membrane using metabolic energy. Uptake of glucose in the human intestines is an example of primary active transport.
Nutrients are concentrated into the cell with the help active transport. In these cases, active transport is required. Primary active transport, also called direct active transport, directly uses chemical energy (such as from adenosine triphosphate or atp in case of cell membrane) to transport all species of solutes across a membrane against their concentration gradient.
 Source: khanacademy.org
Source: khanacademy.org
The main three types of active transport are: There are three protein types or transporters ().a uniporter carries one specific ion or molecule. A few of the essential pumps associated with the main active transport processes are:
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
To move substances against a concentration or electrochemical gradient, a cell must use energy. As sodium ion concentrations build outside of the plasma membrane because of the primary active transport process, this creates an electrochemical gradient. There are two types of active transport:
 Source: opentextbc.ca
Source: opentextbc.ca
Primary active transport and secondary active transport. In most cells, this is usually concerned with accumulating high concentrations of. The carrier proteins that facilitates this process are called as pumps.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
As sodium ion concentrations build outside of the plasma membrane because of the primary active transport process, this creates an electrochemical gradient. Uptake of glucose in the human intestines is an example of primary active transport. Primary active transport, also called direct active transport, directly uses metabolic energy to transport molecules across a membrane.
 Source: quizlet.com
Source: quizlet.com
Active transport mechanisms do just this, expending energy (often in the form of atp) to maintain the right concentrations of ions and molecules in living cells. Therefore, all the groups of atp powered pumps contain one or more binding sites for the atp molecules, which are present on the cytosolic. Active transport requires energy for the process by transporting molecules against a concentration or electrochemical gradient.
Primary active transport utilizes chemical energy from atp to drive protein pumps that are embedded in the cell membrane. Active transport is the process of transferring substances into, out of, and between cells, using energy. An antiporter also carries two different.
Also Read :





